Abstract
Background
Anastomotic leakage is a feared complication following colorectal surgery and is associated with early and long-term morbidity and mortality. The presacral cavity as the result of leakage can be treated with an endo-sponge (B-Braun Medical). The aim of this study was to assess the effectiveness of endo-sponge treatment of the presacral cavity as the result of anastomotic leakage in the Netherlands.
Methods
Between July 2006 and April 2008, 16 patients (M/F = 9:7) with median age 64 years (range 19–78 years) who underwent surgery for rectal cancer (n = 13) or ulcerative colitis (n = 3) were treated with the endo-sponge treatment after anastomotic leakage.
Results
Of the 16 patients, eight patients started with the endo-sponge treatment within 6 weeks after the initial surgery. In these patients the endo-sponge was placed after a median of 24 days (range 13–39 days) following surgery. In the remaining eight patients the endo-sponge treatment was started later than 6 weeks after the initial surgery. In this group there was a median of 74 days (range 43–1,602 days) between surgery and the start of endo-sponge placement. There was closure in six out of eight patients (75%) in the group that started with the endo-sponge treatment within 6 weeks of surgery compared with three out of eight patients (38%) in the group that started later (p = 0.315). Closure was achieved in a median of 40 (range 28–90) days with a median number of 13 sponge replacements (range 8–17).
Conclusions
Endo-sponge placement can be helpful in the treatment for anastomotic leakage after colorectal surgery and might prevent a chronic presacral sinus. However, it is not yet clear if this new treatment modality results in quicker healing.
Keywords: Anastomotic leakage, Rectal surgery, Vacuum-assisted closure
Anastomotic leakage is a serious and feared complication following colorectal surgery and is associated with early and long-term morbidity and mortality [1–4]. Particularly, (low) anterior resections are associated with a high leakage rate ranging from 1% to 24% [5, 6]. For this reason many surgeons prefer defunctioning the colorectal or coloanal anastomosis using a loop ileostomy. Anastomotic leakage of a functioning anastomosis mostly requires surgical reintervention to fashion a loop ileostomy and to drain the pelvic cavity in order to prevent severe septic complications.
Defunctioning of a low anastomosis by loop ileostomy does not prevent the leakage to occur, but diminishes the septic sequelae. Mostly, a presacral cavity originates from the site of the leakage. The cavity probably heals spontaneously when it is small. When it is large, it might delay the closure of the ileostomy and probably results in a devastating future function of the neorectum [7, 8]. Closure of the loop ileostomy in the presence of chronic presacral sinus is considered hazardous since septic complications or bad function can be expected in some cases.
In the treatment of various wounds vacuum-assisted therapy is often used to achieve wound closure [9]. Recently, the application of local vacuum sponge treatment has shown to be effective to treat locally contained anastomotic leakage after low anterior anastomosis in rectal cancer patients. In a recent publication by Weidenhagen et al. [10], a series of 29 patients with anastomotic leakage following rectal resection for malignant disease were treated with endo-sponge. The endo-sponge facilitates closure of the presacral space by negative pressure of the endo-sponge, ensuring continuous drainage and thereby infection control, increased blood flow and therefore the stimulation of granulation tissue and reduction of the size of the cavity. In 28 out of the 29 patients described there was complete closure of the cavity.
The aim of this study was to assess the effectiveness of endo-sponge (B-Braun Medical B.V., Melsungen, Germany) treatment of presacral cavities associated with anastomotic leakage.
Materials and methods
Patient characteristics
Between July 2006 and April 2008, a series of patients with a presacral cavity after anastomotic leakage were treated by using the endo-sponge. All hospitals that had used the endo-sponge were contacted to collect data of experience with the endo-sponge. The endo-sponge had been used in patients following anastomotic leakage after low anterior resections for malignant disease or after restorative proctocolectomy with ileoanal pouch anastomosis for ulcerative colitis.
