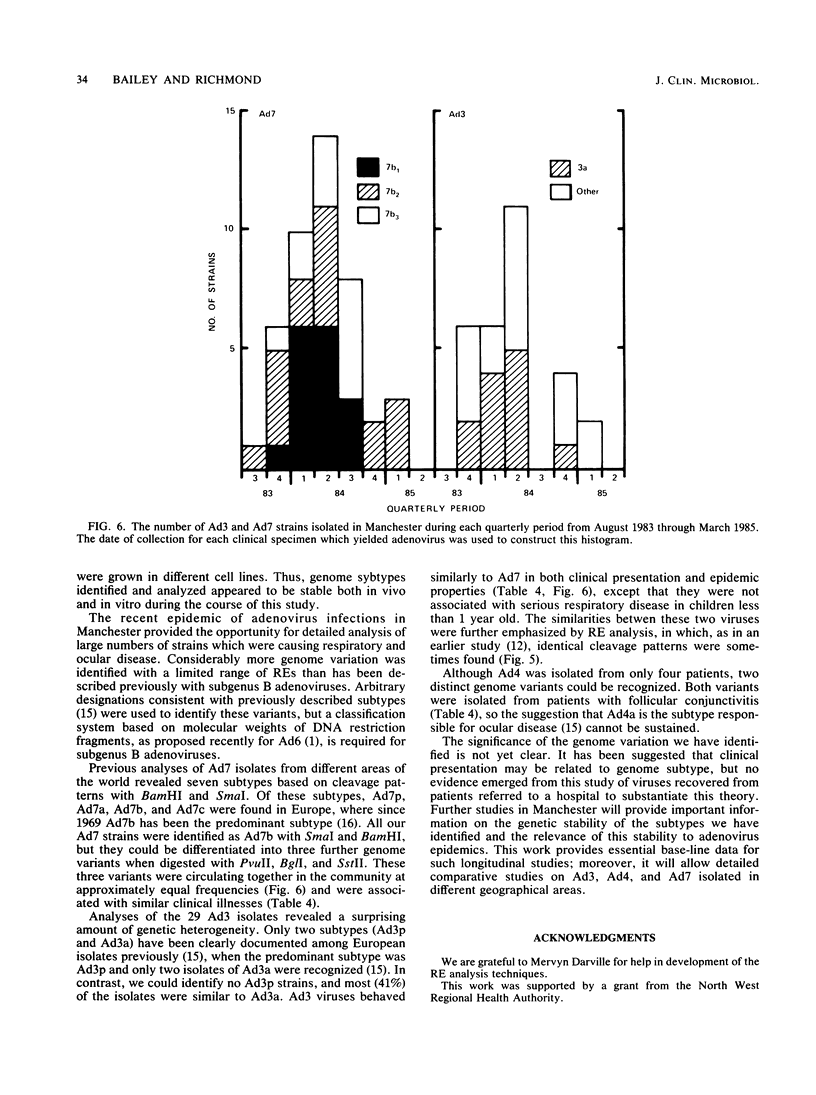
Abstract
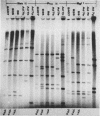
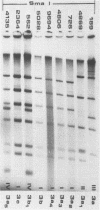
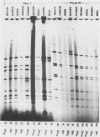
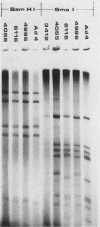
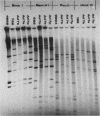
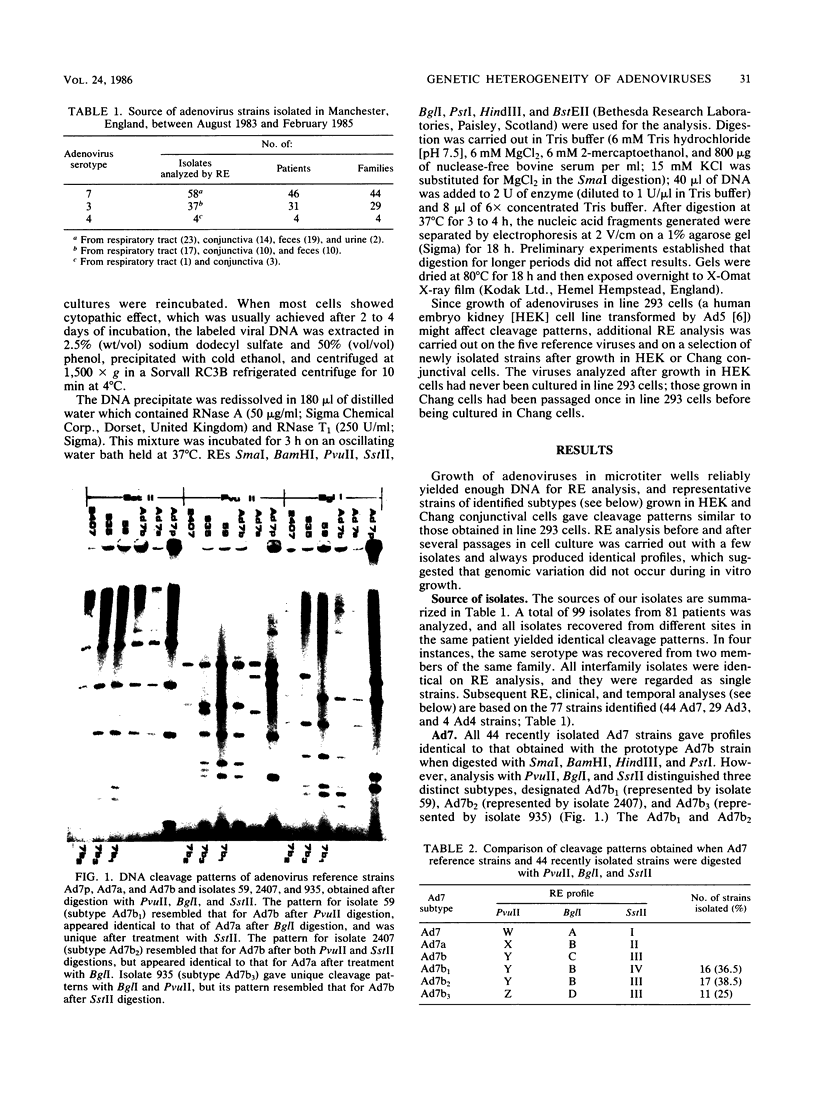
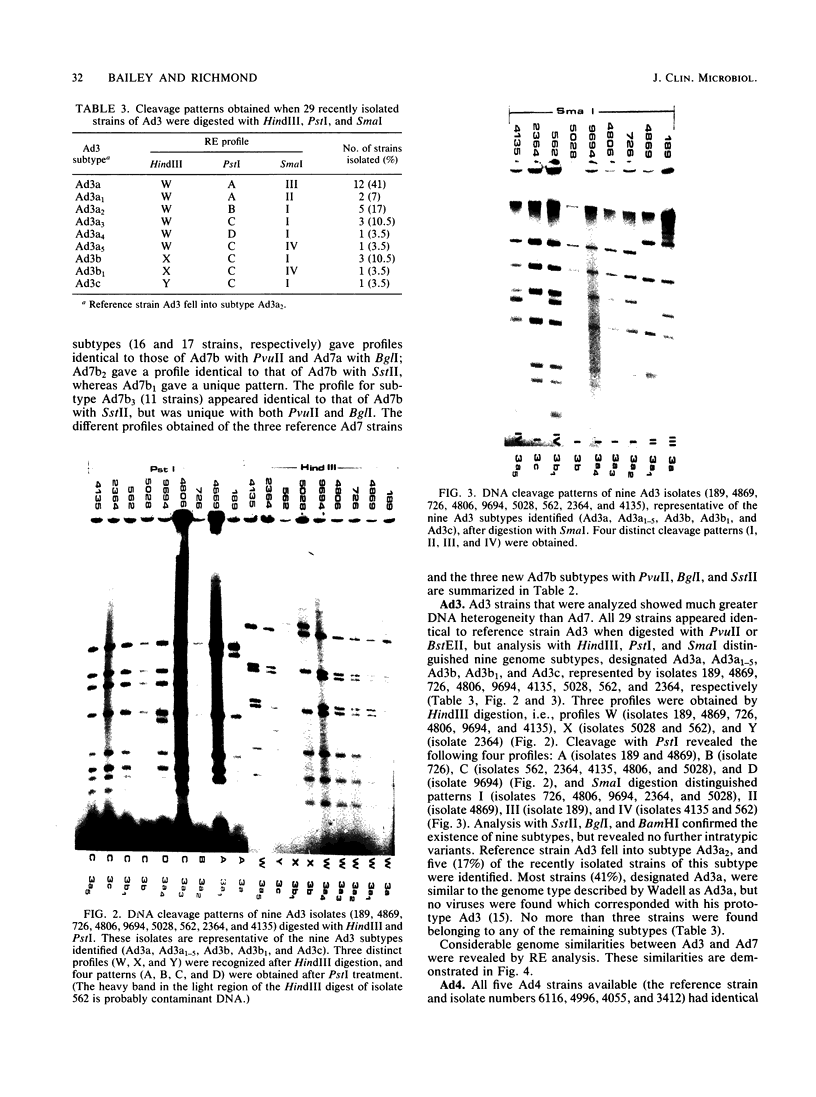
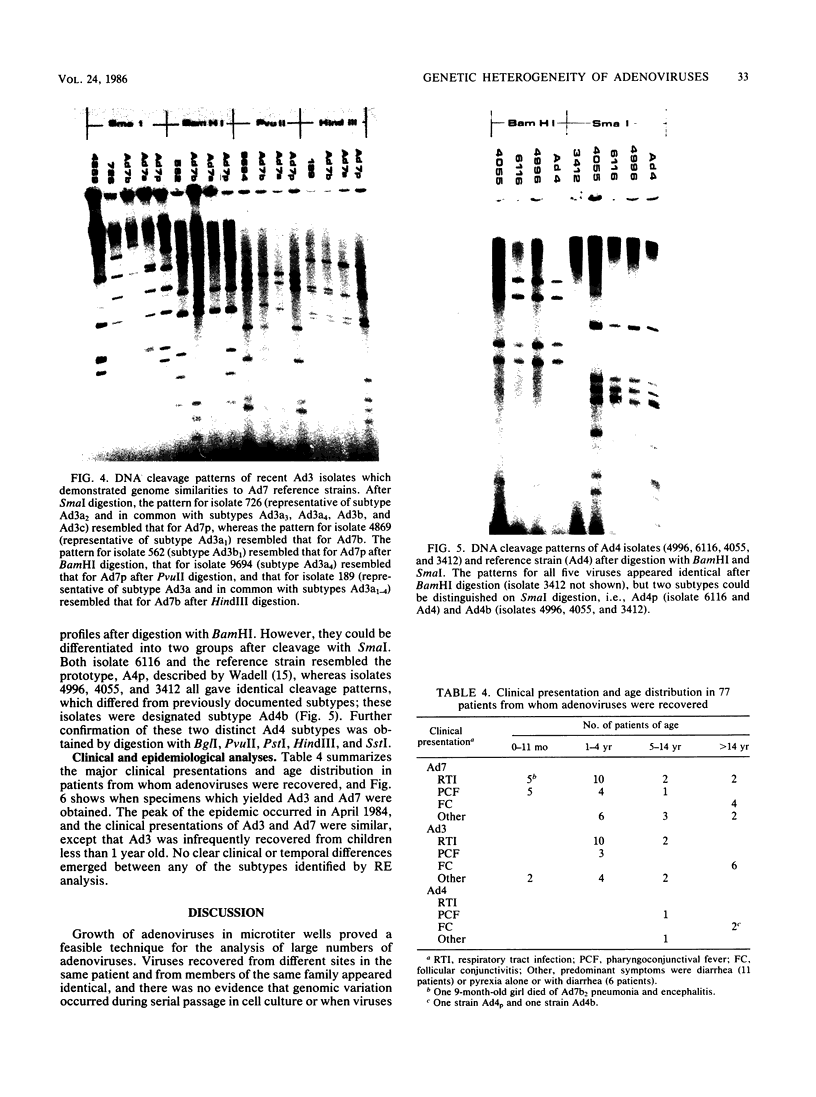
Restriction endonuclease analysis was carried out on adenovirus types 3, 4, and 7 (Ad3, Ad4, and Ad7, respectively) isolated during a 16-month epidemic period. Most of the isolates were associated with respiratory or ocular infection or both. Forty-four strains of the subtype Ad7b were identified with SmaI; these strains could be further subdivided into three distinct genome groups, designated Ad7b1, Ad7b2, and Ad7b3, by digestion with PvuII, BglI, and SstII. These Ad7b variants occurred at approximately similar frequencies throughout the epidemic and were associated with similar clinical illnesses. Nine distinct intratypic genome groups were identified among 29 Ad3 strains with HindIII, PstI, and SmaI; adenoviruses similar to subtype Ad3a, formerly reported to be uncommon in Europe, were isolated most frequently (41% of strains), and the previously predominant prototype (Ad3p) was not found. Considerable similarities among the genomes of some strains of Ad3 and Ad7 