Abstract
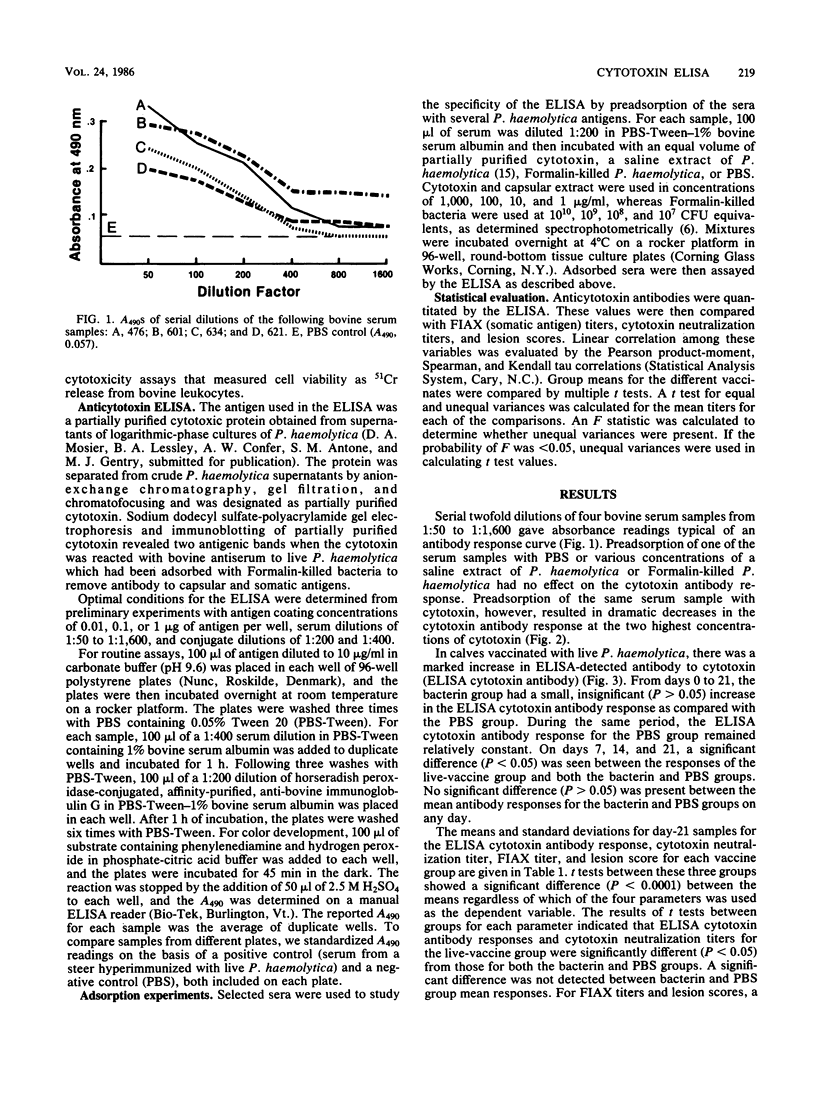
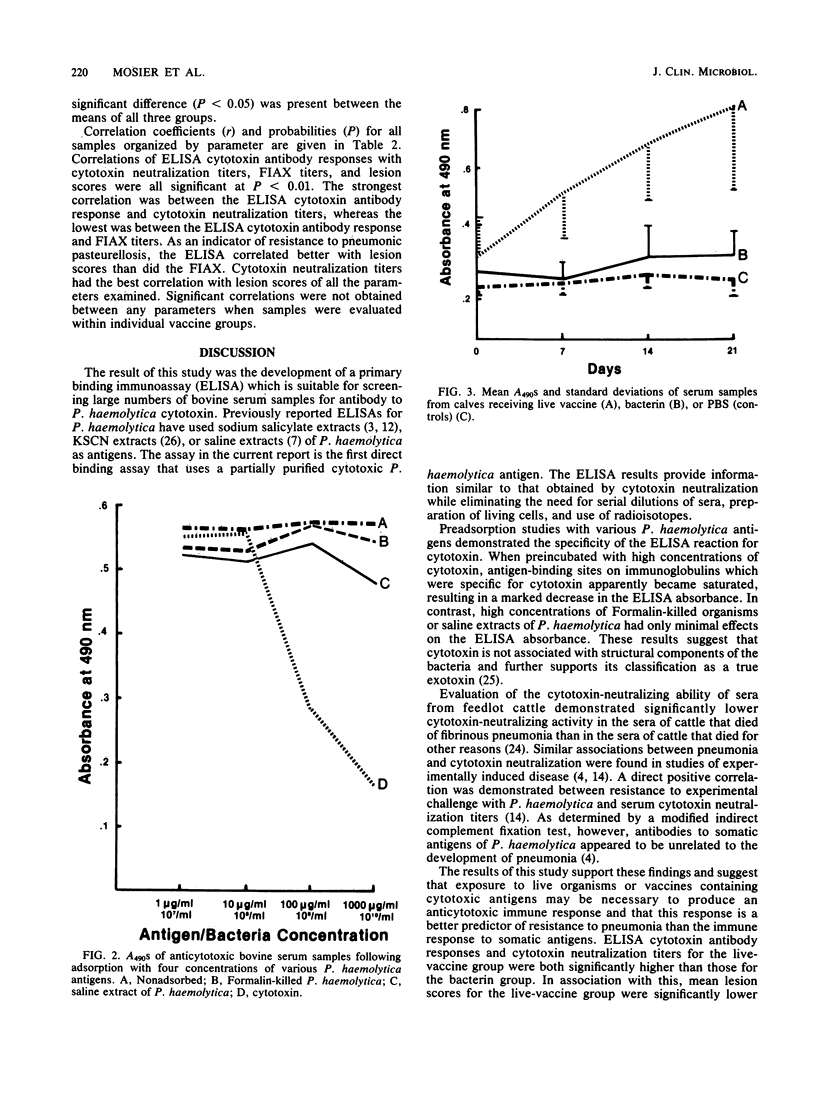
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed for detection of bovine serum antibodies to the cytotoxin (leukotoxin) of Pasteurella haemolytica. A partially purified, cytotoxic, and immunogenic protein obtained from supernatants of logarithmic-phase P. haemolytica was used as the ELISA antigen. Preadsorption of sera with various cytotoxic, somatic, and capsular antigen preparations demonstrated that the assay was specific for anticytotoxin antibodies. ELISA anticytotoxin titers had a strong, significant correlation to cytotoxin-neutralizing-antibody titers. The ELISA, however, was more rapid and allowed for greater numbers of samples to be run than did the neutralization technique. ELISA anticytotoxin titers were high in cattle vaccinated with a live P. haemolytica vaccine, whereas unvaccinated cattle and cattle receiving a P. haemolytica bacterin had low ELISA anticytotoxin titers. A significant positive correlation between ELISA titers and resistance to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis was present.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baluyut C. S., Simonson R. R., Bemrick W. J., Maheswaran S. K. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1920–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrells C., Evans H. B., Dawson A. M. Antigenic relationships between the serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica demonstrable by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Vet Microbiol. 1983 Apr;8(2):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Bohac J. G., Yates W. D., Bielefeldt Ohmann H. Anticytotoxin activity of bovine sera and body fluids against Pasteurella haemolytica A1 cytotoxin. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Apr;48(2):151–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Fox J. C., Newman P. R., Lawson G. W., Corstvet R. E. A quantitative fluorometric assay for the measurement of antibody to Pasteurella haemolytica in cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jan;47(1):37–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Lessley B. A., Panciera R. J., Fulton R. W., Kreps J. A. Serum antibodies to antigens derived from a saline extract of Pasteurella haemolytica: correlation with resistance to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Nov;10(2-3):265–278. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(85)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Corstvet R. E., Rummage J. A., Fulton R. W. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: effect of culture age of Pasteurella haemolytica used as a live vaccine. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2543–2545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Fulton R. W. Effect of prior natural exposure to Pasteurella haemolytica on resistance to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2622–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Fulton R. W., Gentry M. J., Rummage J. A. Effect of vaccination with live or killed Pasteurella haemolytica on resistance to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Feb;46(2):342–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W., Burrells C., Dawson A. M. Specificity of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies in the sera of specific pathogen-free lambs vaccinated with Pasteurella haemolytica antigens. