Abstract
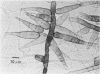
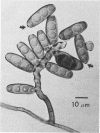
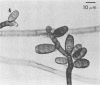
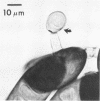
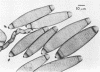
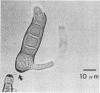
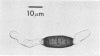
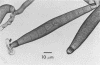
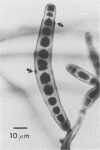
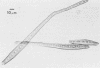
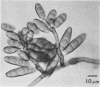
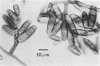
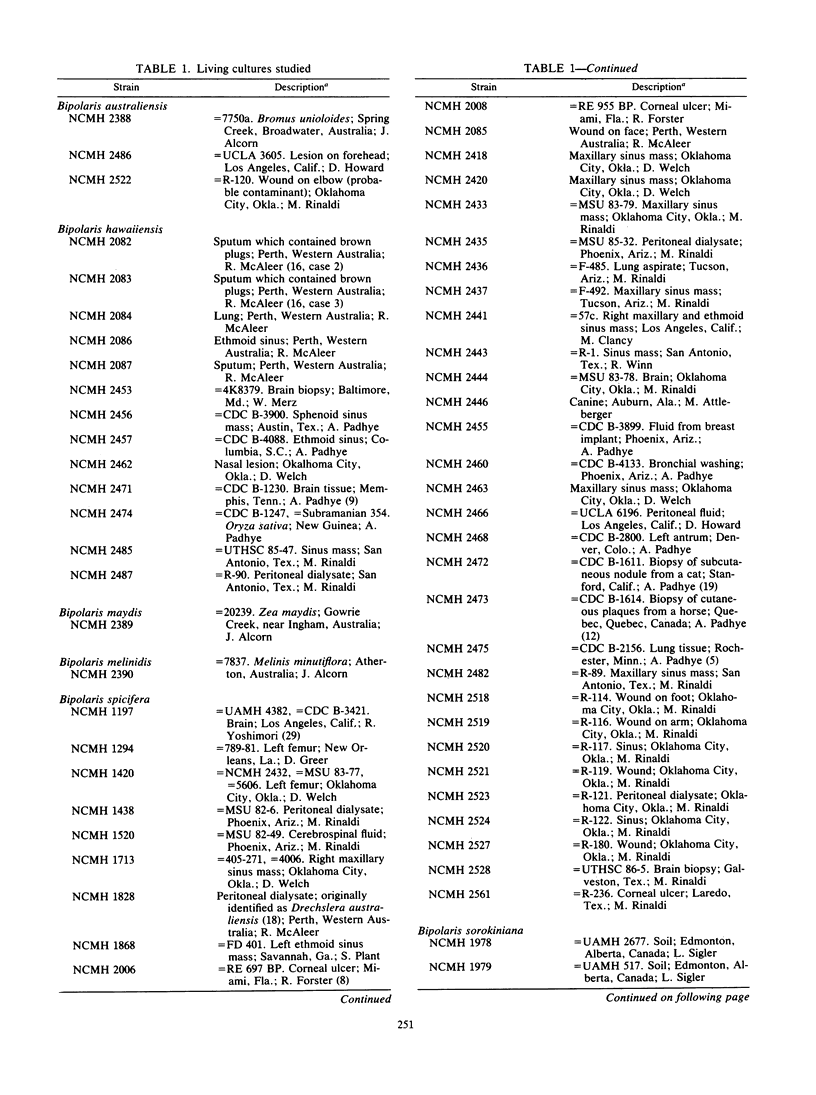
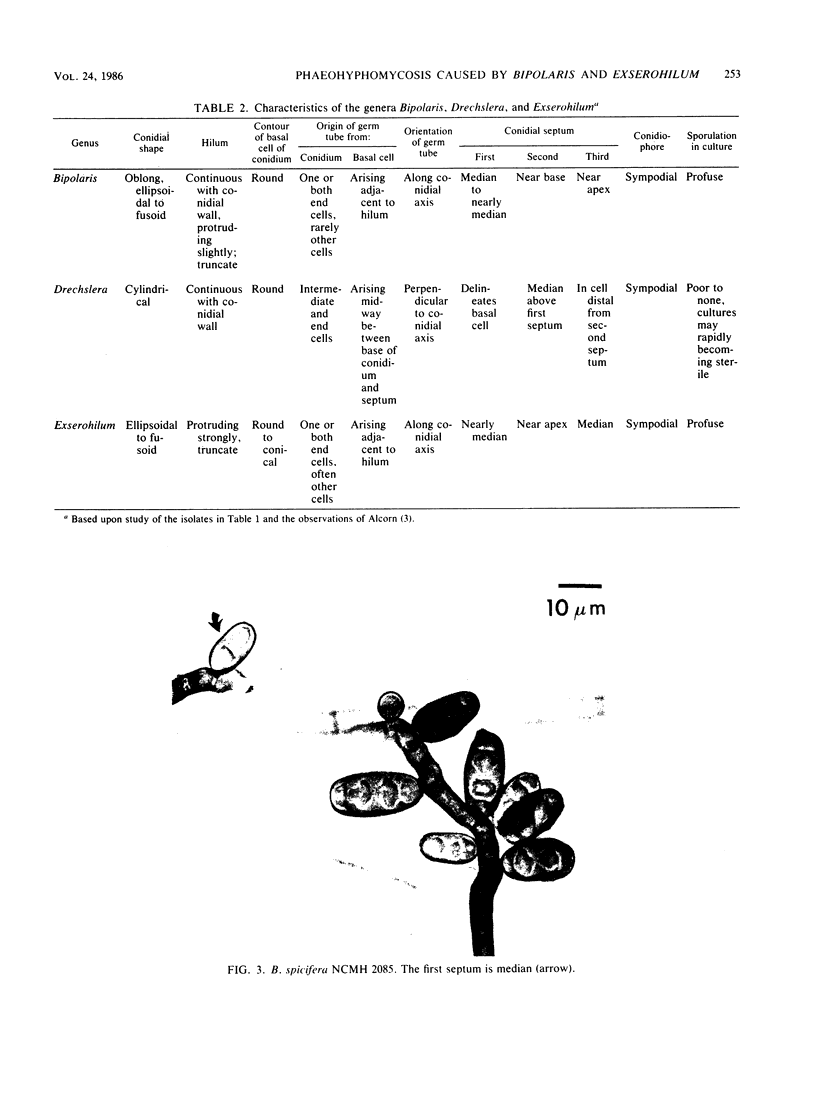
Study of numerous living isolates of Bipolaris, Drechslera, Exserohilum, and Helminthosporium spp., as well as a mycological assessment of published case reports of phaeohyphomycosis attributed to these fungi, showed that Bipolaris australiensis, B. hawaiiensis, B. spicifera, Exserohilum longirostratum, E. mcginnisii, and E. rostratum are well-documented pathogens. Conidial shape, septation, and size, hilar characteristics, the origin of the germ tube from the basal cell and, to a lesser extent, from other conidial cells, and the sequence and location of the conidial septa are useful criteria for distinguishing these taxa.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dolan C. T., Weed L. A., Dines D. E. Bronchopulmonary helminthosporiosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):235–242. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouhet E., Dupont B. Laboratory and clinical assessment of ketoconazole in deep-seated mycoses. Am J Med. 1983 Jan 24;74(1B):30–47. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90512-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouhet E., Guilmet D., Kouvalchouk J. F., Chapman A., Ziza J. M., Laudet J., Brodaty D. Premier cas humain de mycose à Drechslera longirostrata. Spondylodiscite compliquant une endocardite sur prothèse. Traitement par l'association kétoconazole-amphotéricine B. Nouv Presse Med. 1982 Dec 4;11(49):3631–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster R. K., Rebell G., Wilson L. A. Dematiaceous fungal keratitis. Clinical isolates and management. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Jul;59(7):372–376. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.7.