could be demonstrated, and clinical and epidemiological presentations were very similar. The four strains of Ad4 isolated fell into two distinct patterns, i.e., the previously recognized prototype (Ad4p) and a new subtype designated Ad4b. Both of these subtypes were associated with follicular conjunctivitis. Thus we were unable to produce evidence that particular genome types of Ad3, Ad4, and Ad7 are associated with particular clinical presentations. However, restriction endonuclease analysis should prove useful for epidemiological studies on these viruses.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T., Best B., Wigand R. A proposal for naming adenovirus genome types, exemplified by adenovirus type 6. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2685–2691. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T., Wigand R., Hierholzer J. C. Immunological and biochemical characterization of human adenoviruses from subgenus B. II. DNA restriction analysis. Arch Virol. 1985;84(1-2):79–89. doi: 10.1007/BF01310555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darville J. M. A miniaturised and simplified technique for typing and subtyping herpes simplex virus. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Aug;36(8):929–934. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.8.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darville J. M. Simplified restriction endonuclease method for typing and subtyping adenoviruses. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Mar;38(3):331–335. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fife K. H., Ashley R., Corey L. Isolation and characterization of six new genome types of human adenovirus types 1 and 2. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):20–23. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.20-23.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Mackey J. K., Wold W. S., Rigden P. Thirty-one human adenovirus serotypes (Ad1-Ad31) form five groups (A-E) based upon DNA genome homologies. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H., Berkowitz F. E., Blaskovic P. J., Schoub B. D. Genome variants of human adenovirus 40 (subgroup F). J Med Virol. 1984;14(3):235–246. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H. Genome variants of adenovirus 41 (subgroup G) from children with diarrhoea in South Africa. J Med Virol. 1984;14(1):49–59. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Wigand R., Heinrich W. Worldwide epidemiology of human adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Apr;117(4):455–466. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts C. Physical organization of subgroup B human adenovirus genomes. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):564–579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.564-579.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullo A. B., Higgins P. G. An outbreak of adenovirus type 4 conjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1980 Jul;64(7):489–493. doi: 10.1136/bjo.64.7.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G. Classification of human adenoviruses by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of structural polypeptides. Intervirology. 1979;11(1):47–57. doi: 10.1159/000149011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., Cooney M. K., da Costa Linhares A., de Silva L., Kennett M. L., Kono R., Gui-Fang R., Lindman K., Nascimento J. P., Schoub B. D. Molecular epidemiology of adenoviruses: global distribution of adenovirus 7 genome types. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):403–408. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.403-408.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., Hammarskjöld M. L., Winberg G., Varsanyi T. M., Sundell G. Genetic variability of adenoviruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:16–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G. Molecular epidemiology of human adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:191–220. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]