Abstract
The transcription factor NF-κB is required for lymphocyte activation and proliferation as well as the survival of certain lymphoma types1, 2. Antigen receptor stimulation assembles an NF-κB activating platform containing the scaffold protein CARMA1/CARD11, the adaptor BCL10, and the paracaspase MALT1 (CBM complex), linked to the inhibitor of NF-κB kinase (IKK) complex3–12, but signal transduction is not fully understood1. We conducted parallel screens involving a mass spectrometry analysis of CARMA1 binding partners and an RNAi screen for growth inhibition of the CBM-dependent “activated B cell-like” (ABC) subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)12. Here, we report that both screens identified casein kinase 1α (CK1α) as a bifunctional regulator of NF-κB. CK1α dynamically associates with the CBM complex upon T cell receptor (TCR) engagement to augment cytokine production and lymphocyte proliferation. However, CK1α kinase activity plays a counterposing role by subsequently promoting the phosphorylation and inactivation of CARMA1. CK1α has thus a dual “gating” function which first promotes and then terminates receptor-induced NF-κB. ABC DLBCL cells required CK1α for constitutive NF-κB activity indicating that CK1α functions as a “conditionally essential malignancy” (CEMal) gene - a member of a new class of potential cancer therapeutic targets.
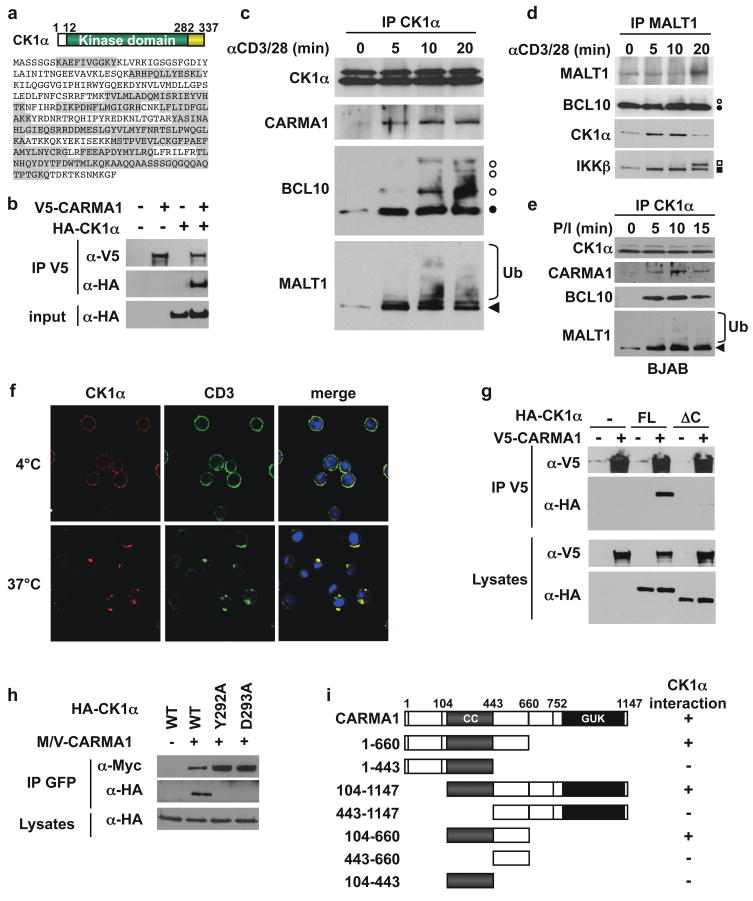
To better understand signal regulation by the CBM complex, we performed a mass spectrometry proteomic screen following CARMA1 immunoprecipitation. Sixteen peptides covering 54% of CK1α were isolated from an excised band (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. 1). CK1α belongs to the CK1 family of serine/threonine protein kinases, which regulates developmental and homeostatic processes including the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and circadian rhythm13. Co-immunoprecipitations in HEK293T cells showed that HA-tagged CK1α interacted with V5-CARMA1 (Fig. 1b). CARMA1, BCL10, and MALT1 associated with CK1α following TCR stimulation in Jurkat T lymphocytes, and in BJAB B cells stimulated with PMA and ionomycin (Fig. 1c–e). Notably, phosphorylated forms of BCL10 and ubiquitinated species of MALT1, modifications due to signaling14, associated with CK1α. Moreover, MALT1 and BCL10 precipitations revealed TCR-induced recruitment of CK1α concomitantly with IKKβ and phosphorylated-IKKβ (P-IKKβ)(Fig. 1d and data not shown). Also, cytosolic CK1α reorganized into punctate structures that colocalized with CD3 clusters upon TCR activation (Fig. 1f), suggesting an association with CBM components within membrane microdomains2, 15. In contrast to TCR agonists, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), which does not employ the CBM, induced no interaction between CK1α and CBM substituents (Supplementary Fig. 2). Lastly, antibody depletion of CK1α from cell lysates removed nearly the entire active CBM complex (Supplemental Fig. 3). Hence, CK1α is a new component selectively entering the active CBM after antigen receptor stimulation.