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuste F. J., Ajello L., Threlkeld R., Henry J. E., Jr Drechslera hawaiiensis: causative agent of a fatal fungal meningo-encephalitis. Sabouraudia. 1973 Mar;11(1):59–63. doi: 10.1080/00362177385190131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan W., Chandler F. W., Ajello L., Gauther R., Higgins R., Cayouette P. Equine phaeohyphomycosis caused by Drechslera spicifera. Can Vet J. 1975 Jul;16(7):205–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAleer R., Kroenert D. B., Elder J. L., Froudist J. H. Allergic bronchopulmonary disease caused by Curvularia lunata and Drechslera hawaiiensis. Thorax. 1981 May;36(5):338–344. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.5.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R. Chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: new concepts, diagnosis, and mycology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 Jan;8(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(83)70001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulsdale M. T., Harper J. M., Thatcher G. N. Fungal peritonitis: complication of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Med J Aust. 1981 Jan 24;1(2):88–88. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb135333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller G. H., Kaplan W., Ajello L., Padhye A. A. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Drechslera spicifera in a cat. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1975 Jan 15;166(2):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhye A. A., Ajello L., Wieden M. A., Steinbronn K. K. Phaeohyphomycosis of the nasal sinuses caused by a new species of Exserohilum. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):245–249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.245-249.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Hopfer R. L., Larson D. L. Infections caused by Drechslera species: case report and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):525–529. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimori R. N., Moore R. A., Itabashi H. H., Fujikawa D. G. Phaeohyphomycosis of brain: granulomatous encephalitis caused by Drechslera spicifera. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Mar;77(3):363–370. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]