Abstract
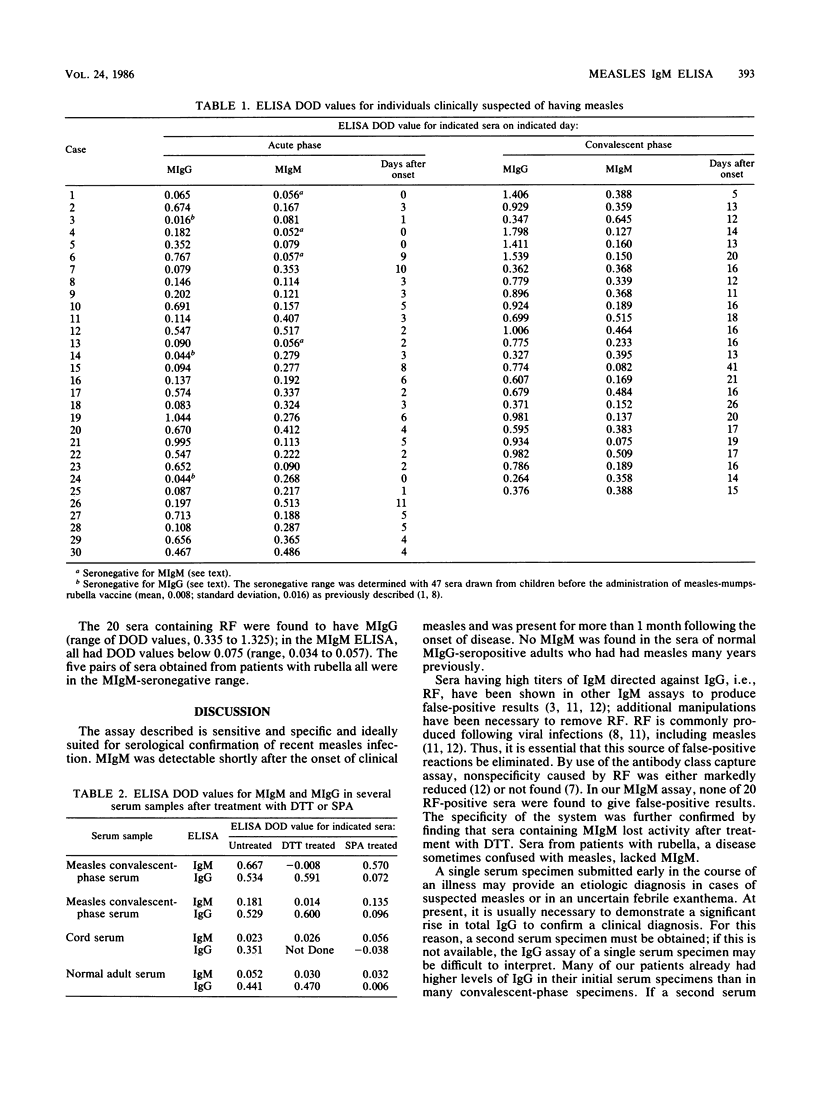
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was evaluated for the detection of measles virus-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) (MIgM). The ELISA was standardized by deriving a seronegative range of values from sera which should not contain MIgM (24 cord sera, 59 sera from immune health care workers, and 47 sera from infants before the administration of measles vaccine). These values were separable from those obtained from individuals convalescing from measles. Twenty sera containing rheumatoid factor were MIgM seronegative. Of 30 acute-phase sera from suspected measles cases, 26 contained MIgM; those that were seronegative were obtained on day 0, 0, 2, or 9. All 25 convalescent-phase samples contained MIgM. Of the 25 paired samples, 22 were IgG positive at the first sampling; 3 of the 22 did not show a rise in IgG titer. The MIgM ELISA can be used for confirming suspected measles cases, often requiring only a single serum specimen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grose C. Immunization of inbred guinea pigs with varicella-zoster virus grown in a syngeneic transformed embryo cell line. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):229–231. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.229-231.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinman A. R., Brandling-Bennet A. D., Bernier R. H., Kirby C. D., Eddins D. L. Current features of measles in the United States: feasibility of measles elimination. Epidemiol Rev. 1980;2:153–170. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman M. B., Blackburn C. K., Zimmerman S. E., French M. L., Wheat L. J. Rapid diagnosis of measles using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measles immunoglobulin M. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;1(3):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. D., Brunell P. A., Lievens A. W., Shehab Z. M. Effect of early immunization on antibody response to reimmunization with measles vaccine as demonstrated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Pediatrics. 1984 Jul;74(1):90–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Desmonts G., Remington J. S. IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test for the diagnosis of congenital Toxoplasma infection. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen I. R., Antonsdottir A., Evald T., Mordhorst C. H. Detection of measles IgM antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Apr;90(2):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Suni J., Wager O. Rheumatoid factor in acute viral infections: interference with determination of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies in an enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):250–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehab Z., Brunell P. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for susceptibility to varicella. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):472–476. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumaya C. V., Ench Y., Pope R. M. Improved test for IgM antibody to Epstein-Barr virus using an absorption step with Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):518–523. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuokko H. Comparison of nonspecific reactivity in indirect and reverse immunoassays for measles and mumps immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):972–976. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.972-976.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuokko H., Salmi A. Detection of IgM antibodies to measles virus by enzyme-immunoassay. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1983;171(4):187–198. doi: 10.1007/BF02123492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle K. A., Murphy M. D., Brunell P. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for evaluation of immunity to measles virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):376–379. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.376-379.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Griethuysen A. J., de Graaf R., van Druten J. A., Heessen F. W., van der Logt J. T., van Loon A. M. Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the early diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;3(2):116–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02014328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


