Abstract
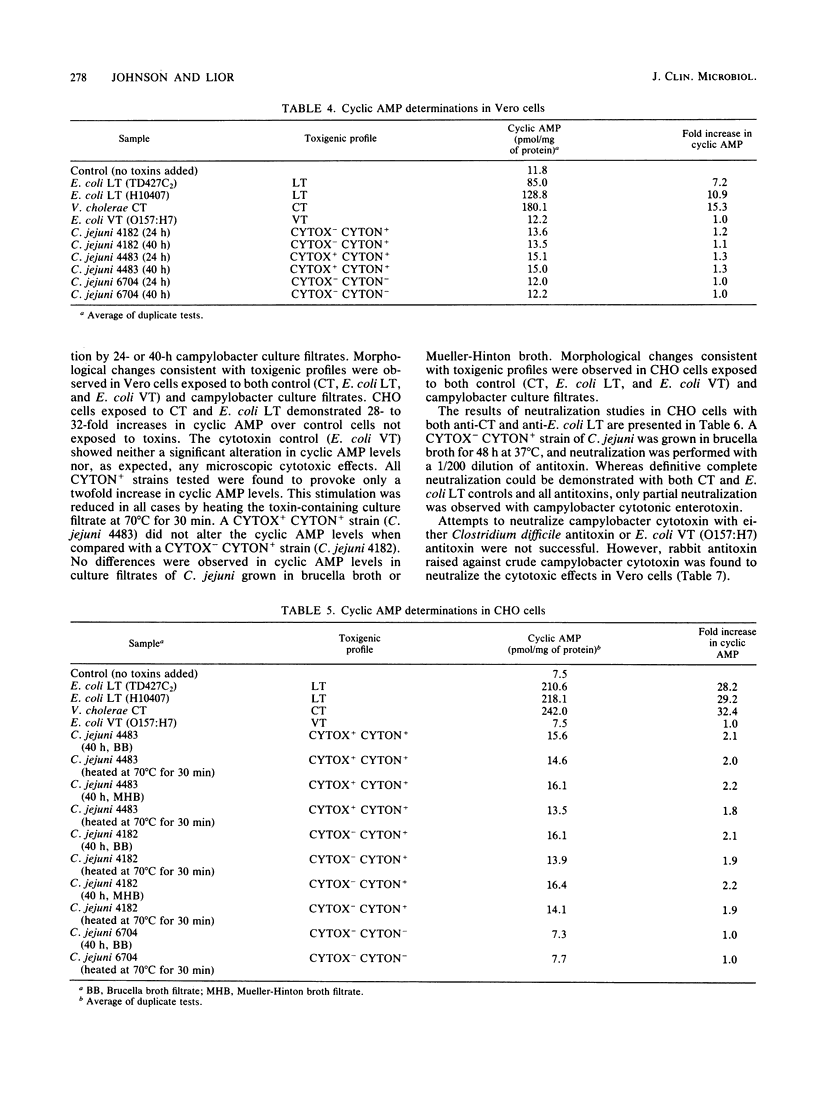
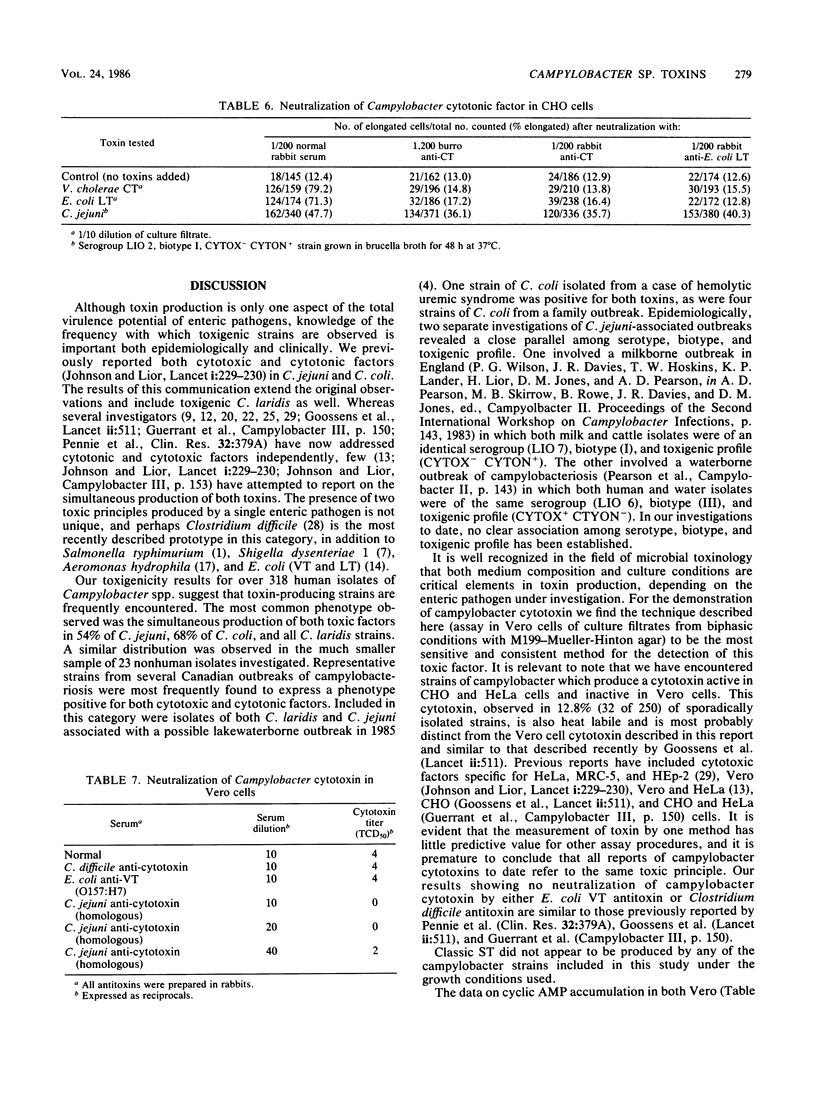
Complete toxigenicity studies were performed on 341 strains of Campylobacter spp., including 23 nonhuman isolates. Toxin profiles based on both cytotonic and cytotoxic factors were determined after analyzing responses in Vero, HeLa, CHO and Y-1 cells. Suckling mouse assays were consistently negative for all culture filtrates tested. Toxin-producing strains were frequently encountered among both the human and nonhuman strains of Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli, and C. laridis investigated. Strains isolated from outbreaks demonstrated parallels in serotype, biotype, and toxigenicity profile, although no clear association could be demonstrated. Biphasic culture conditions conducive to the production of both toxic factors were delineated for the propagation of test Campylobacter strains. Cytotonic effects of Campylobacter culture filtrates were determined in Vero and CHO cells, and cyclic AMP accumulation in cells exposed to these culture filtrates was compared with that in cells exposed to reference toxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Partial neutralization of C. jejuni enterotoxin was demonstrated by using antitoxins to cholera toxin and E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin. No neutralization of C. jejuni cytotoxin could be achieved by using antitoxins to either Clostridium difficile cytotoxin or E. coli Verotoxin (0157:H7).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baloda S. B., Faris A., Krovacek K., Wadström T. Cytotonic enterotoxins and cytotoxic factors produced by Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium. Toxicon. 1983;21(6):785–796. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(83)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Walker R. I., Stewart S. D., Rogers J. E. Simple adult rabbit model for Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1176–1182. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1176-1182.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draskovicová M., Karolcek J., Winkler Experimental Toxigenicity of NAG Vibrios. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977 Feb;237(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Lahita R. G., Winn W. C., Jr, Roberts R. B. Campylobacteriosis in man: pathogenic mechanisms and review of 91 bloodstream infections. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):584–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):527–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Properties of crude Campylobacter jejuni heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):314–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.314-319.