Abstract
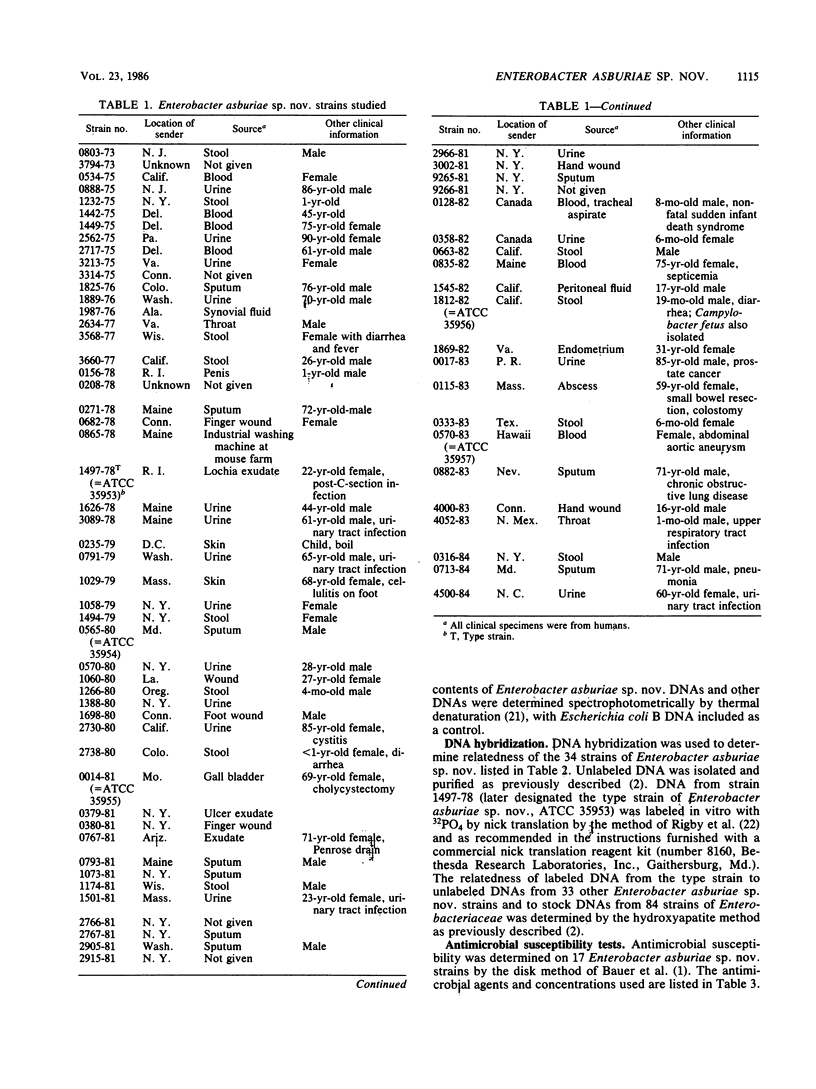
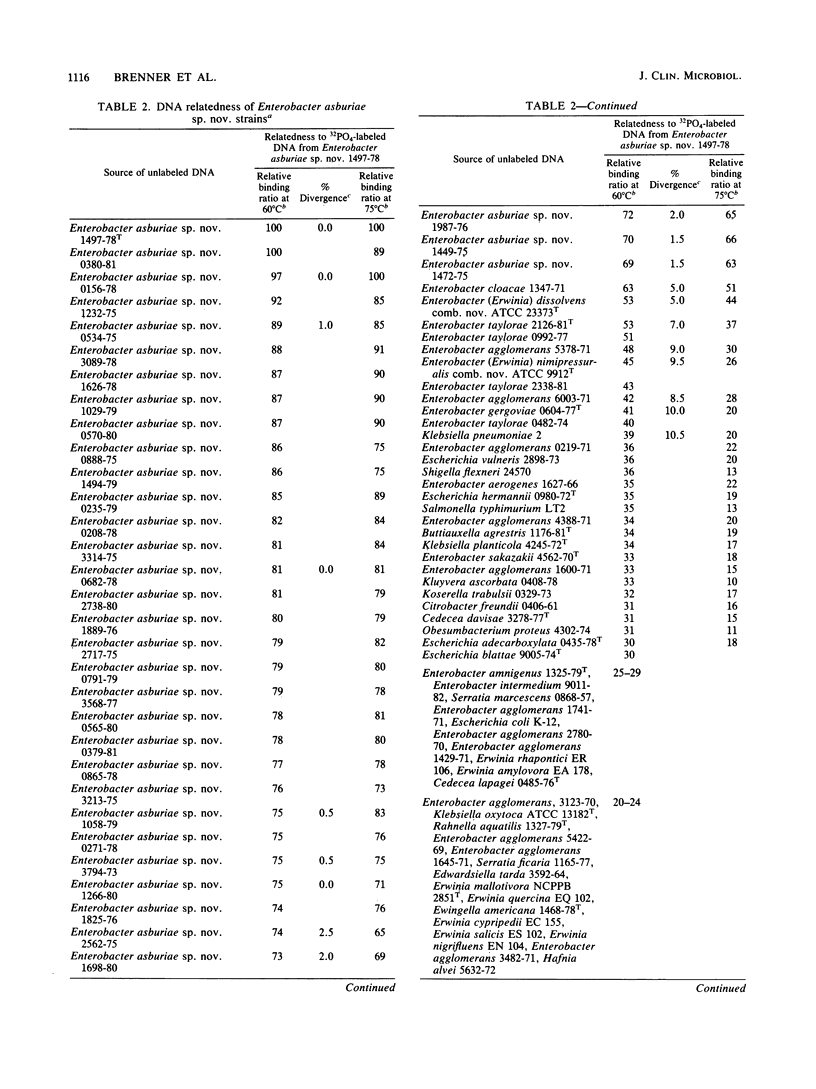
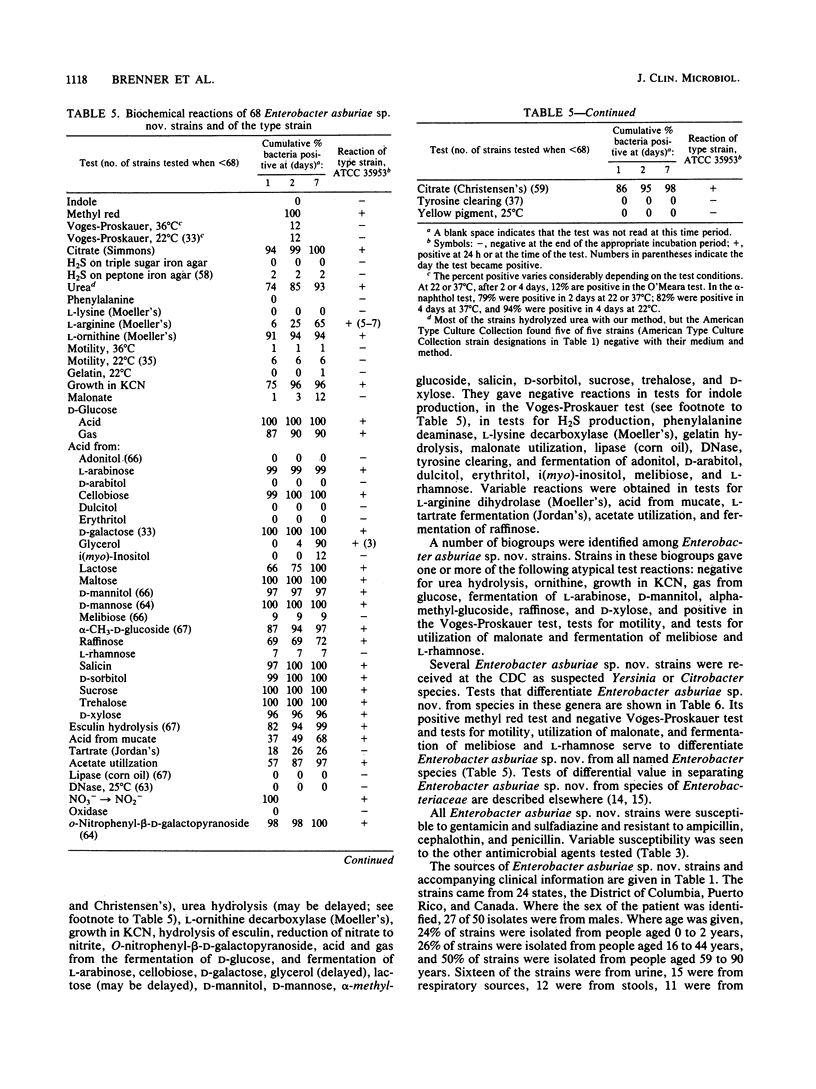
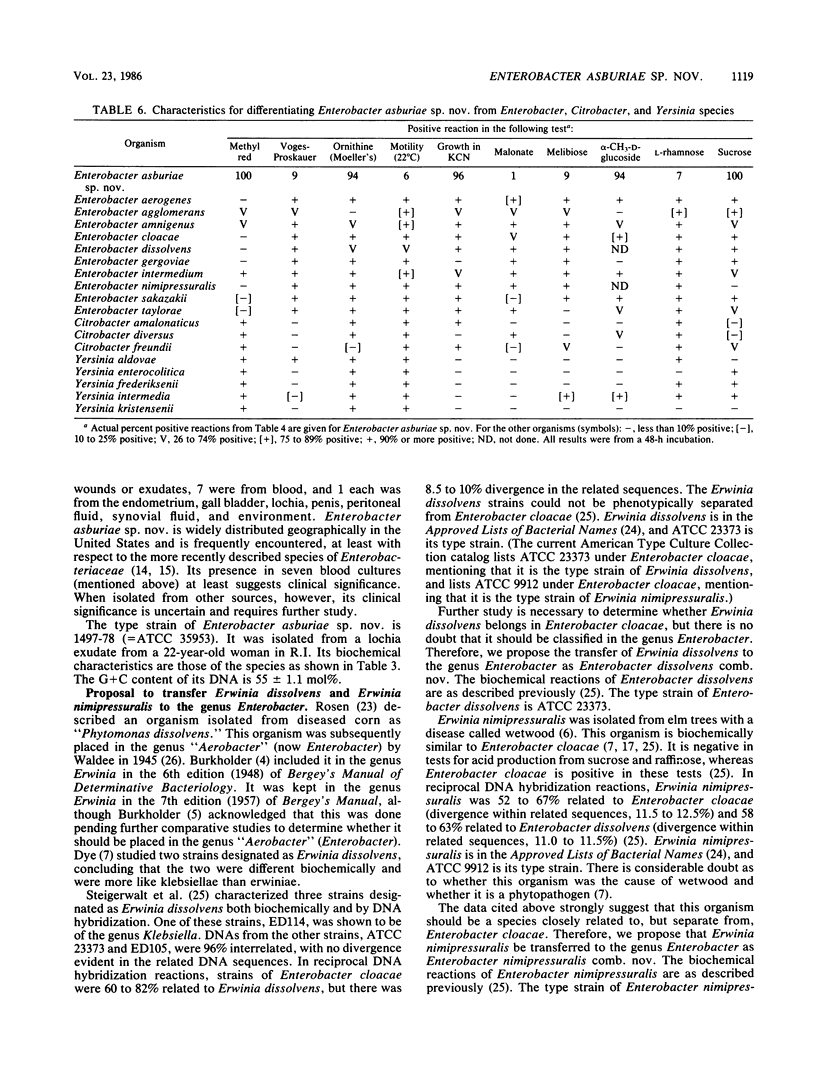
Enterobacter asburiae sp. nov. is a new species that was formerly referred to as Enteric Group 17 and that consists of 71 strains, 70 of which were isolated from humans. Enterobacter asburiae sp. nov. strains gave positive reactions in tests for methyl red, citrate utilization (Simmons and Christensen's), urea hydrolysis, L-ornithine decarboxylase, growth in KCN, acid and gas production from D-glucose, and acid production from L-arabinose, cellobiose, glycerol (negative in 1 to 2 days, positive in 3 to 7 days), lactose, D-mannitol, alpha-methyl-D-glucoside, salicin, D-sorbitol, sucrose, trehalose, and D-xylose. They gave negative reactions in the Voges-Proskauer test and in tests for indole, H2S production, phenylalanine, L-lysine decarboxylase, motility, gelatin, utilization of malonate, lipase, DNase, tyrosine clearing, acid production from adonitol, D-arabitol, dulcitol, erythritol, i(myo)-inositol, melibiose, and L-rhamnose. They gave variable reactions in tests for L-arginine dihydrolase (25% positive after 2 days) and acid production from raffinose (69% positive after 2 days). Thirty-four Enterobacter asburiae sp. nov. strains were tested for DNA relatedness by the hydroxyapatite method with 32PO4-labeled DNA from the designated type strain (1497-78, ATCC 35953). The strains were 69 to 100% related in 60 degrees C reactions and 63 to 100% related in 75 degrees C reactions. Divergence within related sequences was 0 to 2.5%. Relatedness of Enterobacter asburiae sp. nov. to 84 strains of members of the Enterobacteriaceae was 5 to 63%, with closest relatedness to strains of Enterobacter cloacae, Erwinia dissolvens, Enterobacter taylorae, Enterobacter agglomerans, Erwinia nimipressuralis, and Enterobacter gergoviae. All strains tested were susceptible to gentamicin and sulfdiazine, and most were susceptible to chloramphenicol, colistin, kanamycin, nalidixic acid, carbenicillin and streptomycin. All strains were resistant to ampicillan, cephalothin, and penicillin, and most were resistant or moderately resistant to tetracycline. Enterobacter asburiae sp. nov strains were isolated from a variety of human sources, most prevalent of which were urine (16 strains), respiratory sources (15 strains), stools (12 strains), wounds (11 strains), and blood (7 strains). The clinical significance of Enterobacter aburiae is not known. As a result of this and previous studies, proposals are made to transfer Erwinia dissolvens and Erwinia nimipressuralis to the genus Enterobacter as Enterobacter dissolvens comb. nov. and Enterobacter nimipressuralis comb. nov., respectively.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS P. R., FIFE M. A. Capsule types of Klebsiella. J Infect Dis. 1952 Jul-Aug;91(1):92–104. doi: 10.1093/infdis/91.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIFE M. A., McWHORTER C., EDWARDS P. R. Ten new Arizona serotypes isolated from animals and animal food products. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1962;28:369–372. doi: 10.1007/BF02538749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Davis B. R., Hickman-Brenner F. W., McWhorter A., Huntley-Carter G. P., Asbury M. A., Riddle C., Wathen-Grady H. G., Elias C., Fanning G. R. Biochemical identification of new species and biogroups of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):46–76. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.46-76.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Fanning G. R., Davis B. R., O'Hara C. M., Riddle C., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Asbury M. A., Lowery V. A., 3rd, Brenner D. J. Escherichia fergusonii and Enterobacter taylorae, two new species of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.77-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Salmonella typhi: identification, antibiograms, serology, and bacteriophage typing. Am J Med Technol. 1978 Dec;44(12):1149–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Framer J. J., 3rd, Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Unusual groups of Morganella ("Proteus") morganii isolated from clinical specimens: lysine-positive and ornithine-negative biogroups. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.88-94.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigerwalt A. G., Fanning G. R., Fife-Asbury M. A., Brenner D. J. DNA relatedness among species of Enterobacter and Serratia. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;22(2):121–137. doi: 10.1139/m76-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


