Abstract
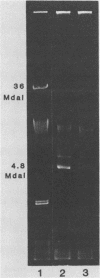
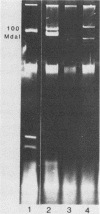
Pseudomonas aeruginosa was isolated from the corneal scrapings of 11 of 14 patients with gram-negative corneal ulcers and from salt tablet-prepared saline solutions from 6 of these patients wearing soft contact lenses. Comparison of physiological properties, antibiograms, serotypes, and plasmid profiles for five of the patients indicated that the isolates from the ulcer and the saline solution of a given patients were of the same strain. Improper hygienic practices of contact lens wearers appeared to be a major factor in the epidemiology of pseudomonad corneal ulcers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford K. B., Weinstein R. A., Nathan C. R., Kabins S. A. Selective survival in pentazocine and tripelennamine of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype O11 from drug addicts. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):209–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokopp C. D., Gomez-Lus R., Farmer J. J., 3rd Serological typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: use of commercial antisera and live antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):640–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.640-649.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. L., Wachsmuth K., Johnson S. R., Birkness K. A., Samadi A. R. Persistence of plasmids, cholera toxin genes, and prophage DNA in classical Vibrio cholerae O1. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):222–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.222-226.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton S. L., Blasi D., Chipps D. D., Smith R. F. Epidemiological tracing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: antibiogram and serotyping. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1167–1169. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1167-1169.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Suskind R. R., Macmillan B. G., Holder I. A. Epidemiology of pseudomonas aeruginosa in a burn hospital: evaluation of serological, bacteriophage, and pyocin typing methods. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Aug;24(2):213–218. doi: 10.1128/am.24.2.213-218.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Weinstein R. A., Zierdt C. H., Brokopp C. D. Hospital outbreaks caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: importance of serogroup O11. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):266–270. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.266-270.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. W., Devlin H. B., Gnabasik F. J. New immunotype schema for Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on protective antigens. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):835–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.835-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galentine P. G., Cohen E. J., Laibson P. R., Adams C. P., Michaud R., Arentsen J. J. Corneal ulcers associated with contact lens wear. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984 Jun;102(6):891–894. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030711025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman D. J., Gowland P. C. Large plasmids in bacteria. Part 2. Genetics and evolution. Microbiol Sci. 1985 Jun;2(6):184–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insler M. S., Gore H. Pseudomonas keratitis and folliculitis from whirlpool exposure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986 Jan 15;101(1):41–43. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(86)90462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusama H. Serological classification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by a slide agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):181–188. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.181-188.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Aliferopoulou M., Papavassiliou J., Papapetropoulou M. Serotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinical specimens in relation to antibiotic susceptibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):458–463. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.458-463.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod L. D., Smith R. E. Contact lens-associated microbial keratitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Jan;104(1):79–83. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050130089027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott P. L., Terry P. M., Whitworth E. N., Frawley L. W., Coble R. S., Wachsmuth I. K., McGowan J. E., Jr Pseudomonas aeruginosa peritonitis associated with contaminated poloxamer-iodine solution. Lancet. 1982 Sep 25;2(8300):683–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90712-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett S., Bigley D. V., Grimes D. J. Distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a riverine ecosystem. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.328-332.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Thomas D. M. Lipopolysaccharide and high-molecular-weight polysaccharide serotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):217–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam S., Hogan K., March S. B., Butler R. W. Whirlpool-associated folliculitis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: report of an outbreak and review. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.655-659.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale T. W., Thirkill H., Tarpay M., Flux M., Rennert O. M. Serotypes and antibiotic susceptibilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from single sputa of cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.72-78.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shekar R., Rice T. W., Zierdt C. H., Kallick C. A. Outbreak of endocarditis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype O11 among pentazocine and tripelennamine abusers in Chicago. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):203–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt R., LaRue D., Parry M. F., Brokopp C. D., Klaucke D., Allen J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa skin infections in persons using a whirlpool in Vermont. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):571–574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.571-574.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman B. A., Mondino B. J., Pettit T. H., Hofbauer J. D. Corneal ulcers associated with extended-wear soft contact lenses. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Apr;97(4):476–481. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A., Ahearn D. G. Pseudomonas-induced corneal ulcers associated with contaminated eye mascaras. Am J Ophthalmol. 1977 Jul;84(1):112–119. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(77)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A., Schlitzer R. L., Ahearn D. G. Pseudomonas corneal ulcers associated with soft contact-lens wear. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981 Oct;92(4):546–554. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(81)90649-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. M., Moody M. R. Serotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S47–S52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]