Abstract
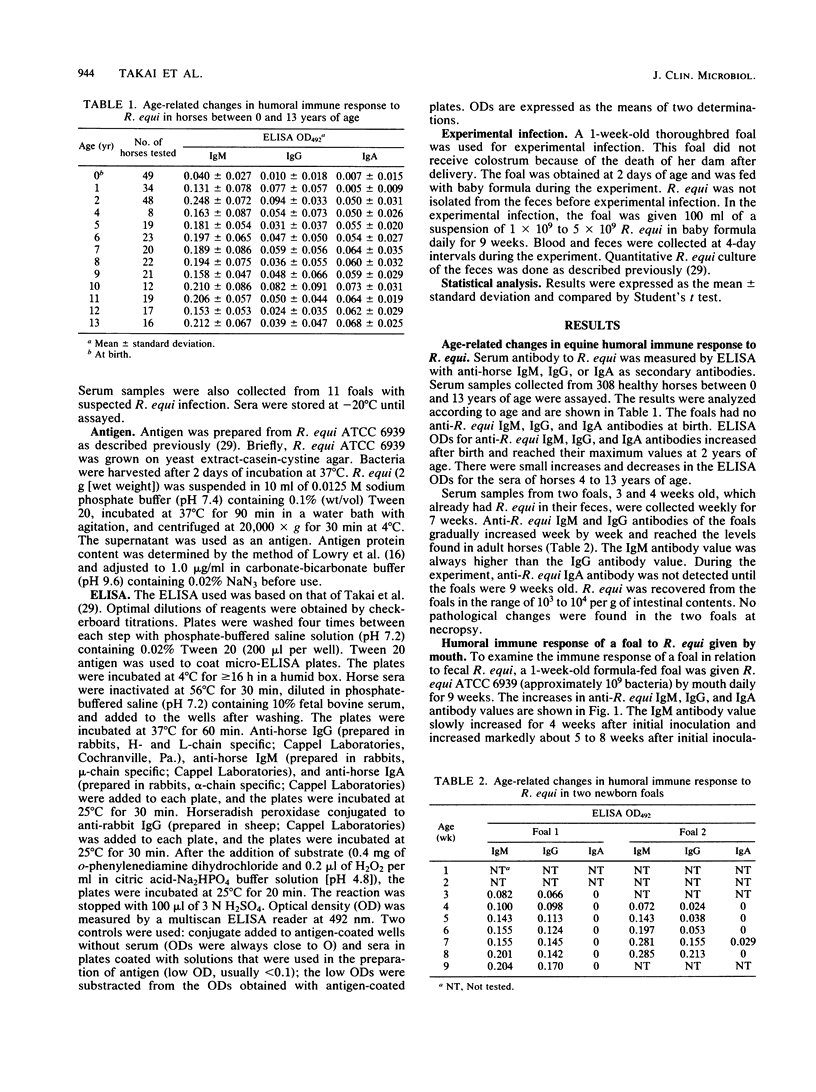
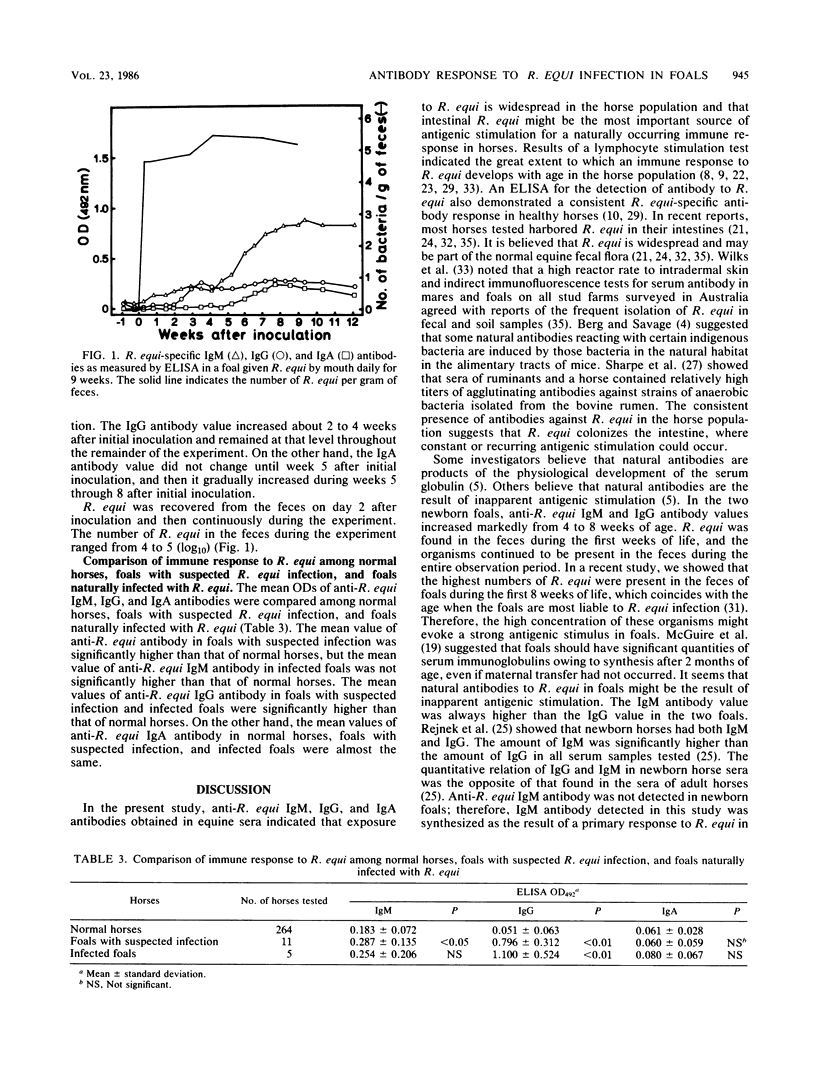
Humoral immune response to intestinal Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi in horses was studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anti-R. equi immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG, and IgA antibodies were demonstrated in the healthy horse population. Adult horse levels of anti-R. equi IgM and IgG antibodies were reached by 5 to 9 weeks of age in two healthy newborn foals. R. equi was recovered from the foals in the range of 10(3) to 10(4) per g of intestinal contents. A 1-week-old foal was infected with R. equi by mouth daily for 9 weeks. The foal did not show any clinical signs of illness. Anti-R. equi IgM antibody values in the foal increased about 5 to 8 weeks after initial inoculation, similar to the naturally occurring immune response to intestinal R. equi. There were differences among the antibody responses to R. equi in healthy horses, foals with suspected infection, and infected foals. These results suggest that exposure to R. equi is widespread in the horse population and that intestinal R. equi is the most important source of antigenic stimulation for a naturally occurring immune response in horses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton M. D., Hughes K. L. Comparison of three techniques for isolation of Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi from contaminated sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):219–221. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.219-221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton M. D., Hughes K. L. Ecology of Rhodococcus equi. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Feb;9(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Savage D. C. Immune responses of specific pathogen-free and gnotobiotic mice to antigens of indigenous and nonindigenous microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):320–329. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.320-329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyden S. V. Natural antibodies and the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1966;5:1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimprich R. E., Rooney J. R. Corynebacterium equi enteritis in foals. Vet Pathol. 1977 Mar;14(2):95–102. doi: 10.1177/030098587701400201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elissalde G. S., Renshaw H. W., Walberg J. A. Corynebacterium equi: an interhost review with emphasis on the foal. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1980;3(4):433–445. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(80)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger M. A., Kaeberle M. L., Roth J. A. Equine cell-mediated immune response to Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2424–2427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger M. A., Kaeberle M. L., Roth J. A. Equine humoral immune response to Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2428–2430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietala S. K., Ardans A. A., Sansome A. Detection of Corynebacterium equi-specific antibody in horses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffcott L. B. Duration of permeability of the intestine to macromolecules in the newly-born foal. Vet Rec. 1971 Mar 27;88(13):340–341. doi: 10.1136/vr.88.13.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffcott L. B. Some practical aspects of the transfer of passive immunity to newborn foals. Equine Vet J. 1974 Jul;6(3):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1974.tb03942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffcott L. B. Studies on passive immunity in the foal. 1. Gamma-globulin and antibody variations associated with the maternal transfer of immunity and the onset of active immunity. J Comp Pathol. 1974 Jan;84(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(74)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Prescott J. F., Markham R. J. The pathology of experimental Corynebacterium equi infection in foals following intragastric challenge. Vet Pathol. 