Abstract
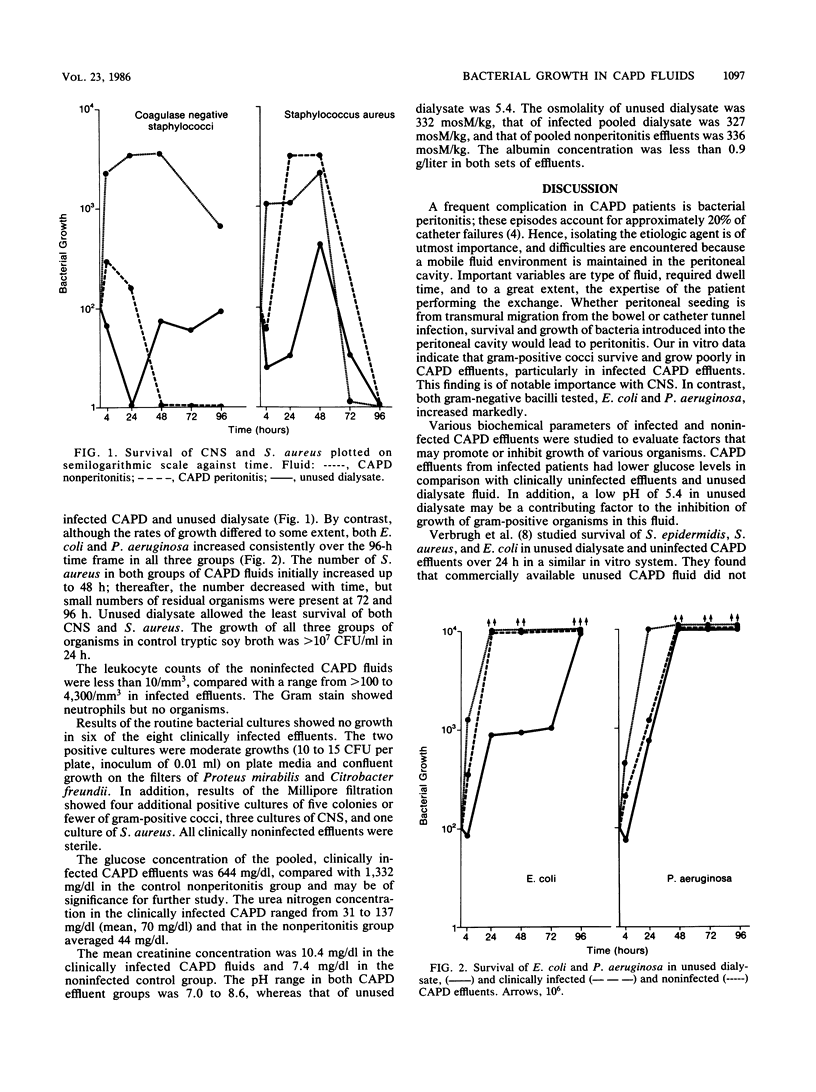
We examined the in vitro survival of bacteria in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis effluents of patients with clinical peritonitis and those without peritonitis. Standard strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS), Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were inoculated into the fluids, and portions were plated for bacterial counts at 0.5, 4, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h. Unused dialysate fluid was also inoculated simultaneously. Our results show that CNS increased minimally up to 48 h in the noninfected continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis effluents and decreased by 96 h, whereas survival was only minimal in the infected effluent. S. aureus showed trends similar to those of CNS, but differences in survival in infected and noninfected effluents were less marked. By contrast, E. coli and P. aeruginosa increased by greater than 1,000-fold in all solutions tested. Based on the above findings, it is likely that a proportionate number of culture-negative cases of peritonitis are due to gram-positive cocci, especially CNS, which are not retrievable by standard culture techniques because of poor survival rate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binswanger U., Keusch G., Bammatter F., Heule H., Kiss D. Peritonitis during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: improving patient defense by type of buffer of dialysate? Nephron. 1981;28(6):300–302. doi: 10.1159/000182223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton P. Laboratory diagnosis of peritonitis in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Nov;35(11):1181–1184. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.11.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krothapalli R., Duffy W. B., Lacke C., Payne W., Patel H., Perez V., Senekjian H. O. Pseudomonas peritonitis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Oct;142(10):1862–1863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J., Adair C. M., Raju S., Bower J. D. The Tenckhoff catheter for peritoneal dialysis--an appraisal. Nephron. 1982;32(4):370–374. doi: 10.1159/000182882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J., Rogers W. A., Taylor H. M., Everett E. D., Prowant B. F., Fruto L. V., Nolph K. D. Peritonitis during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):7–13. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I., Law L. Microbiological diagnosis of peritonitis in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):522–523. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.522-523.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I. Microbiologic aspects of chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. 1983 Jan;23(1):83–92. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Keane W. F., Conroy W. E., Peterson P. K. Bacterial growth and killing in chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis fluids. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):199–203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.199-203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


