Abstract
Three liquid media that differ slightly in composition but not in the method of preparation were developed for the propagation of Treponema hyodysenteriae and Treponema innocens. The three media are unique in that all components are sterilized by autoclaving before use. These media supported better growth of T. hyodysenteriae than did previously used liquid media.
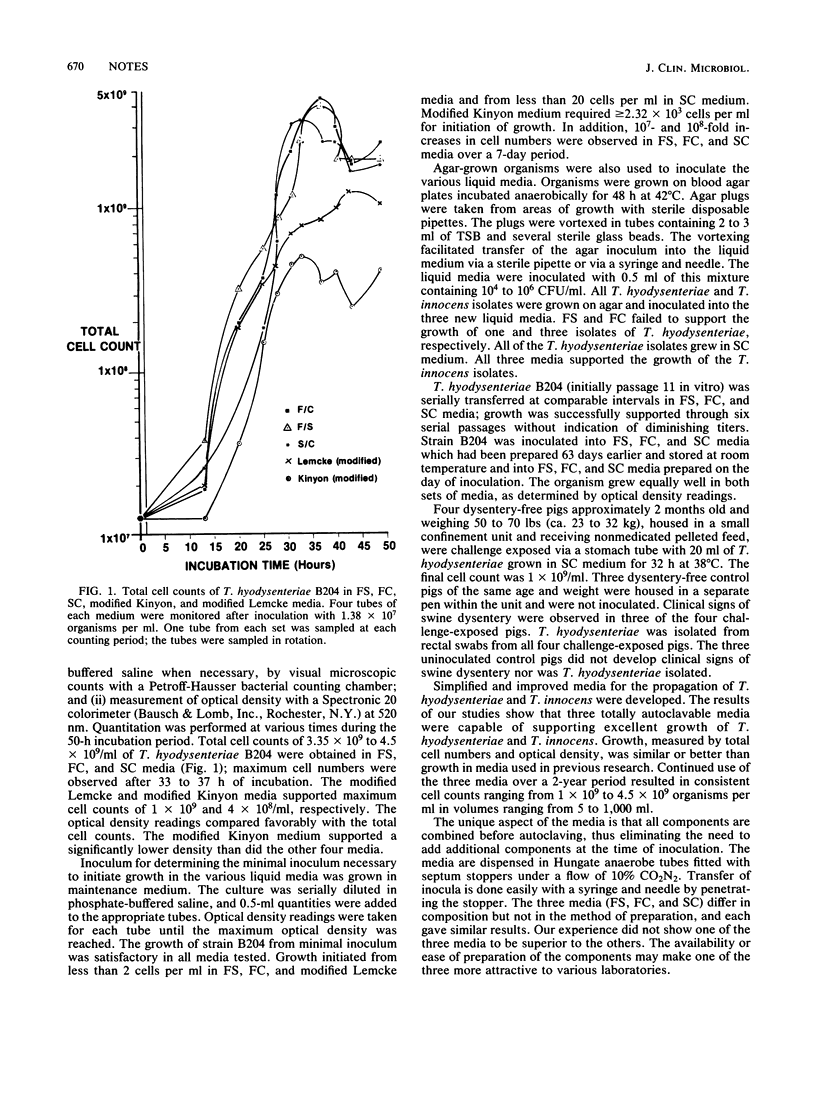
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinyon J. M., Harris D. L., Glock R. D. Enteropathogenicity of various isolates of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):638–646. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.638-646.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinyon J. M., Harris D. L. Growth in Treponema hyodysenteriae in liquid medium. Vet Rec. 1974 Sep 7;95(10):219–220. doi: 10.1136/vr.95.10.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Bew J., Burrows M. R., Lysons R. J. The growth of Treponema hyodysenteriae and other porcine intestinal spirochaetes in a liquid medium. Res Vet Sci. 1979 May;26(3):315–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Burrows M. R. Sterol requirement for the growth of Treponema hyodysenteriae. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):539–543. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


