Abstract
Pseudomonas mesophilica was isolated from fungal blood cultures of two bone marrow transplant recipients who consecutively occupied the same room. The isolation of P. mesophilica was temporally associated with febrile illness in these two granulocytopenic patients at 1 and 3 weeks posttransplant. A third patient, housed separately on the same bone marrow transplant unit, had nasopharyngeal colonization by this organism. Epidemiologic risk factors in common included staff, medications, and oral and perineal irrigations with tap water. Surveillance cultures detected P. mesophilica in none of 24 pharmaceutical preparations and in 10 of 40 tap water samples (100 to 600 CFU/ml) from implicated and control rooms on the same floor. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of 14 patients and environmental isolates by agar dilution revealed similar profiles; some environmental isolates exhibited higher MICs. Because of restrictive nutritional and temperature requirements, P. mesophilica is undetected by many clinical laboratory protocols and may represent a previously undetected source of febrile illness in neutropenic patients.
Full text
PDF
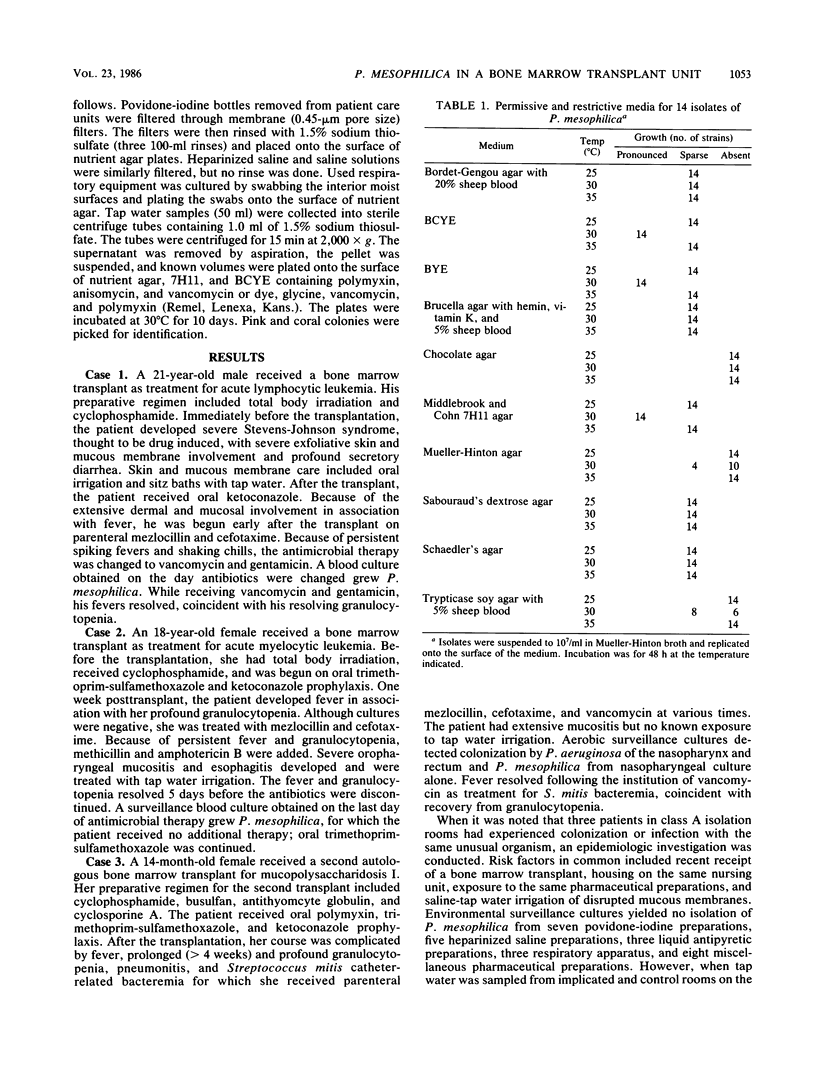
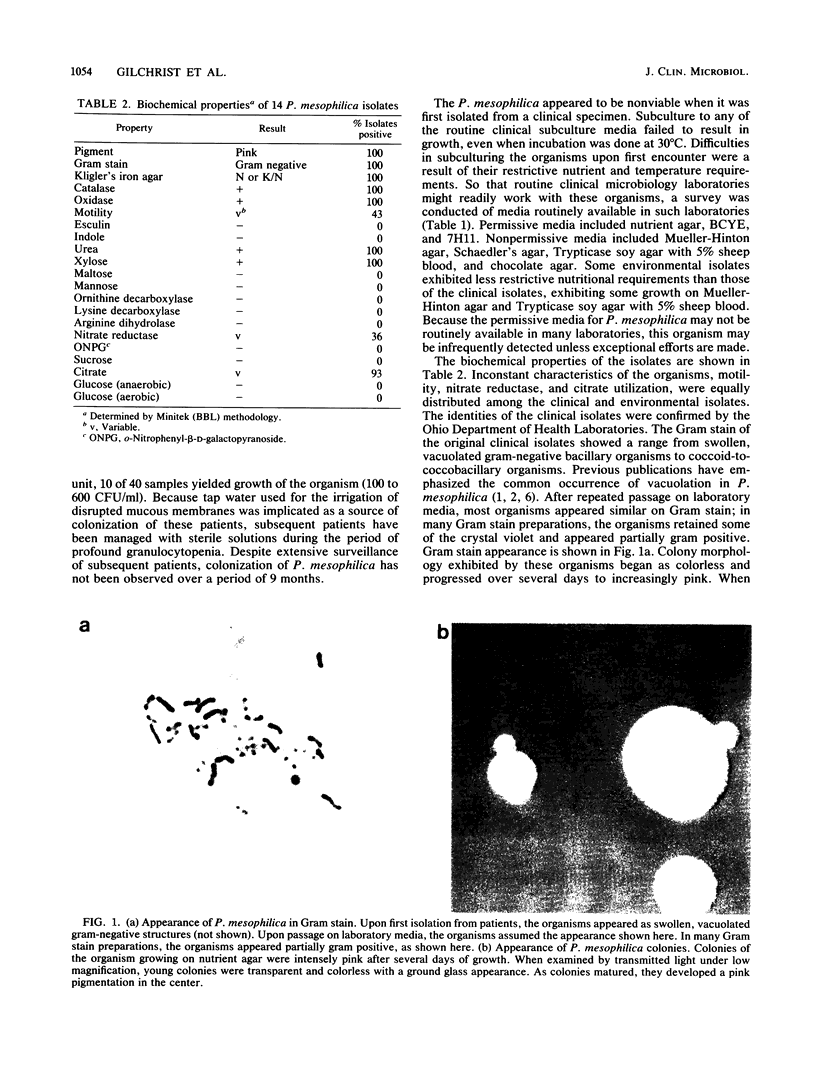

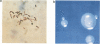
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gilardi G. L., Faur Y. C. Pseudomonas mesophilica and an unnamed taxon, clinical isolates of pink-pigmented oxidative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):626–629. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.626-629.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C. M., Massanari R. M., Zeitler R., Streed S., Gilchrist M. J., Hall N., Hausler W. J., Jr, Sywassink J., Johnson W., Wintermeyer L. Legionnaires' disease associated with a hospital water system: a cluster of 24 nosocomial cases. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):172–178. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-2-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B., ALTURE WERBER E., O'HARE D. AN INTERESTING MICROORGANISM RECOVERED FROM THREE PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC DISEASE. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Sep;90:437–447. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.90.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert W. C., Pathan A. K., Imaeda T., Kaminski Z. C., Reichman L. B. Culture of Vibrio extorquens from severe, chronic skin ulcers in a Puerto Rican woman. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 Aug;9(2):262–268. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(83)80359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H., Forrester C. Pseudomonas mesophilica infections in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):314–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.314-317.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]