Figure 1. Identification of CK1α as a CARMA1-binding partner.
a, Schematic and sequence of CK1α. Peptides identified by a mass spectrometry analysis of CARMA1-containing complexes are highlighted in grey. b, Interaction between HA-CK1α and V5-CARMA1 in HEK293T cells by immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblot (IB). c–e, IP/IB as indicated, in Jurkat T lymphocytes stimulated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 (c–d), and in BJAB B cells stimulated with 20 ng/ml PMA and 300 ng/ml ionomycin (e). Filled and open symbols, non phosphorylated and phosphorylated forms. Ub, ubiquitin. f, Confocal images of CD3 and CK1α following CD3 crosslinking in Jurkat. Nuclei counterstaining is shown in blue. g, IP/IB of V5- CARMA1 binding to HA-tagged CK1α full-length (FL) or lacking residues 283-337 (ΔC) in HEK293T cells. h, Myc-Venus (M/V)-tagged CARMA1 association with HA-CK1α mutants in HEK293T cells by IP/IB. i, Mapping of the minimal CK1α-binding domain of CARMA1 by IP/IB in HEK293T cells expressing HA-CK1α and M/V-CARMA1 truncation mutants.
CK1α harbors a short and unique carboxy-terminal portion attached to the conserved kinase domain13 (Fig. 1a). Removing this region (Δ283-337) abolished CK1α binding to CARMA1 (Fig. 1g). In addition, the human (residues 283-337) and mouse (283-325) CK1α C-terminal domains were sufficient, with Y292 and D293 as the key residues, for CARMA1 association (Fig. 1h and Supplementary Fig. 4a, and 4b). We also found that both the coiled-coil (CC) and linker regions (CCL) of CARMA1 together were critical for CK1α binding. (Fig. 1i, and Supplementary Fig. 4c).
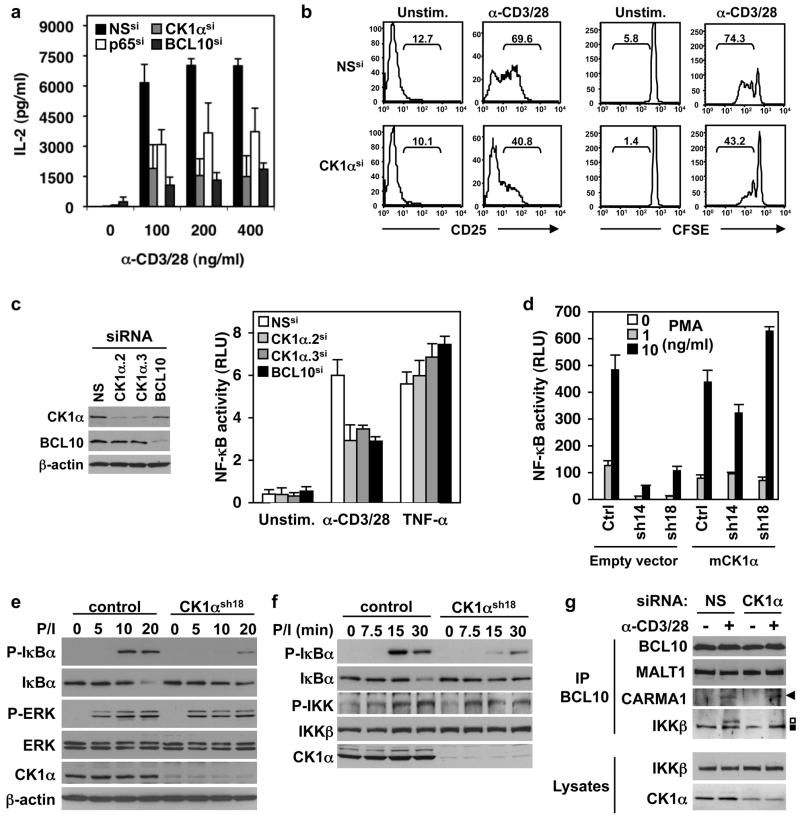
The CBM complex is an obligate gateway from lymphocyte antigen receptors to NF-κB activation1, 3, 8–11. To define the functional importance of CK1α, we first decreased its endogenous levels by RNA interference in primary human T cells. CK1α silencing reduced TCR-induced interleukin-2 (IL-2) production as did silencing of NF-κB p65 and BCL10 (Fig. 2a). This was accompanied by diminished IL-2 receptor (CD25) up-regulation, and reduced proliferation (Fig. 2b). In Jurkat cells, CK1α knockdown with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) decreased the TCR induction of an NF-κB luciferase reporter as efficiently as a BCL10 siRNA (Fig. 2c). Again, TNF-α-mediated NF-κB was unaffected, underscoring the selective involvement of CK1α in the TCR-NF-κB pathway. Accordingly, CK1α-silenced primary T cells and Jurkat also displayed diminished p65 NF-κB nuclear translocation following TCR, but not TNF-α stimulation (Supplementary Fig. 5a–c). By contrast, NF-κB activation proceeded normally when CK1δ- or CK1ε were reduced (Supplementary Fig. 6). Thus, among the CK1s, CK1α provides an essential, non-redundant function in regulating TCR-induced NF-κB activation.