After surgery, when anastomotic leakage was suspected a computed tomography (CT) scan was performed in the majority of the cases. Using flexible endoscopy, the presence of an abscess cavity was confirmed. Subsequently a diverting stoma was routinely constructed when this had not been done during the primary operation. Primary outcome parameters were closure of the cavity and the ability to close the ileostomy. Factors associated with successful closure were analyzed, e.g., time of initiation of endo-sponge treatment after surgery, and experience with endo-sponge treatment (number of cases treated).
Approval of the Medical Ethics Committees was not necessary, since in the Netherlands for nonexperimental clinical case series such as this approval is not required.
Endo-sponge treatment
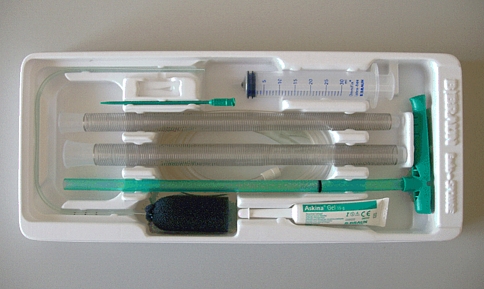
The endo-sponge is an open-pored polyurethane sponge (B. Braun Medical B.V., Melsungen, Germany). A photograph of the introduction set is presented in Fig. 1. The sponge is installed transanally after examination and rinsing (saline 0.9%) of the abscess cavity using a small-calibre flexible gastroscope (GIF-100 Video Gastroscope, Olympus, 9.8 mm diameter). The length and size of the abscess cavity is estimated and the size of the endo-sponge is cut accordingly. When the cavity is too large for one sponge, multiple sponges are placed. After introduction of a small-calibre gastroscope into the deepest point of the cavity, a plastic tube, positioned over the gastroscope, is advanced into the deepest point of the cavity. After withdrawal of the gastroscope, the endo-sponge is inserted through the lubricated tube by using a pushing probe, while retracting the plastic tube. Next, the sponge is connected to a low-vacuum suction bottle (Redyron® TRANS PLUS suction device), creating a constant negative pressure in the sponge. The correct positioning of the sponge is endoscopically checked. Fixation of the sponge is not necessary, because low-pressure suction fixes the sponge in the abscess cavity. The endo-sponge is changed every 3–4 days to prevent the tissue from growing into the sponge causing painful sponge exchanges. Saline (0.9%) is introduced into the sponge just before removal to facilitate the painless extraction. Some hospitals use lidocaine instead of saline for this matter. During every endo-sponge exchange the size of the endo-sponge is reduced. Closure of the sinus is confirmed by flexible endoscopy and water-soluble contrast enema.
Fig. 1.
Endo-sponge
Data collection
Patients’ charts were reviewed and data was extracted on demographic data, body mass index (BMI), preoperative chemo and/or radiotherapy, type and indication of surgery (possible ileostomy/colostomy), level of anastomosis, morbidity, mortality, time between surgery and start of treatment, duration of endo-sponge treatment, amount of sponge exchanges, sponge related complications, follow-up, and short-term outcome.
Statistical analysis
Continuous data are presented as median values (range) unless otherwise specified. Categorical data are presented as frequencies or percentages. For the comparison of categorical variables, the chi-square or Fisher exact test was used. A p-value of 5% or lower was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 14.0.2 for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Patient characteristics
In total 16 patients (M/F = 9:7) with median age 64 years (range 19–78 years) were included (Table 1). Thirteen patients had undergone surgery for rectal cancer and three for therapy-resistant ulcerative colitis. Nine of the 13 patients who underwent colorectal resection for malignant disease received preoperative radiotherapy. Two patients had chemoradiation preoperatively. In 4 patients the procedure was performed laparoscopically and in 12 patients an open procedure was performed. The anastomosis was constructed at a median height of 5 cm (range 2–8 cm) from the anal verge. During the initial operation a defunctioning ileostomy was created in eight patients. In seven patients the diverting stoma was created after the discovery of the anastomotic leakage. In one patient a previously present diverting loop ileostomy was changed into an end ileostomy.
Table 1.
