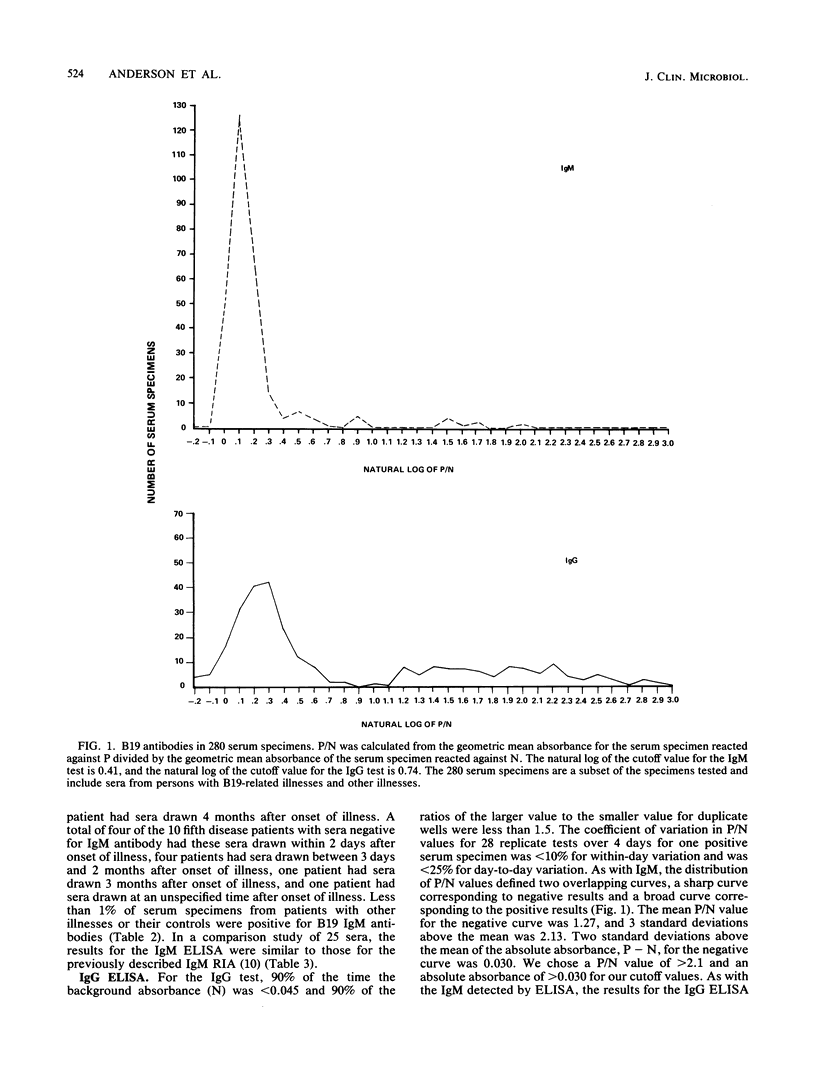
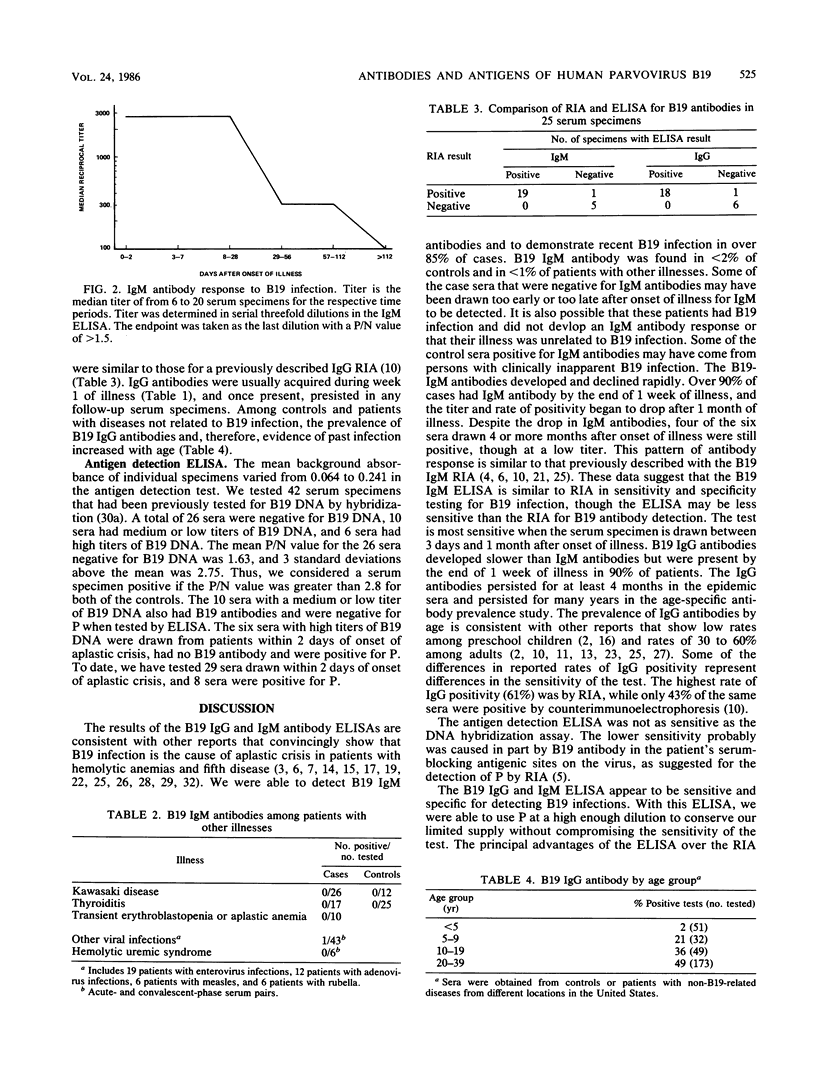
Abstract
Acute-phase serum from a patient with aplastic crisis provided sufficient human parvovirus B19 to make a monoclonal antibody against B19 and to develop antigen and immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibody detection enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). The indirect capture antibody method was used for all three assays. Antigen was detected in 8 of 29 sera drawn within 2 days of onset of illness from patients with aplastic crisis. These sera had high titers of virus by electron microscopy and DNA hybridization and had no detectable B19 antibody. Antigen was not detected in serum specimens that had low titers of B19 DNA and had B19 antibody. With the IgM ELISA, we detected B19 IgM in over 85% of clinical cases of aplastic crisis and fifth disease and less than 2% of controls. The prevalence of B19 IgG antibodies increased with age. Approximately 2% of children less than 5 years of age and 49% of adults greater than 20 years of age had B19 IgG antibodies. The B19 antibody ELISAs are sensitive and specific tests to detect B19 infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Davis L. R., Hodgson J., Jones S. E., Murtaza L., Pattison J. R., Stroud C. E., White J. M. Occurrence of infection with a parvovirus-like agent in children with sickle cell anaemia during a two-year period. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jul;35(7):744–749. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.7.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Higgins P. G., Davis L. R., Willman J. S., Jones S. E., Kidd I. M., Pattison J. R., Tyrrell D. A. Experimental parvoviral infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):257–265. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Jones S. E., Minson A. C. Diagnosis of human parvovirus infection by dot-blot hybridization using cloned viral DNA. J Med Virol. 1985 Feb;15(2):163–172. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Lewis E., Kidd I. M., Hall S. M., Cohen B. J. An outbreak of erythema infectiosum associated with human parvovirus infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Aug;93(1):85–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Pattison J. R. The human parvovirus. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1984;82(3-4):137–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01311158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J. The emerging story of a human parvovirus-like agent. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Aug;89(1):1–8. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Anand A., Ritchie L. D., Clewley J. P., Reid T. M. Intrauterine parvovirus infection associated with hydrops fetalis. Lancet. 1984 Nov 3;2(8410):1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P. Detection of human parvovirus using a molecularly cloned probe. J Med Virol. 1985 Feb;15(2):173–181. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P., Pereira M. S. Diagnostic assays with monoclonal antibodies for the human serum parvovirus-like virus (SPLV). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Aug;91(1):113–130. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart Y. E., Field A. M., Cant B., Widdows D. Parvovirus-like particles in human sera. Lancet. 1975 Jan 11;1(7898):72–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. Characterization and molecular cloning of a human parvovirus genome. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1161–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.6095448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courouce A. M., Ferchal F., Morinet F., Muller A., Drouet J., Soulier J. P., Perol Y. Human parvovirus infections in France. Lancet. 1984 Jan 21;1(8369):160–160. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. J., Brown T., Wiseman D. Human parvovirus infection and aplastic crisis in hereditary spherocytosis. J Infect. 1984 Nov;9(3):298–300. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)90750-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Potter C. B., Cappellini M. D., Kurtz J. B., Anderson M. J., Weatherall D. J. Aplastic crisis due to parvovirus infection in pyruvate kinase deficiency. Lancet. 1983 Jul 2;2(8340):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. M., Kessel I., Gardner S. D., Eaton B. R., Pollock T. M., Fleck D. G., Gibson P., Woodroof M., Porter A. D. A search for a characteristic illness in children with serological evidence of viral or toxoplasma infection. J Infect. 1981 Dec;3(4):316–323. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)91863-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. H., Bellingham A. J., Anderson M. J. Parvovirus infection in a family associated with aplastic crisis in an affected sibling pair with hereditary spherocytosis. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Oct;37(10):1144–1146. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.10.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher J. F., Jr, Luban N. L., Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P. Human serum parvovirus as the cause of aplastic crisis in sickle cell disease. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Apr;138(4):401–403. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140420067020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott P. D., Welply G. A., Anderson M. J. Serologically proved intrauterine infection with parvovirus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Dec 15;289(6459):1660–1660. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6459.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrère J. J., Boutard P., Couroucé A. M., Lacaze T., Girot R. Familial human parvovirus infections. Lancet. 1985 Aug 10;2(8450):333–334. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P. Hypothesis: the aplastic crisis of hereditary spherocytosis is due to a single transmissible agent. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Apr;36(4):445–448. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Luban N. L., Kelleher J. F., Cohen B. J. Transmission of serum parvovirus-like virus by clotting-factor concentrates. Lancet. 1983 Aug 27;2(8348):482–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe N., Koboyashi S., Tatsuzawa O., Mortimer P. P. Detection of antibodies to human parvovirus in erythema infectiosum (fifth disease). Arch Dis Child. 1984 Nov;59(11):1016–1019. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.11.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison J. R., Jones S. E., Hodgson J., Davis L. R., White J. M., Stroud C. E., Murtaza L. Parvovirus infections and hypoplastic crisis in sickle-cell anaemia. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):664–665. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91579-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paver W. K., Clarke S. K. Comparison of human fecal and serum parvo-like viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):67–70. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.67-70.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer F. A., Hammond G. W., Forward K., Sekla L., Thompson L. M., Jones S. E., Kidd I. M., Anderson M. J. An erythema infectiosum-like illness caused by human parvovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 11;313(2):74–79. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507113130203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. R., Patel A. R., Anderson M. J., Hodgson J., Jones S. E., Pattison J. R. Infection with parvovirus-like virus and aplastic crisis in chronic hemolytic anemia. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jun;98(6):930–932. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-6-930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. M., Reid T. M., Brown T., Rennie J. A., Eastmond C. J. Human parvovirus-associated arthritis: a clinical and laboratory description. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):422–425. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarinen U. M., Chorba T. L., Tattersall P., Young N. S., Anderson L. J., Palmer E., Coccia P. F. Human parvovirus B19-induced epidemic acute red cell aplasia in patients with hereditary hemolytic anemia. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1411–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeant G. R., Topley J. M., Mason K., Serjeant B. E., Pattison J. R., Jones S. E., Mohamed R. Outbreak of aplastic crises in sickle cell anaemia associated with parvovirus-like agent. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):595–597. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi H., Wong D., Purcell R. H., Shirachi R., Kumasaka E., Numazaki Y. Antibody to human parvovirus in outbreak of erythema infectiosum in Japan. Lancet. 1985 Apr 27;1(8435):982–983. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91752-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. G., Woolf A. D., Mortimer P. P., Cohen B. J., Blake D. R., Bacon P. A. Human parvovirus arthropathy. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):419–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