Figure 2. Requirement of CK1α for NF-κB activation and proliferation in lymphocytes.
a and b, Human peripheral blood T lymphocytes were transfected with siRNA for CK1α, NF-κB p65, BCL10, or scrambled nonspecific (NS) siRNA. IL-2 secretion (mean ± s.d. of triplicate measurements), and CD25 induction 12 hours post-stimulation. CFSE dilution was assessed after 96 hours. Percentage of CD25-positive cells, and of dividing cells is shown. c, NF-κB luciferase assay (mean ± s.d. of triplicate experiments) of Jurkat cells transfected with CK1α (CK1α.2 and CK1α.3), BCL10 or NS siRNA, and stimulated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD3 and anti-CD28, or with 25 ng/ml TNF-α. Left panel, IB for CK1α, BCL10, and β-actin. RLU, relative light units. d, NF-κB luciferase assay of Jurkat stably expressing CK1α-shRNA (sh14 and sh18) reconstituted with a control vector or with mouse CK1α (mCK1α), stimulated with PMA and 100 ng/ml ionomycin, and analyzed as in (c). e and f, IB of control and CK1α-shRNA (sh18) expressing Jurkat exposed to 10 ng/ml PMA and 100 ng/ml ionomycin. g, IP/IB of NS- and CK1α-silenced Jurkat stimulated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 20 min. Arrowhead, CARMA1; black and open squares, IKKβ and phosphorylated-IKKβ.
To achieve a better knockdown, single Jurkat clones stably expressing a small hairpin RNA (shRNA) against CK1α were generated. As expected, NF-κB activation was dramatically reduced upon stimulation, as IκBα phosphorylation and degradation were inhibited (Fig. 2d–f). Other early TCR signaling events, such as ERK1/2 phosphorylation, overall tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium mobilization, and NF-AT activation occurred normally (Fig. 2e, and Supplementary Fig. 5d–f). Of note, NF-κB activity was restored when CK1α-silenced cells were rescued with ectopic mouse CK1α (mCK1α), but not with mCK1α mutants lacking CARMA1 binding ability, suggesting that CK1α function requires association with CARMA1 (Fig. 2d, and Supplemental Fig. 7). Hence, CK1α is selectively required for optimal physiological activation of NF-κB upon TCR stimulation in normal lymphocytes.