Characteristics of patients with anastomotic leakage that underwent endo-sponge treatmen
| Variable | n = 16 |
|---|---|
| Male/female (n) | 9:7 |
| Age (years), median (range) | 64 (19–78) |
| Indication for surgery | |
| Benign | 3 |
| Malignancy | 13 |
| BMI (kg/m2), median (range) | 26 (23–31) |
| Preoperative treatment | |
| Radiotherapy | 9 |
| Chemoradiation | 2 |
| Type of surgery | |
| Open | 12 |
| Laparoscopic | 4 |
| Anastomosis level (cm), mean (range) | 5 (2–8) |
| Stoma created during primary surgery | 8 |
BMI body mass index
Outcome
Postoperatively, anastomotic leakage was diagnosed by CT scan in 15 patients. In one patient the leakage was discovered by flexible endoscopy. None of the patients had generalized peritonitis during the use of the endo-sponge. After endoscopic confirmation of the abscess cavity the endo-sponge was placed. The median duration between the initial surgery and the discovery of the leakage was 11 days (range 3–150 days). Of the 16 patients, 8 patients started with the endo-sponge treatment within 6 weeks after the initial surgery. In these patients the endo-sponge was placed after a median of 24 days (range 13–39 days) following surgery (Table 2). In the remaining eight patients the endo-sponge treatment was started later than 6 weeks after the initial surgery. In this group there was a median of 74 days (range 43–1,602 days) between surgery and the start of the endo-sponge placement. Experience in the different hospitals ranged from one to five patients in the study period. The median number of sponges initially placed ranged from one to three. In six patients the endo-sponge was placed under general anaesthesia. In three patients replacements were performed under a light sedative (5 mg midazolam). The remaining seven patients underwent sponge placement without any anaesthesia. Definitive resolution of the sinus was achieved in the total group in 9 out of 16 patients (56%). Closure was achieved in a median of 40 (range 28–90) days with a median amount of 13 sponge replacements (range 8–17). There was closure in six out of eight patients (75%) in the group that started with the endo-sponge treatment within 6 weeks of surgery compared with three out of eight patients (38%) in the group that started later (p = 0.315). In the malignant group in six patients (46%) the endo-sponge treatment was successful compared with three out of three patients in the benign group (p = 0.213).
Table 2.
Results of the use of the endo-sponge
| Variable | n = 16 |
|---|---|
| Start amount sponges, median (range) | 1 (1–3) |
| Time between surgery and start sponge treatment (days), median (range) | 41 (13-1, 602) |
| ≤6 weeks (n = 8, days) | 24 (13–39) |
| >6 weeks (n = 8, days) | 74 (43–1,602) |
| Time until closure (days), median (range) | 40 (28–90) |
| Number of sponge exchanges, median (range) | 13 (8–17) |
| Closure of abcsess cavity, n (%) | 9 (56%) |
In one patient the sponge exchange was complicated by a bleeding in abscess cavity (500 cc blood loss). Endo-sponge treatment was stopped in one patient after 13 exchanges because the vacuum therapy was very painful. A possible explanation for this was that the abscess cavity was close to the hypogastric plexus. In a third patient, with a nearly complete dehiscent anastomosis, the sponge treatment was stopped after eight exchanges because there was insufficient progress in the closure of the cavity. Finally an end colostomy was constructed. In two patients, due to recurrent abscesses, an intersphincteric proctectomy was performed.
Median follow-up after closure of the abscess cavity was 4 months (range 2–16 months).
Out of nine patients with a closed abscess cavity the stoma had been closed in five patients. One of these patients underwent relaparotomy after stoma closure as a result of anastomotic leakage of the short bowel anastomosis. A diverting ileostomy was constructed. Two patients are currently on the waiting list to close the stoma. In the remaining two patients the stoma is considered definitive because of patient preference or metastatic disease.
Discussion
The present study shows that the endo-sponge is a promising device and could potentially be helpful in the treatment of anastomotic leakage after colorectal surgery. Furthermore, it may prevent the development of a chronic presacral sinus.
