Abstract
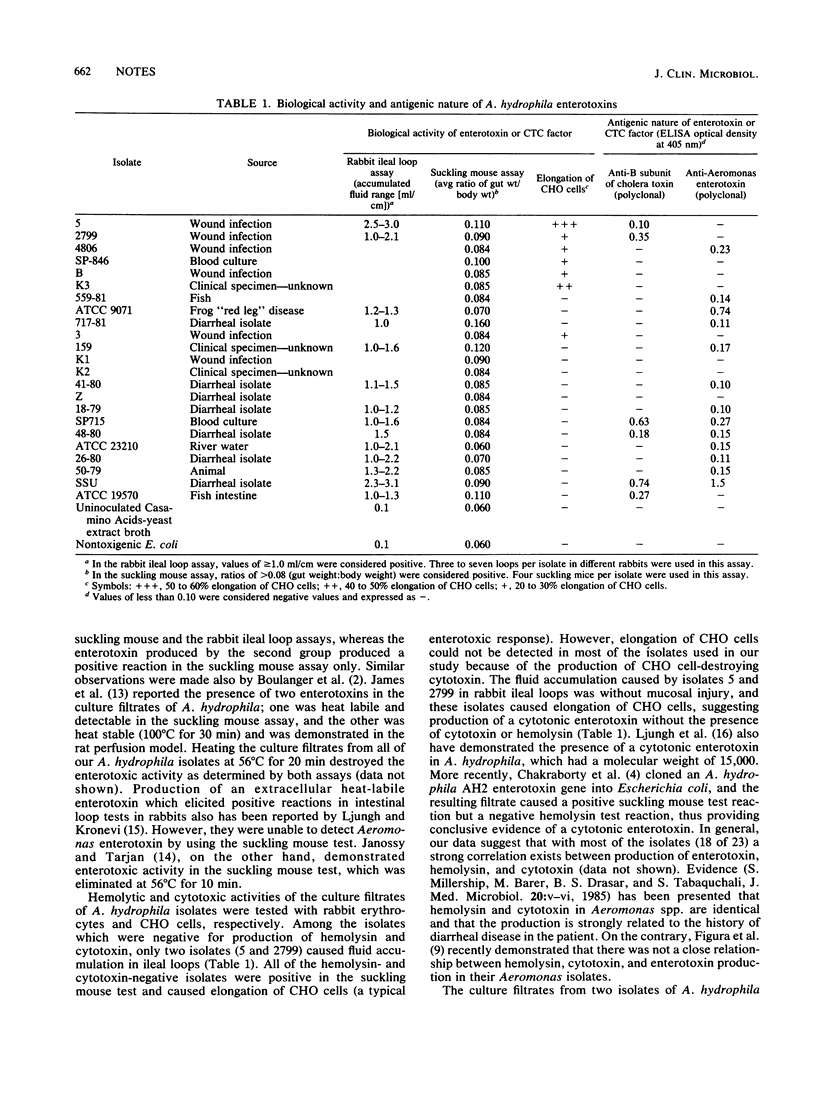
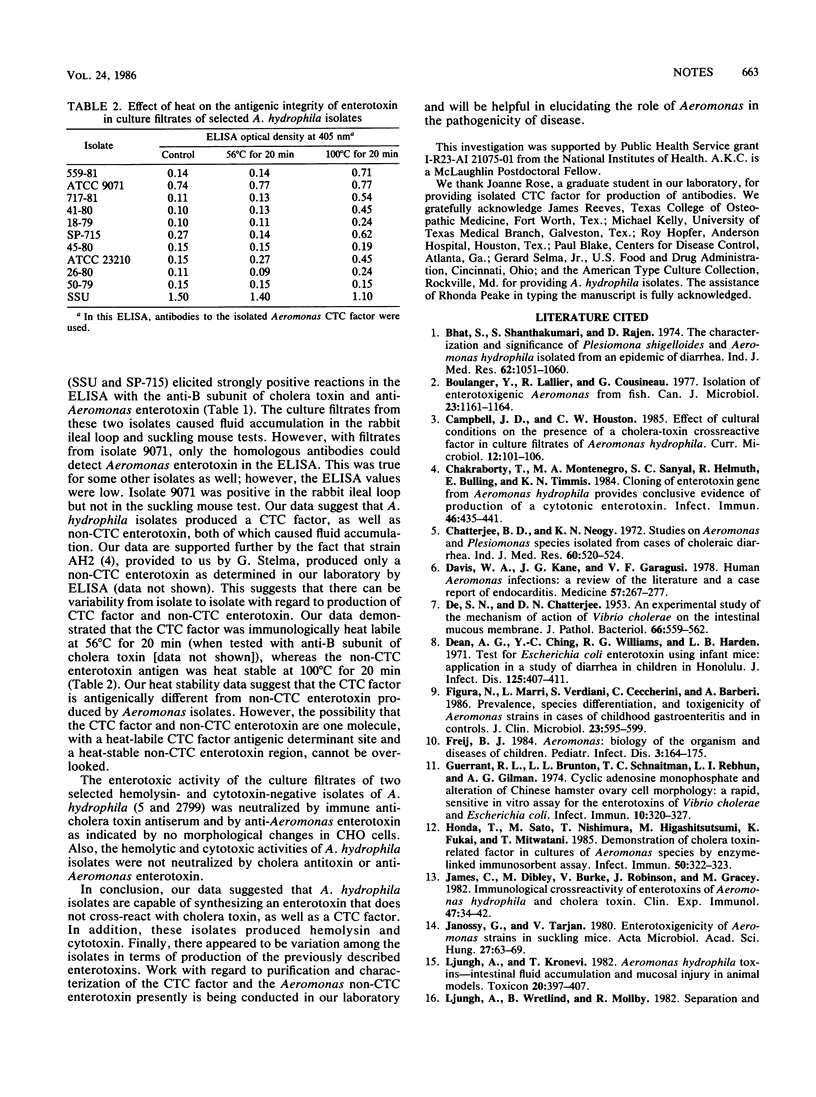
The enterotoxins produced by Aeromonas hydrophila were examined for biological activity by the rabbit ileal loop and suckling mouse assays, as well as by elongation of CHO cells. Antigenic evaluation of the culture filtrates from various isolates of A. hydrophila was performed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with anti-cholera toxin and anti-Aeromonas enterotoxin. Heat stability data demonstrated the presence of a heat-labile cholera toxin cross-reactive factor and a heat stable non-cholera toxin cross-reactive enterotoxin. The biological activities of both enterotoxins were heat labile at 56 degrees C for 20 min.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhat P., Shanthakumari S., Rajan D. The characterization and significance of Plesiomonas shigelloides and Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from an epidemic of diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1974 Jul;62(7):1051–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Montenegro M. A., Sanyal S. C., Helmuth R., Bulling E., Timmis K. N. Cloning of enterotoxin gene from Aeromonas hydrophila provides conclusive evidence of production of a cytotonic enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.435-441.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B. D., Neogy K. N. Studies on Aeromonas and Plesiomonas species isolated from cases of choleraic diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Apr;60(4):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Kane J. G., Garagusi V. F. Human aeromonas infections: a review of the literature and a case report of endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Marri L., Verdiani S., Ceccherini C., Barberi A. Prevalence, species differentiation, and toxigenicity of Aeromonas strains in cases of childhood gastroenteritis and in controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freij B. J. Aeromonas: biology of the organism and diseases in children. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):164–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Sato M., Nishimura T., Higashitsutsumi M., Fukai K., Miwatani T. Demonstration of cholera toxin-related factor in cultures of Aeromonas species by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):322–323. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.322-323.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James C., Dibley M., Burke V., Robinson J., Gracey M. Immunological cross-reactivity of enterotoxins of Aeromonas hydrophila and cholera toxin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jan;47(1):34–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jánossy G., Tarján V. Enterotoxigenicity of aeromonas strains in suckling mice. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1980;27(1):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Kronevi T. Aeromonas hydrophila toxins - intestinal fluid accumulation and mucosal injury in animal models. Toxicon. 1982;20(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Wretlind B., Möllby R. Separation and characterization of enterotoxin and two haemolysins from Aeromonas hydrophila. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Dec;89(6):387–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00205_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman A. F., Willoughby J. M. Dysentery-like syndrome associated with Aeromonas hydrophila. Br Med J. 1980 Oct 11;281(6246):976–976. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6246.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Sakazaki R., Horigome K., Uesaka Y., Niwano K. Production of cholera-like enterotoxin by Aeromonas hydrophila. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1984 Jun;37(3):141–144. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.37.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotnick I. J. Aeromonas species isolates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):503–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd Aeromonas hydrophila in clinical bacteriologic specimens. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):611–614. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