Promptly following TCR ligation, PKCθ phosphorylates CARMA1 and unleashes its adaptor functions16, 17. CARMA1 then promotes IκBα phosphorylation by recruiting signaling molecules, including BCL10, MALT1, and IKK17, 18. Although IKK was phosphorylated following stimulation of CK1α-silenced cells, P-IKKβ was no longer recruited to CBM (Fig. 2f, g). This parallels previous observations in CARMA1- and BCL10-deficient cells19. Hence, the recruitment of P-IKK and consequent alterations of IκBα are defective without CK1α. Nonetheless, CK1α still associated with CARMA1 in PKCθ- or BCL10-silenced cells, or after treatment with the PKC inhibitor rottlerin, although BCL10/MALT1 recruitment to CK1α/CARMA1 and NF-κB activation were diminished (Supplementary Fig. 8). Thus, CK1α associates with CARMA1 independently of PKCθ and BCL10, and does not require PKCθ-dependent modifications of CARMA1.
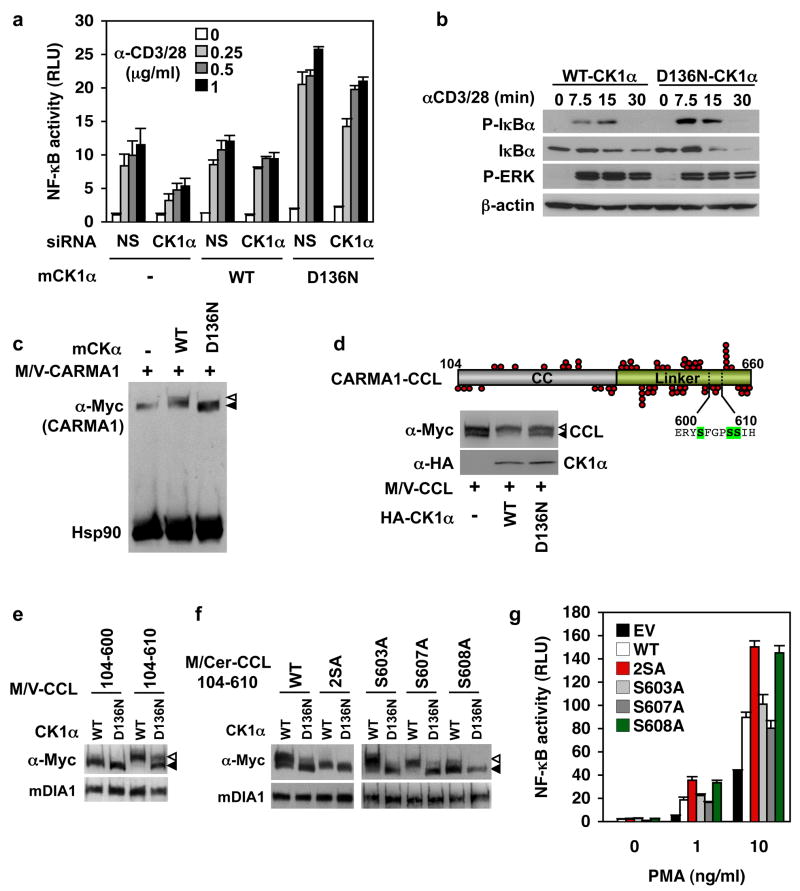
To investigate the role of CK1α enzyme activity, we generated kinase-dead CK1α by introducing point mutations in the ATPase domain (K46R, D136N, or D136A)20, 21. In CK1α-silenced Jurkat, D136N-mCK1α markedly enhanced TCR-induced NF-κB, surpassing the response in cells reconstituted with WT-CK1α (Fig. 3a). Human K46R-, D136N-, and D136A-CK1α mutants gave similar results (Supplemental Fig. 9a). Accordingly, IκBα phosphorylation and degradation was augmented in D136N-mCK1α expressing cells compared to WT-mCK1α (Fig. 3b). The D136N-CK1α synergistic effect was abolished in BCL10-silenced cells, or when D136N/D293A-mCK1α was used (Supplementary Fig. 9d, e), suggesting that enhanced NF-κB requires BCL10, and binding to CARMA1. Thus, CK1α kinase activity plays a negative role in TCR-induced NF-κB activation, in addition to the positive signaling role of CK1α in the CBM complex.