Anastomotic leakage after surgery is a complication that has major consequences for the patient, resulting in major morbidity and even mortality [1, 2, 11, 12]. Small anastomotic leakages after surgery in the pelvic area can potentially be treated by a wait-and-see policy. This is not the case when the leakage involves a significant part of the circumference. This frequently leads to a large presacral sinus which often requires additional surgical procedures and long-term drainage of the abscess cavity. Furthermore, the purulent discharge and the often accompanying foul odour have an inevitable influence on the patient’s quality of life. The prolonged pelvic sepsis and fibrosis is held responsible for impaired long-term neorectum function after ileostomy closure in many of those patients [7, 8]. Aggressive treatment of the presacral abscess enforcing quick resolution of the pelvic sepsis might be important for long-term outcome.
Following the application of vacuum sponges for the closure of abdominal wounds [13], the endo-sponge was developed for the resolution of presacral abscess cavities as a result of anastomotic leakages following colorectal surgery.
In the literature a small group of patients (n = 4) with significant anastomotic leakage after rectal resection that were treated in 2004 with a transanal vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) has been reported by Nagell and Holte [14]. All patients had a protective ileostomy before the start of the vacuum treatment. The median healing time of these patients was 51 (range 43–195) days.
Weidenhagen et al. [10] described a series of 29 patients treated with endo-sponge. The majority of these patients underwent surgery for malignant disease and nine patients received preoperative chemoradiation. Definitive closure was achieved in 28 of the 29 patients (97%). Mean total duration of the treatment was 34 days (range 4–79 days) and the number of sponge exchanges was 11 (range 1–27). Twenty-two out of the 25 patients with a protecting stoma the stoma could be closed after the abscess cavity was obliterated. Mees et al. described a small series of five patients with a presacral abscess following anastomotic leakage after low anterior resection and restorative proctocolectomy [15]. Median time to closure was 45 days (range 32–68 days).
In the present series, closure of the abscess cavity after low anastomotic leakage after colorectal surgery was achieved in 9 of 16 patients. This is lower than reported by Weidenhagen et al. in their series (97%). In our series endo-sponge treatment was not started shortly after the initial surgical procedure in all patients. Although not significantly, the results were better in the group of patients that started within 6 weeks after surgery compared with the group that started later than 6 weeks (75% versus 56%). A difference in closure rate between the groups that started early compared to late can be explained by the development of fibrosis of the neorectum precluding alignment of the bowel with the abscess cavity. As a result, endo-sponge treatment of chronic presacral sinuses probably has an unsatisfactory effect. Up to now five out of nine patients with a closed cavity had their stoma removed and in two cases stoma closure is planned.
In these series, all patients had a diverting stoma after anastomotic leakage. The question is whether it is necessary to divert the faecal stream when an endo-sponge is inserted. If the endo-sponge closes the abscess cavity effectively, it prevents faeces and debris being pushed into the sinus. In the series of Weidenhagen et al. four patients were treated without the construction of a diverting stoma.
With the current endoluminal vacuum therapy patients have to undergo sponge exchanges every 3–4 days. This is done to prevent tissue growing into the sponge causing painful sponge exchanges. In the majority of the patients in these series the early exchanges were done in a clinical setting. After a few sponge exchanges most patients were discharged and treated in an outpatient setting. The patient has to return to the hospital two times a week. This cycle has a considerable impact on the patient and is demanding for the team performing the sponge exchanges in terms of time, effort, and availability of operating room and/or endoscopy suite space. Furthermore the costs are considerable. A complete set with the vacuum bottle that is used for one sponge exchange costs €195.
Until now, there is insufficient literature to determine whether endo-sponge treatment is superior to wait-and-see policy after faecal deviation. There is enough information on the different aspects of anastomotic leakage, e.g., potential risk factors and oncological outcome [3, 4, 5, 6, 11, 16]. However, there are only few reports on the long-term outcome of anastomotic leakage after colorectal surgery in terms of functional outcome. A series of 19 patients with a median follow-up duration of 30 months was reported by Hallbook and Sjodahl [7]. It showed that neorectal volume and compliance were significantly reduced in patients with anastomotic leakage. Nesbakken et al. [8] reported on the functional outcome after anastomotic leakage following low anterior resection for rectal cancer. In their series, 11 patients with anastomotic leakage were compared with patients without leakage after surgery. In the group with leakage the neorectal capacity was significantly lower compared with the group without, 120 versus 180 ml (p = 0.04), respectively. Furthermore, significantly more evacuation problems were reported.
