Abstract
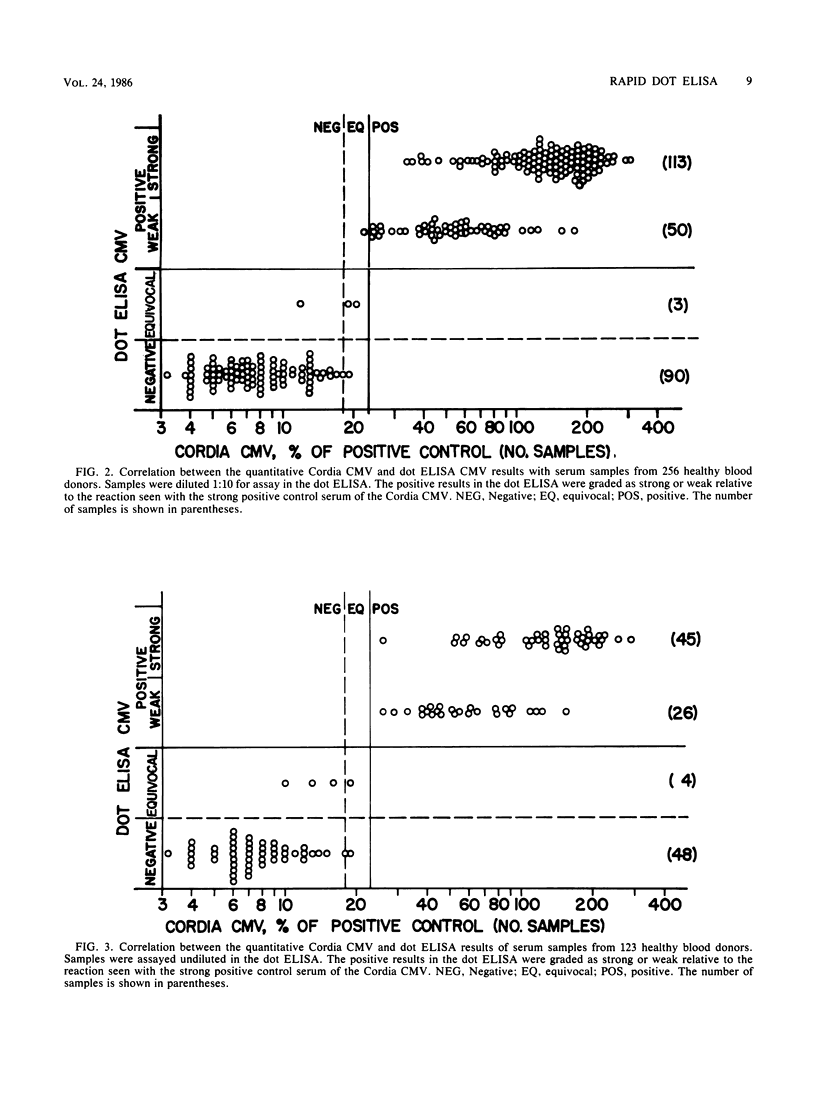
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) antigen was coated onto a white opaque plastic card as small dots inside circles marked in the microtiter plate well pattern. The card with antigen dots could be cut according to the number of test samples to be assayed. Small drops of undiluted serum samples, goat antibodies to human immunoglobulin G labeled with alkaline phosphatase, and finally substrate (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate) were sequentially added to the antigen spots and incubated in the open air at room temperature for 5 min each. The antigen dots showed blue color for sera with immunoglobulin G antibodies to cytomegalovirus but no color for those without. The developed antigen dots could be rinsed with water and kept as permanent records. For the assay of a large number of serum samples, a modified procedure with serum diluted 1:10 and longer first two incubations (20 min each) was found to be more comfortable to perform. The results of this assay for 123 undiluted and 256 diluted serum samples revealed very good correlations with those obtained by a commercially available test kit for immunoglobulin G antibodies to cytomegalovirus with 97 and 99% agreement, respectively. This dot test was very reproducible and required no instrumentation. The reagents, including coated antigen dots, are stable at room temperature for at least 2 months and are ready for use.