Figure 3. CK1α kinase activity participates to the negative feedback control of the CBM and NF-κB activation.
a, NF-κB luciferase assay (mean ± s.d. of triplicate experiments) of nonspecific (NS)-and CK1α-silenced Jurkat cells reconstituted with an empty vector (−), WT- or D136N-mouse CK1α (mCK1α). RLU, relative luciferase units. b, IB of Jurkat cells expressing WT-, or D136N-mCK1α stimulated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD3 and anti-CD28. c, IB of HEK293T cells expressing Myc/Venus (M/V)-CARMA1 together with an empty vector (−), WT-, or D136N-mCK1α. Filled and open triangles, CARMA1 and its shifted form; Hsp90, loading control. d, Schematic of CARMA1 coiled-coil linker region (CARMA1-CCL, residues 104-660). Red circles, serine/threonine residues. IB of HEK293T cells overexpressing a vector alone (−), WT-, and D136N-CK1α with M/V-CARMA1-CCL(104-660). Open and solid arrowheads, phosphorylated and dephosphorylated CCL. e, Experiment as in (d) using M/V-tagged CCL residues 104-610 or 104-600. Diaphanous (mDIA1), loading control. f, Experiment as in (d) using Myc/Cerulean (M/Cer)-tagged CCL(104-610) with the indicated serine to alanine substitution. g, NF-κB luciferase assay (mean ± s.d. of triplicate experiments) of CARMA1-deficient Jurkat JPM50.6 cells reconstituted with either an empty vector (EV), or the indicated CARMA1 plasmid, and stimulated with PMA and 1 μg/ml anti-CD28.
By analogy with IKKβ, which marks BCL10 for degradation by phosphorylation22, we inferred that CK1α might phosphorylate a substrate to downregulate the CBM. CARMA1, which binds CK1α, was an attractive candidate. We observed that WT- but not D136N-CK1α retarded the electrophoretic migration of CARMA1 in a λ-phosphatase-dependent manner, suggesting that CK1α phosphorylates it (Fig. 3c, and Supplementary Fig. 10). Because CARMA1 contains 142 potential phospho-acceptors, we used truncation mutants to identify CK1α phosphorylation sites. In HEK293T cells, CARMA1-CCL(104-660) existed as two species, and WT- but not D136N-CK1α shifted essentially all the CARMA1-CCL to the slow migrating, λ-phosphatase-sensitive species (Fig. 3d and Supplementary Fig. 10a, b). CARMA1-CCL(104-610) was the shortest CK1α-sensitive construct, as a mutant lacking residues 601-610 was not modified (Fig. 3e). This narrowed the search to three serines, namely S603, S607, and S608. Their substitution to alanine showed that only S608A and S603A/608A (2SA) were insensitive to CK1α, suggesting that S608 might be the key CK1α phosphorylation site (Fig. 3f). NF-κB enhancement was observed in CARMA1-deficient Jurkat cells11 reconstituted with 2SA- and S608A-CARMA1 (Fig. 3g and Supplementary Fig. 10c and d). This evidence indicates that CK1α specifically phosphorylates CARMA1 at S608, which impairs its ability to activate NF-κB.
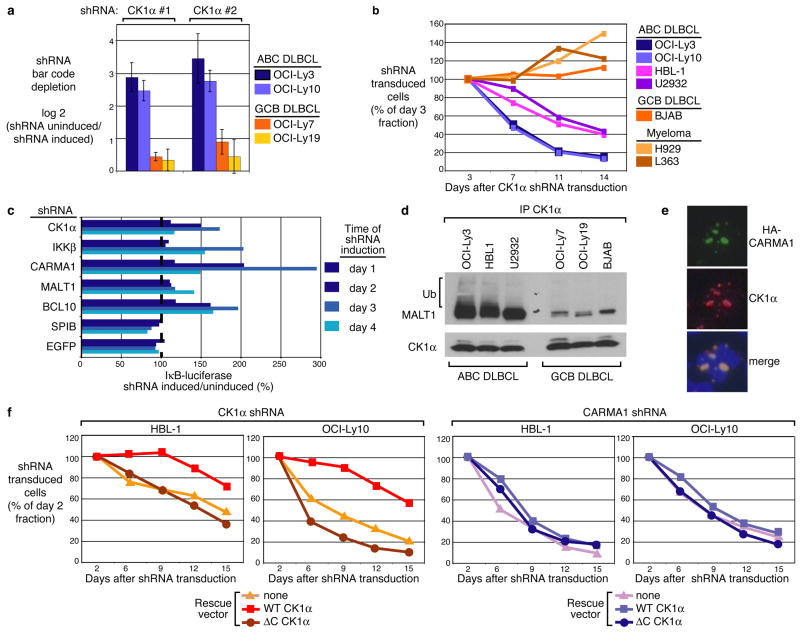
Using a doxycycline-inducible shRNA retroviral library, we conducted a systematic screen for essential survival genes for two molecularly and clinically distinct lymphoma types, ABC and GCB (germinal centre B cell-like) DLBCL12,23, 24. ABC, but not GCB, DLBCL cells rely on constitutive NF-κB activation for proliferation and survival25. Previously, this screen identified CARMA1, BCL10, and MALT1 as critical components for ABC DLBCL cell survival12. Additional screening uncovered two CK1α shRNAs that were selectively lethal for ABC DLBCL cell lines (Fig. 4a). We cloned these CK1α shRNA sequences into a GFP-expressing retroviral vector12, and infected cell lines representing ABC DLBCL, GCB DLBCL, and multiple myeloma. CK1α shRNA expression decreased the fraction of GFP-positive, shRNA-expressing cells over time in all four ABC DLBCL cell lines but not in GCB DLBCL or multiple myeloma cell lines, confirming that CK1α knockdown is specifically lethal to ABC DLBCL cells (Fig. 4b).