In conclusion, endo-sponge placement can be helpful in treatment of anastomotic leakage after colorectal surgery and may prevent chronic presacral sinus. Starting early with endo-sponge treatment is probably more effective than late treatment of the presacral sinus. The long-term follow-up and functional outcome of the neorectum must be awaited.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Footnotes
Presented at the 16th International Congress of the European Association of Endoscopic Surgery (EAES), 12–14 June 2008, Stockholm, Sweden.
Contributor Information
P. J. van Koperen, Email: p.j.vankoperen@amc.uva.nl
W. A. Bemelman, Phone: +31 20-566618, FAX: +31 20-6914858, Email: w.a.bemelman@amc.uva.nl
References
- 1.Ptok H, Marusch F, Meyer F et al (2007) Impact of anastomotic leakage on oncological outcome after rectal cancer resection. Br J Surg 94(12):1548–1554 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Jung SH, Yu CS, Choi PW et al (2008) Risk factors and oncologic impact of anastomotic leakage after rectal cancer surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 51(6):902–908 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Jestin P, Pahlman L, Gunnarsson U (2008) Risk factors for anastomotic leakage after rectal cancer surgery: a case–control study. Colorectal Dis 10(7):715–721 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Lee WS, Yun SH, Roh YN et al (2008) Risk factors and clinical outcome for anastomotic leakage after total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. World J Surg 32(6):1124–1129 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Rullier E, Laurent C, Garrelon JL et al (1998) Risk factors for anastomotic leakage after resection of rectal cancer. Br J Surg 85(3):355–358 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Matthiessen P, Hallbook O, Andersson M, Rutegard J, Sjodahl R (2004) Risk factors for anastomotic leakage after anterior resection of the rectum. Colorectal Dis 6(6):462–469 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Hallbook O, Sjodahl R (1996) Anastomotic leakage and functional outcome after anterior resection of the rectum. Br J Surg 83(1):60–62 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Nesbakken A, Nygaard K, Lunde OC (2001) Outcome and late functional results after anastomotic leakage following mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Br J Surg 88(3):400–404 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.Hunter JE, Teot L, Horch R, Banwell PE (2007) Evidence-based medicine: vacuum-assisted closure in wound care management. Int Wound J 4(3):256–269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Weidenhagen R, Gruetzner KU, Wiecken T, Spelsberg F, Jauch KW (2007) Endoscopic vacuum-assisted closure of anastomotic leakage following anterior resection of the rectum: a new method. Surg Endosc 22(8):1818–1825 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.Law WL, Chu KW (2004) Anterior resection for rectal cancer with mesorectal excision: a prospective evaluation of 622 patients. Ann Surg 240(2):260–268 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Wind J, Koopman AG, van Berge Henegouwen MI et al (2007) Laparoscopic reintervention for anastomotic leakage after primary laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 94(12):1562–1566 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Mendonca DA, Papini R, Price PE (2006) Negative-pressure wound therapy: a snapshot of the evidence. Int Wound J 3(4):261–271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Nagell CF, Holte K (2006) Treatment of anastomotic leakage after rectal resection with transrectal vacuum-assisted drainage (VAC). A method for rapid control of pelvic sepsis and healing. Int J Colorectal Dis 21(7):657–660 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 15.Mees ST, Palmes D, Menninger R et al (2008) Endo-vacuum assisted closure treatment for rectal anastomotic insufficiency. Dis Colon Rectum 51(4):404–410 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 16.Lipska MA, Bissett IP, Parry BR, Merrie AE (2006) Anastomotic leakage after lower gastrointestinal anastomosis: men are at a higher risk. ANZ J Surg 76(7):579–585 [DOI] [PubMed]