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Apr;8(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. C., Thomson R. G., Wilkie B. N. Pulmonary lesions induced by Pasteurella hemolytica in cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Apr;41(2):219–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. J., Confer A. W., Panciera R. J. Serum neutralization of cytotoxin from Pasteurella haemolytica, serotype 1 and resistance to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Jul;9(3):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(85)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. J., Corstvet R. E., Panciera R. J. Extraction of capsular material from Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Nov;43(11):2070–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Pierson R. E., Braddy P. M., Saari D. A., Lauerman L. H., England J. J., Keyvanfar H., Collier J. R., Horton D. P., McChesney A. E. Shipping fever pneumonia in yearling feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Sep 1;169(5):500–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie L. E. The bovine respiratory disease complex. Can Vet J. 1974 Sep;15(9):233–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Thomson R. G., Johnson J. A., Lopez A., Stephens L., Curtis R. A., Prescott J. F., Rosendal S. Factors associated with mortality in feedlot cattle: the Bruce County Beef Cattle Project. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jan;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W. Vaccination: Is it Effective in Preventing Respiratory Disease or Influencing Weight Gains in Feedlot Calves? Can Vet J. 1983 Jan;24(1):10–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panciera R. J., Corstvet R. E. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: model for Pasteurella haemolytica- and Pasteurella multocida-induced pneumonia in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2532–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panciera R. J., Corstvet R. E., Confer A. W., Gresham C. N. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: effect of vaccination with live Pasteurella species. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2538–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Evidence for the Pasteurella haemolytica cytotoxin as a product of actively growing bacteria. Am J Vet Res. 1985 May;46(5):1212–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Pasteurella haemolytica cytotoxin neutralizing activity in sera from Ontario beef cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Oct;47(4):497–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Ziola B., Stockdale P. H. Solid-phase enzyme immunoassay of bovine antibody responses following immunization against and natural infection with Pasteurella haemolytica. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Nov;5(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(83)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie B. N., Markham R. J., Shewen P. E. Response of calves to lung challenge exposure with Pasteurella haemolytica after parenteral or pulmonary immunization. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Nov;41(11):1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