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H., Schenk E. A. Pathogenic properties of Campylobacter jejuni: assay and correlation with clinical manifestations. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.43-49.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Wretlind B., Möllby R. Separation and characterization of enterotoxin and two haemolysins from Aeromonas hydrophila. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Dec;89(6):387–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00205_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manninen K. I., Prescott J. F., Dohoo I. R. Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from animals and humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Umeda A., Amako K. Motility as an intestinal colonization factor for Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Saunders F., Dehele Y., Pearson A. D. The virulence of clinical and environmental isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Feb;94(1):45–54. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Still C. S., Isaäcson M., Koornhof H. J., Appelbaum P. C., Scragg J. N. Pathogenic mechanisms of a non-agglutinable Vibrio cholerae strain: demonstration of invasive and enterotoxigenic properties. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):542–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.542-545.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., López-Vidal Y., Torres J., Torres N. Serum antibodies to heat-labile enterotoxin of Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):413–416. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Torres J., Torres N. I., Escamilla E., Ruiz-Palacios B. R., Tamayo J. Cholera-like enterotoxin produced by Campylobacter jejuni. Characterisation and clinical significance. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):250–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Islam K. M., Neogy P. K., Islam M., Speelman P., Huq M. I. Campylobacter jejuni diarrhea model in infant chickens. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):931–936. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.931-936.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N. S., Thorne G. M., Bartlett J. G. Comparison of two toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1036-1043.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeen W. P., Puthucheary S. D., Pang T. Demonstration of a cytotoxin from Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;36(11):1237–1240. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.11.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


