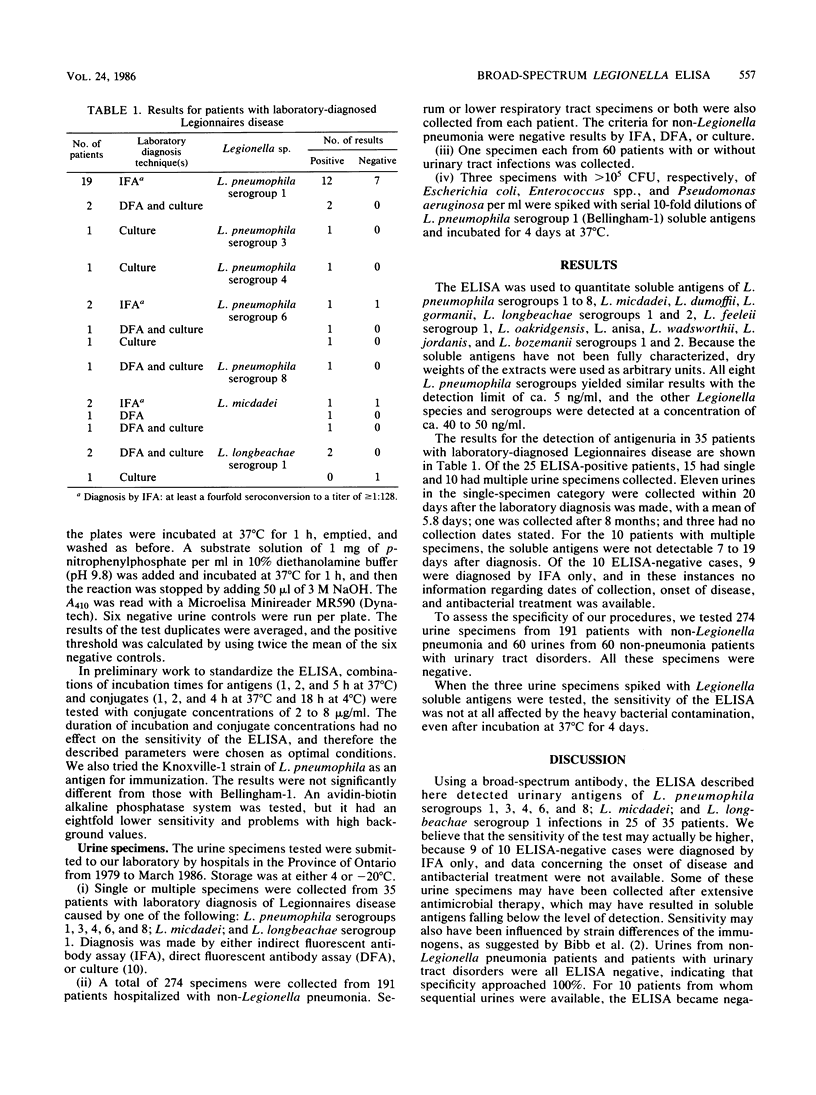
Abstract
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed which detected soluble antigens from culture extracts of Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 to 8, L. micdadei, L. bozemanii serogroups 1 and 2, L. dumoffii, L. gormanii, L. longbeachae serogroups 1 and 2, L. wadsworthii, L. oakridgensis, L. anisa, L. feeleii serogroup 1, and L. jordanis. The assay was approximately 10-fold more sensitive for the eight L. pneumophila serogroups than for the other Legionella species tested. The ELISA detected Legionella antigens in the urine specimens of 25 of 35 patients with L. pneumophila serogroup 1, 3, 4, 6, and 8; L. micdadei; and L. longbeachae serogroup 1 infections. None of the 334 urine specimens from patients with either non-Legionella pneumonia or urinary tract infections was positive. For 10 patients from whom sequential urine specimens were available, Legionella antigens were not detectable from 7 to 19 days after laboratory diagnosis. Test sensitivity was not affected by heavy bacterial contamination. This ELISA offers the detection of a broad spectrum of Legionella antigens by a single test.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berdal B. P., Farshy C. E., Feeley J. C. Detection of Legionella pneumonophila antigen in urine by enzyme-linked immunospecific assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):575–578. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.575-578.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Arnow P. M., Thacker L., McKinney R. M. Detection of soluble Legionella pneumophila antigens in serum and urine specimens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):478–482. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.478-482.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R. B. Antigen detection for the rapid diagnosis of mycoplasma and Legionella pneumonia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;4(3 Suppl):47S–59S. doi: 10.1016/s0732-8893(86)80042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R. B., Wheat L. J., French M. L., Meenhorst P. L., Winn W. C., Jr, Edelstein P. H. Cross-reactive urinary antigens among patients infected with Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 and 4 and the Leiden 1 strain. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):1007–1012. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R. B., Winn W. C., Jr, Wheat L. J. Onset and duration of urinary antigen excretion in Legionnaires disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):605–607. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.605-607.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R. B., Zimmerman S. E., Wilson E., Allen S. D., Edelstein P. H., Wheat L. J., White A. Rapid radioimmunoassay diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease: detection and partial characterization of urinary antigen. Ann Intern Med. 1981 May;94(5):601–605. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-5-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiafico J. A., Hedlund K. W., Knott A. R. Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigen from human urine. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):843–845. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.843-845.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thomason B. M., Harris P. P., Thacker L., Lewallen K. R., Wilkinson H. W., Hebert G. A., Moss C. W. Recognition of a new serogroup of Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):103–107. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.103-107.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathapatayavongs B., Kohler R. B., Wheat L. J., White A., Winn W. C., Jr, Girod J. C., Edelstein P. H. Rapid diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease by urinary antigen detection. Comparison of ELISA and radioimmunoassay. Am J Med. 1982 Apr;72(4):576–582. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathapatayavongs B., Kohler R. B., Wheat L. J., White A., Winn W. C., Jr Rapid diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease by latex agglutination. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):559–562. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang P. W., de Savigny D., Toma S. Detection of Legionella antigenuria by reverse passive agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):998–1000. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.998-1000.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C. Legionnaires' disease antigen detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):697–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