Full text
PDF
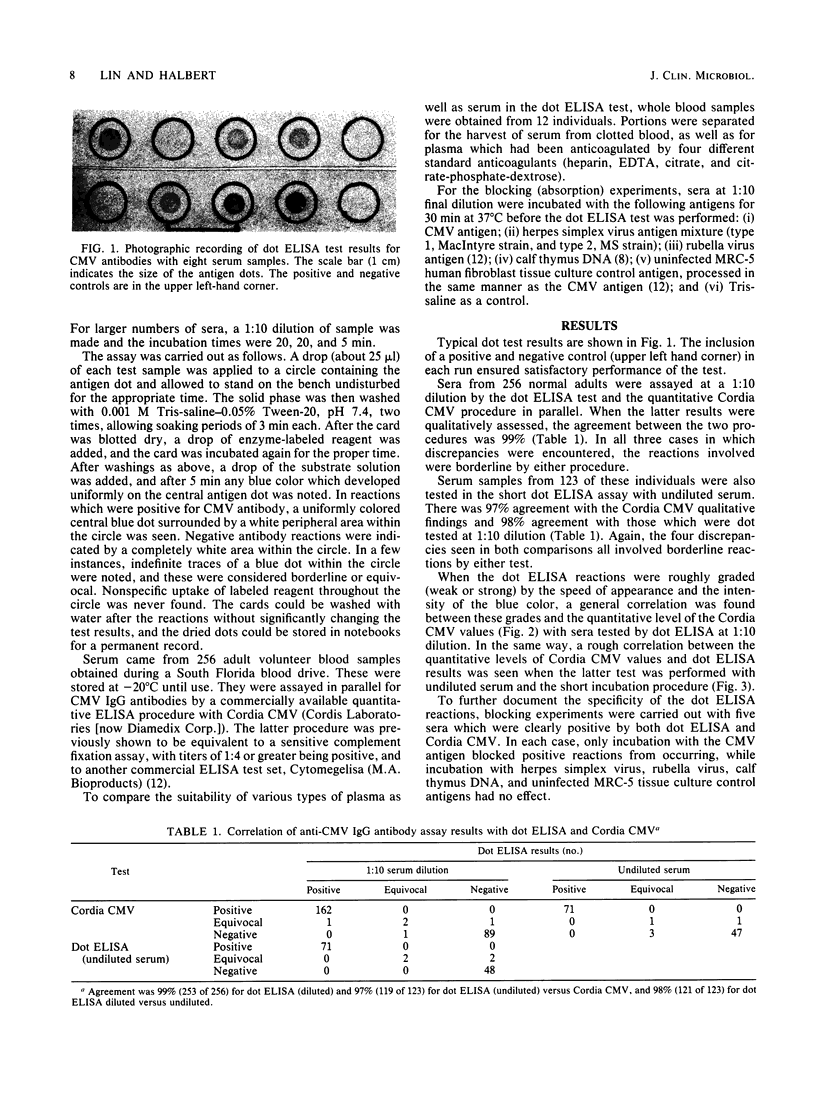


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckwith D. G., Halstead D. C., Alpaugh K., Schweder A., Blount-Fronefield D. A., Toth K. Comparison of a latex agglutination test with five other methods for determining the presence of antibody against cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.328-331.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Lin T. M., Schubert C. M., Halbert S. P. Treponemal antibody-absorbent enzyme immunoassay for syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):876–880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.876-880.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Anken M. Detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBS Ag) with use of alkaline phosphatase-labeled antibody to HBS Ag. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136 (Suppl):S318–S323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_2.s318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Anken M., Henle W., Golubjatnikov R. Detection of infectious mononucleosis heterophil antibody by a rapid, standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay procedure. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):610–616. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.610-616.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Bastomsky C. H., Anken M. A rapid standardized enzyme immunoassay for autoantibodies to thyroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 7;127(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. A quantitative enzyme immunoassay for IgM rheumatoid factor using human immunoglobulin G as substrate. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;74(6):776–784. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.6.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. Studies on autoantibodies to deoxyribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleoprotein with enzyme-immunoassay (ELISA). J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):97–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Poiesz B., Friedman-Kien A. E., Montagna R., Blattner W. A., Anken M. Quantitative estimation by a standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I antibodies in adult T-cell leukemia and acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):212–216. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.212-216.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer D. J., Phelps D. A., Halbert S. P. Normalized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determining immunoglobulin G antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.33-39.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleeman K. T., Kiefer D. J., Halbert S. P. Rubella antibodies detected by several commercial immunoassays in hemagglutination inhibition-negative sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1131–1137. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1131-1137.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Chin-See M. W., Halbert S. P., Joseph J. M. An enzyme immunoassay for immunoglobulin M antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii which is not affected by rheumatoid factor or immunoglobulin G antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):77–82. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.77-82.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Chin-See M. W., Halbert S. P. The stability of prostatic acid phosphatase, as measured by a capture immunoenzyme assay. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Mar 27;138(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Halbert S. P., Chiu C. T., Zarco R. Simple standardized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human antibodies to Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):646–651. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.646-651.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Halbert S. P., Cort R., Blaschke M. J. An enzyme-linked immunoassay for circulating immune complexes using solid phased goat Clq. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 14;63(2):187–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90423-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. M., Halbert S. P., O'Connor G. R. Standardized quantitative enzyme-linked immunoassay for antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.675-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Shahrabadi M. S., Ince B. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus gastroenteritis by a commercial latex agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):846–850. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.846-850.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas M. G., Hajkowski R., Hockmeyer W. T. Dot enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Dot-ELISA): a micro technique for the rapid diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. D., Holt P. G. A solid-phase immunoenzymatic technique for the enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 25;57(1-3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vänänen P., Häivä V. M., Koskela P., Meurman O. Comparison of a simple latex agglutination test with hemolysis-in-gel, hemagglutination inhibition, and radioimmunoassay for detection of rubella virus antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):793–795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.793-795.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