Figure 4. Role of CK1α in activated B-cell-like (ABC) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) survival and NF-κB signaling.
a, A genetic screen using 1,854 shRNA vectors targeting 683 genes identified two CK1α shRNAs that block the survival of ABC but not GCB DLBCL cell lines. Shown are the relative fluorescent signals from bar code microarrays comparing shRNA-induced versus uninduced cells 21 days post-shRNA induction. Data are mean ± s.d. of four independent infections of the shRNA retroviral library. b, Survival analysis by flow cytometry of the indicated lymphoma and multiple myeloma cell lines retrovirally infected to express CK1α shRNA and GFP. c, An OCI-Ly3 cell line stably expressing an IκBα-luciferase reporter was retrovirally infected with the indicated shRNAs. Shown is the percentage of luciferase activity in shRNA-induced cells compared to uninduced cells. d, IP/IB of cell lysates from the indicated cell lines. Ub, ubiquitin. e, Immunofluorescent staining for CARMA1 mutant 326 (HA epitope), and endogenous CK1α in OCI-Ly19 retrovirally transduced to express HA-tagged CARMA1 mutant 3. Shown are 2 adjacent cells with nuclei counterstained (blue). f, Indicated ABC DLBCL cells were transduced with WT-CK1α or ΔC-CK1α (Δ283-337), and subsequently with vectors co-expressing GFP and either CK1α shRNA or CARMA1 shRNA. GFP+ cell fraction was monitored as in (b).
To evaluate CK1α participation in the NF-κB pathway in ABC DLBCL, the OCI-Ly3 cell line harboring an IKK activity reporter consisting of an IκBα-luciferase fusion protein was used12. If IKK is inactivated, there is less phosphorylation and degradation of the IκBα-luciferase fusion protein and luciferase activity rises. Induction of CK1α shRNA expression increased luciferase activity, as did shRNAs targeting IKKβ, CARMA1, MALT1, and BCL10, whereas control shRNAs targeting the Spi-B transcription factor (SPIB) and EGFP had no effect (Fig. 4c). Consistently, CK1α knockdown decreased NF-κB in the nuclei of OCI-Ly3 cells and reduced IκBα phosphorylation in HBL1, U2932 and OCI-Ly3 cell lines (Supplementary Fig. 11). Thus, CK1α is required for the IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway in ABC DLBCL cells. We also detected a strong binding of CK1α to MALT1 and ubiquitinated MALT1 in ABC DLBCL but not GCB DLBCL cell lines (Fig. 4d). Some ABC DLBCLs harbor mutant forms of CARMA1 that constitutively activate NF-κB and generate cytoplasmic aggregates that colocalize with MALT1 and IKK26. Such CARMA1 aggregates also contain CK1α, further implicating CK1α in CBM complex activity in ABC DLBCL (Fig. 4e). We next tested whether the lethality of an shRNA targeting the CK1α 3′-untranslated region could be prevented by WT-CK1α or ΔC-CK1α, which does not bind CARMA1. WT-, but not ΔC-CK1α rescued two ABC DLBCL cell lines from CK1α shRNA toxicity (Fig. 4f). In contrast, neither WT-CK1α nor ΔC-CK1α rescued ABC DLBCL cells from CARMA1 shRNA toxicity. Thus, direct interaction of CK1α with CARMA1 is apparently required for ABC DLBCL cell survival.
