Abstract
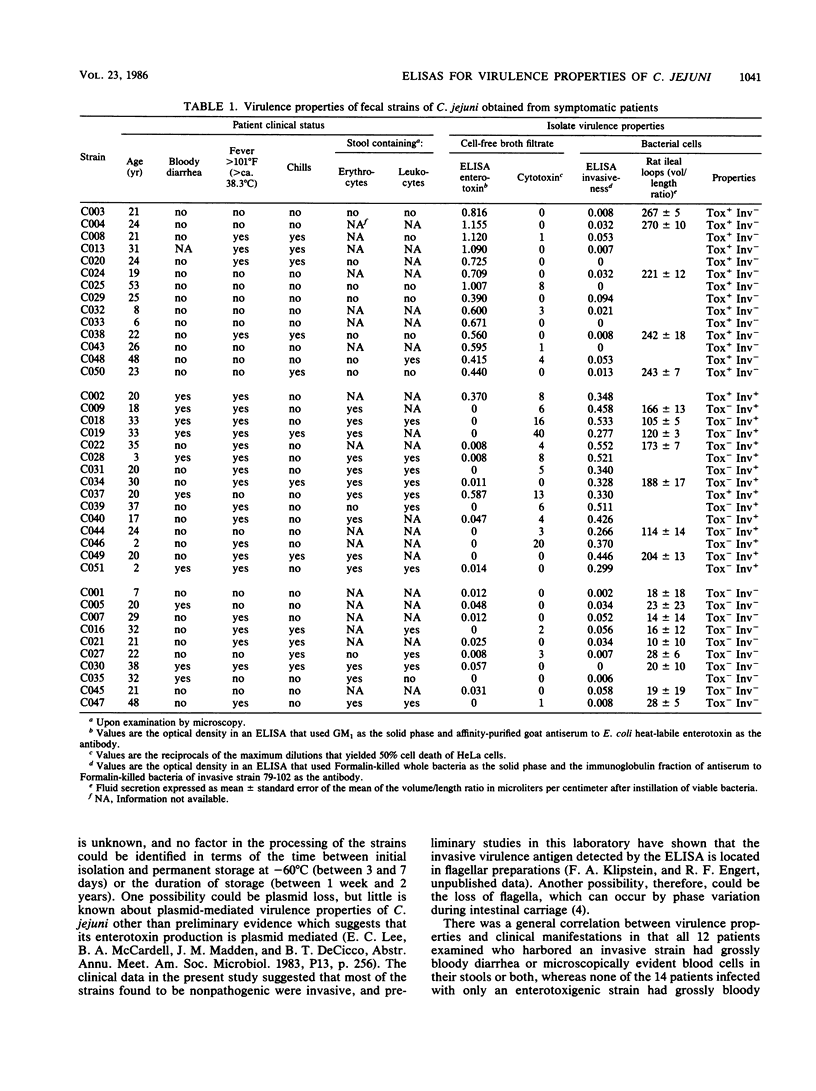
To evaluate the capacity of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) to identify pathogenic strains among clinical fecal isolates of Campylobacter jejuni, 40 consecutively obtained strains from 39 sick patients and 1 asymptomatic person were tested by respective ELISAs for enterotoxin production in culture filtrates and for the invasive virulence antigen of bacterial cells. Of the 40 strains, 14 produced the enterotoxin; 15 strains, two of which were also enterotoxigenic, were invasive; and 11 strains had no detectable virulence property. The presence or absence of these virulence properties was confirmed by the demonstration that viable cells of all 12 randomly selected enterotoxigenic or invasive strains tested, but none of 9 nonpathogenic strains tested, caused fluid secretion in rat ligated ileal loops. All 12 patients examined who were infected with an invasive strain had grossly or microscopically evident blood cells in their stools or both, whereas none of those infected with an enterotoxigenic strain had overtly bloody diarrhea, and only 1 of 8 patients examined had microscopically evident blood cells in the stool. Twelve of the invasive, five of the enterotoxigenic, and three of the nonpathogenic strains also produced small amounts of cytotoxin, but there was no correlation between cytotoxin production and an abnormal response in rat ligated ileal loops. These observations show that enterotoxin production or invasiveness or both can be detected by ELISAs in three-fourths of C. jejuni fecal isolates and that there is usually a relationship between the specific pathogenic property of the infecting strain and the clinical mainfestations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Glass R. I., Huq M. I., Stoll B., Kibriya G. M., Alim A. R. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from Bangladeshi children. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):744–747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.744-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Parsons R. B., Wang W. L. Acute colitis caused by Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni. Gastroenterology. 1980 Mar;78(3):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Wells J. G., Feldman R. A., Pollard R. A., Allen J. R. Campylobacter enteritis in the United States. A multicenter study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):360–365. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Guerry P., Lee E. C., Burans J. P., Walker R. I. Reversible expression of flagella in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):941–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. A., Gilchrist M. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Huizenga K. A., Van Scoy R. E. Diarrhea due to Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni. A clinical review of 63 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981 Jul;56(7):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Dalrymple J. M. Quantitative microtiter cytotoxicity assay for Shigella toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.361-366.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Stoll B. J., Huq M. I., Struelens M. J., Blaser M., Kibriya A. K. Epidemiologic and clinical features of endemic Campylobacter jejuni infection in Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):292–296. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey C. D., Montag D. M., Pittman F. E. Experimental infection of hamsters with Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):485–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Lambert M. A., Blaser M. J., Moss C. W. 30 years of campylobacters: biochemical characteristics and a biotyping proposal for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1065-1073.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. Toxins produced by Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):229–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirubakaran C., Davidson G. P. Campylobacter as a cause of acute enteritis in children in South Australia. II. Clinical comparison with salmonella, rotavirus and non-specific enteritis. Med J Aust. 1981 Oct 3;2(7):336–337. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb100992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological relationship of the B subunits of Campylobacter jejuni and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):629–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.629-633.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Properties of crude Campylobacter jejuni heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):314–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.314-319.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H., Schenk E. A. Pathogenic properties of Campylobacter jejuni: assay and correlation with clinical manifestations. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.43-49.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Schofield P. F., Ironside A. G., Mandal B. K. Campylobacter colitis. Br Med J. 1979 Mar 31;1(6167):857–859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6167.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longfield R., O'Donnell J., Yudt W., Lissner C., Burns T. Acute colitis and bacteremia due to Campylobacter fetus. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Dec;24(12):950–953. doi: 10.1007/BF01311952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee A. S., Shield M., Burke M. Campylobacter colitis: differentiation from acute inflammatory bowel disease. J R Soc Med. 1985 Mar;78(3):217–223. doi: 10.1177/014107688507800309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed I., Bujanover Y., Spirer Z., Schwartz D., Conforty N. Polymicrobial infection in campylobacter enteritis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Sep 7;291(6496):633–634. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6496.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Saunders F., Dehele Y., Pearson A. D. The virulence of clinical and environmental isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Feb;94(1):45–54. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., Pearson A. The invasion of epithelial cell lines and the intestinal epithelium of infant mice by Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1984 Mar;2(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pál T., Pácsa A. S., Emödy L., Vörös S., Sélley E. Modified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting enteroinvasive Escherichia coli and virulent Shigella strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):415–418. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.415-418.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan D. P., Mathan V. I. Prevalence of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni in healthy populations in southern India. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):749–751. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.749-751.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Escamilla E., Torres N. Experimental Campylobacter diarrhea in chickens. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):250–255. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.250-255.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Torres J., Torres N. I., Escamilla E., Ruiz-Palacios B. R., Tamayo J. Cholera-like enterotoxin produced by Campylobacter jejuni. Characterisation and clinical significance. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):250–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Echeverria P., Blaser M. J., Pitarangsi C., Blacklow N., Cross J., Weniger B. G. Polymicrobial aetiology of travellers' diarrhoea. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):381–383. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L. Experimental gastroenteritis in newly-hatched chicks infected with Campylobacter jejuni. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Oct;18(2):233–248. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeen W. P., Puthucheary S. D., Pang T. Demonstration of a cytotoxin from Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;36(11):1237–1240. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.11.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


