Abstract
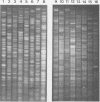
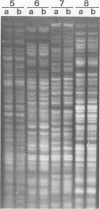
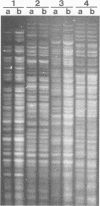
Campylobacter pyloridis isolates recovered from gastric biopsy specimens of 16 patients were examined by restriction endonuclease DNA analysis with HindIII. For 8 of these 16 patients two different isolates were compared to study the persistence of the colonizing strains and the stability of their DNA digest patterns during a period of 2 years (two patients), the identity or nonidentity of different colony types within one culture (two patients), and the nature of the relapses after apparently successful antibacterial therapy (four patients). The isolates from the 16 patients all produced different DNA digest patterns. Comparison of the two different isolates recovered from the same patients showed that these isolates were identical in all eight cases. Laboratory subculturing of a C. pyloridis strain (10 times) did not change its DNA digest pattern. These results indicate the stability of the DNA digest patterns and a marked variability of these patterns among isolates from different patients. Using restriction endonuclease DNA analysis, we found the persistence in the stomach of the same C. pyloridis strain during a period of 2 years and the identity of different colony types within one culture. The relapses after apparently successful antibacterial treatment could be attributed to recrudescence rather than reinfection. Restriction endonuclease DNA analysis is a sensitive and useful method for identifying C. pyloridis isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradbury W. C., Pearson A. D., Marko M. A., Congi R. V., Penner J. L. Investigation of a Campylobacter jejuni outbreak by serotyping and chromosomal restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):342–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.342-346.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen W. B. Urea Decomposition as a Means of Differentiating Proteus and Paracolon Cultures from Each Other and from Salmonella and Shigella Types. J Bacteriol. 1946 Oct;52(4):461–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.4.461-466.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Blincow E. D., Warren J. R., Waters T. E., Sanderson C. R., Easton L. Evaluation of cultural techniques for isolating Campylobacter pyloridis from endoscopic biopsies of gastric mucosa. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Oct;38(10):1127–1131. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.10.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Lessells A. M., Eldridge J. Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1002–1006. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakoyiannis C. K., Winter P. J., Marshall R. B. Identification of Campylobacter coli isolates from animals and humans by bacterial restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):545–549. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.545-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Bradford H. B., Roberts N. C., Falkow S. Molecular epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae in the U.S. Gulf Coast. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):129–134. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.129-134.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Armstrong J. A., McGechie D. B., Glancy R. J. Attempt to fulfil Koch's postulates for pyloric Campylobacter. Med J Aust. 1985 Apr 15;142(8):436–439. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb113443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Wilton B. E., Robinson A. J. Identification of Leptospira serovars by restriction-endonuclease analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):163–166. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megraud F., Bonnet F., Garnier M., Lamouliatte H. Characterization of "Campylobacter pyloridis" by culture, enzymatic profile, and protein content. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1007–1010. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1007-1010.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J., ter Schegget J., Zanen H. C. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):362–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.362-364.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]