In summary, our results have unveiled CK1α as an important bifunctional modulator of lymphocyte adaptive immune responses. While CK1α associates with CARMA1 and positively conveys TCR-induced NF-κB, it also phosphorylates CARMA1, thereby dampening signaling. This provides a conceptual framework for CK1α as a signaling gate, using both positive and negative influences to control the flow of information leading to gene induction. The phosphorylation and inactivation of CARMA1 by CK1α is reminiscent of the GSK3β-/CK1α cooperation to promote β-catenin destruction27, and our preliminary data indicate that CK1α contributes to CARMA1 degradation (Supplementary Fig. 10). We also provide genetic, biochemical and functional evidence that CK1α is an essential participant in the aberrant NF-κB activity required for ABC DLBCL subtype survival. Similar to IKKβ22, the positive function of CK1α supplants its negative role, likely because of the constitutive upstream activation signals. Of note, CK1α was neither mutated nor amplified in ABC DLBCL cell lines (data not shown), indicating that this CK1α dependency resembles to the “non-oncogene addiction” phenomenon in which the cancer cell phenotype depends on specific cellular genes28, 29. These “conditionally essential malignancy” (CEMal) genes may or may not be oncogenes or the initiator genes for cancer, but they are essential for the propagation of a specific transformed phenotype and therefore attractive therapeutic targets28, 29. Interestingly, CK1α is required for the survival of ABC DLBCL cells with either mutant or WT-CARMA1, revealing it to be a CEMal gene. However, CK1α is a complex target for chemotherapy given its counterposing roles in signaling.
Methods summary
Cell culture, and reagents
Jurkat E6.1, BJAB, and HEK293T cells were purchased from ATCC. Peripheral blood T cells were isolated from normal healthy donors as previously described30. CARMA1-deficient JPM50.6 Jurkat cells were provided by Xin Lin11. Lymphocytes were activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 (BD Biosciences), or with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, Sigma) and ionomycin (Sigma), or with 25 ng/ml tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α, R&D). siRNA used (Invitrogen) were BCL10, 5′-GCCACGAACAACCUCUCCAGAUCAA-3′; CK1α.2, 5′-CCTAGCCTCGAAGACCTCTTCAATT-3′; CK1α.3, 5′-GGCAAGGGCTAAAGGCTGCAACAAA-3′; PKCθ, 5′-AAAUGGUGAUUUCACUUUCGGCCGG-3′; p65, 5′-GAGCACCAUCAACUAUGAUGAGUUU-3′.
CARMA1-binding partner screen by mass spectrometry
CARMA1 was immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells overexpressing V5-tagged CARMA1. CARMA1-containing complexes were resolved on SDS-PAGE and stained with colloidal Coomassie Blue (Invitrogen). Bands were excised, in gel trypsin digested, and subjected to LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry analysis.
shRNA library screen
A retroviral shRNA library was constructed in the modified pRSMX plasmid containing a doxocyline-inducible H1 promoter for shRNA expression and a random 60-mer “bar-code” sequence. The association of each bar code with an shRNA sequence in each library plasmid was determined by sequencing. Screening utilized engineered cells that express the bacterial tetracycline repressor (TETR)12. 500–1000 individual shRNA plasmids were combined to generate retroviral pools, which were used to infect TETR-expressing lymphoma and multiple myeloma cell lines. Puromycin-selected, infected cells were induced with doxycycline for shRNA expression in half of the culture. Three weeks after shRNA induction, bar code sequences were amplified from the genomic DNA of induced and uninduced cells, fluorescently labeled, and hybridized to bar code microarrays to identify shRNA vectors that were relatively depleted from the induced population. The effective CK1α shRNA sequences identified from the screen are: CK1α#1, 5′-GACTCTGCATTAACTCTATAA-3′ and CK1α#2, 5′-GAGCAAGCTCTATAAGATTCT-3′.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, NIAID, NCI, NIDDK, and by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR). We thank Marie-Thérèse Auffredou for technical assistance; Xin Lin and Julie Gavard for reagents; Ron Germain, Ron Schwartz, Ulrich Siebenlist, Pamela Schwartzberg, Joao Bosco de Oliveira, Li Yu, David Baltimore, Phil Sharp, Harold Varmus and Andrew Snow for discussions and comments; and Stephen Porcella and the DNA sequencing core facility of the Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID.