1983 Jul;20(4):450–459. doi: 10.1177/030098588302000408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight H. D. Corynebacterial infections in the horse: problems of prevention. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969 Jul 15;155(2):446–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R., Larson K. A. Immune response of equine fetus to coliphage T2. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Oct;34(10):1363–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B. Passive immunity in the foal: measurement of immunoglobulin classes and specific antibody. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Oct;34(10):1299–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Poppie M. J., Banks K. L. Hypogammaglobulinemia predisposing to infection in foals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1975 Jan 1;166(1):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M. Detection of colt serum antibody against Corynebacterium equi by agar gel diffusion. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1980 Oct;42(5):551–555. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.42.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y. Quantitative culture of Rhodococcus equi from the feces of horse. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1983 Summer;23(2):67–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Johnson J. A., Markham R. J. Experimental studies on the pathogenesis of Corynebacterium equi infection in foals. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jul;44(3):280–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Ogilvie T. H., Markham R. J. Lymphocyte immunostimulation in the diagnosis of Corynebacterium equi pneumonia of foals. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Dec;41(12):2073–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Travers M., Yager-Johnson J. A. Epidemiological survey of Corynebacterium equi infections on five Ontario horse farms. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Jan;48(1):10–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rejnek J., Prokesovà L., Sterzl J., Matousek V. The presence of IgG and IgM in full term horse umbilical cord sera. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jun;10(6):397–399. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. E., Latham M. J., Reiter B. The occurrence of natural antibodies to rumen bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jun;56(3):353–364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-56-3-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel W. L., Keahey E. E., Bullard T. L. Corynebacterium infection in foals: etiology, pathogenesis, and laboratory diagnosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1968 Dec 15;153(12):1610–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Kawazu S., Tsubaki S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of Corynebacterium (Rhodococcus) equi infection in foals. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Oct;46(10):2166–2170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Michizoe T., Matsumura K., Nagai M., Sato H., Tsubaki S. Correlation of in vitro properties of Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi with virulence for mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(12):1175–1184. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb00907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Ohkura H., Watanabe Y., Tsubaki S. Quantitative aspects of fecal Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi in foals. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):794–796. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.794-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Tsubaki S. The incidence of Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi in domestic animals and soil. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Jun;47(3):493–496. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks C. R., Barton M. D., Allison J. F. Immunity to and immunotherapy for Rhodococcus equi. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1982;32:497–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B., Mutimer M. D., Farmer A. M. Epidemiology of Corynebacterium equi in horses. Res Vet Sci. 1980 Jan;28(1):87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