Footnotes
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Hacker H, Karin M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci STKE 2006. 2006:re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schulze-Luehrmann J, Ghosh S. Antigen-receptor signaling to nuclear factor kappa B. Immunity. 2006;25:701–15. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Egawa T, et al. Requirement for CARMA1 in antigen receptor-induced NF-kappa B activation and lymphocyte proliferation. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1252–8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00491-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gaide O, et al. CARMA1 is a critical lipid raft-associated regulator of TCR-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:836–43. doi: 10.1038/ni830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hara H, et al. The MAGUK family protein CARD11 is essential for lymphocyte activation. Immunity. 2003;18:763–75. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jun JE, Goodnow CC. Scaffolding of antigen receptors for immunogenic versus tolerogenic signaling. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:1057–64. doi: 10.1038/ni1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Newton K, Dixit VM. Mice lacking the CARD of CARMA1 exhibit defective B lymphocyte development and impaired proliferation of their B and T lymphocytes. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1247–51. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ruefli-Brasse AA, French DM, Dixit VM. Regulation of NF-kappaB-dependent lymphocyte activation and development by paracaspase. Science. 2003;302:1581–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1090769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ruland J, et al. Bcl10 is a positive regulator of antigen receptor-induced activation of NF-kappaB and neural tube closure. Cell. 2001;104:33–42. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ruland J, Duncan GS, Wakeham A, Mak TW. Differential requirement for Malt1 in T and B cell antigen receptor signaling. Immunity. 2003;19:749–58. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang D, et al. A requirement for CARMA1 in TCR-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:830–5. doi: 10.1038/ni824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ngo VN, et al. A loss-of-function RNA interference screen for molecular targets in cancer. Nature. 2006;441:106–10. doi: 10.1038/nature04687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Price MA. CKI, there’s more than one: casein kinase I family members in Wnt and Hedgehog signaling. Genes Dev. 2006;20:399–410. doi: 10.1101/gad.1394306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Oeckinghaus A, et al. Malt1 ubiquitination triggers NF-kappaB signaling upon T-cell activation. Embo J. 2007;26:4634–45. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bidere N, Snow AL, Sakai K, Zheng L, Lenardo MJ. Caspase-8 regulation by direct interaction with TRAF6 in T cell receptor-induced NF-kappaB activation. Curr Biol. 2006;16:1666–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.06.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Matsumoto R, et al. Phosphorylation of CARMA1 plays a critical role in T Cell receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Immunity. 2005;23:575–85. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sommer K, et al. Phosphorylation of the CARMA1 linker controls NF-kappaB activation. Immunity. 2005;23:561–74. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shinohara H, et al. PKC beta regulates BCR-mediated IKK activation by facilitating the interaction between TAK1 and CARMA1. J Exp Med. 2005;202:1423–31. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shambharkar PB, et al. Phosphorylation and ubiquitination of the IkappaB kinase complex by two distinct signaling pathways. Embo J. 2007;26:1794–805. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Davidson G, et al. Casein kinase 1 gamma couples Wnt receptor activation to cytoplasmic signal transduction. Nature. 2005;438:867–72. doi: 10.1038/nature04170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Peters JM, McKay RM, McKay JP, Graff JM. Casein kinase I transduces Wnt signals. Nature. 1999;401:345–50. doi: 10.1038/43830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wegener E, et al. Essential role for IkappaB kinase beta in remodeling Carma1-Bcl10-Malt1 complexes upon T cell activation. Mol Cell. 2006;23:13–23. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Alizadeh AA, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–11. doi: 10.1038/35000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rosenwald A, et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1937–47. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Davis RE, Brown KD, Siebenlist U, Staudt LM. Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J Exp Med. 2001;194:1861–74. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lenz G, et al. Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science. 2008;319:1676–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1153629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu C, et al. Control of beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell. 2002;108:837–47. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00685-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shaffer AL, et al. IRF4 addiction in multiple myeloma. Nature. 2008;454:226–31. doi: 10.1038/nature07064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Solimini NL, Luo J, Elledge SJ. Non-oncogene addiction and the stress phenotype of cancer cells. Cell. 2007;130:986–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Su H, et al. Requirement for caspase-8 in NF-kappaB activation by antigen receptor. Science. 2005;307:1465–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1104765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wan F, et al. Ribosomal Protein S3: a KH domain subunit in NF-kappaB complexes that mediates selective gene regulation. Cell. 2007;131:927–39. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.