Abstract
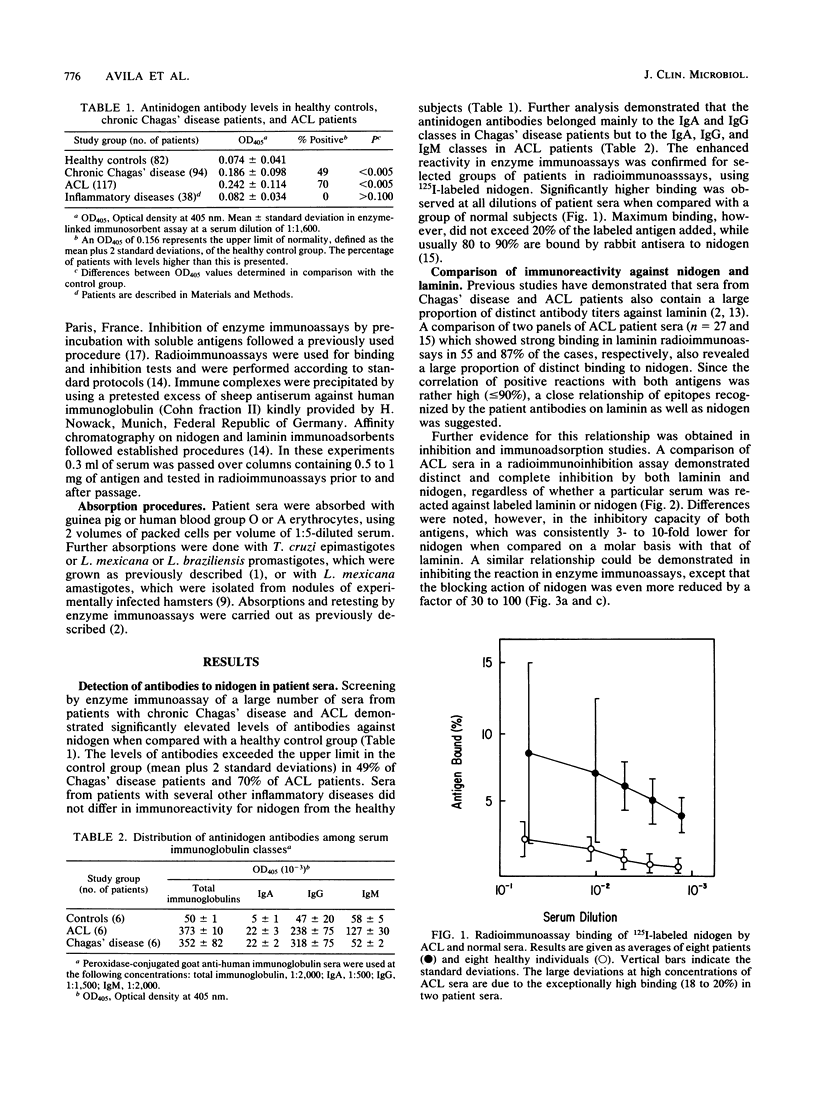
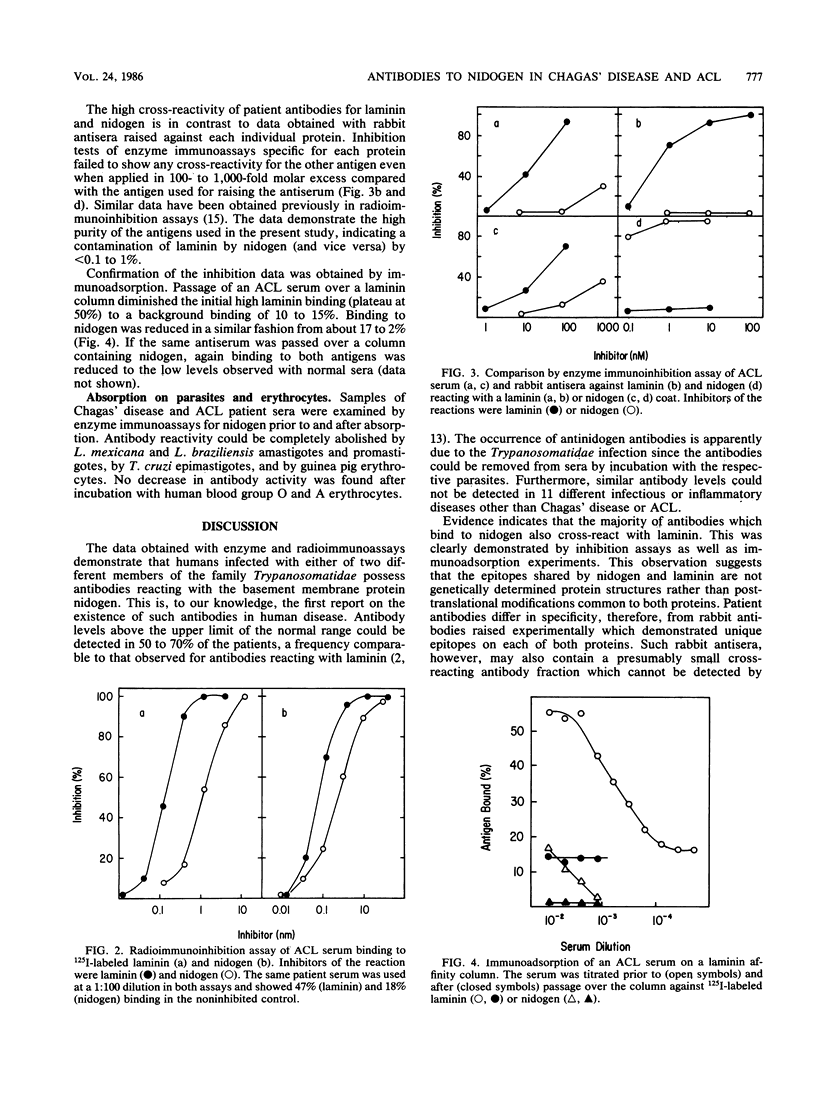
About 50 to 70% of sera from patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis and chronic Chagas' disease possessed antibodies which reacted in enzyme and radioimmunoassays with nidogen obtained from a tumor basement membrane. The antibodies were of the immunoglobulin M and G classes in acute American cutaneous leishmaniasis but mainly of the immunoglobulin G class in chronic Chagas' disease. Similar antibodies could not be detected in patients suffering from a variety of other infectious or inflammatory diseases when compared with healthy control groups. Inhibition and immunoadsorption studies indicated a close relationship of epitopes recognized by patients' antibodies on nidogen and on another basement membrane protein, laminin. Since rabbit antisera to both proteins do not cross-react, a special nature of the epitopes involved in the reaction with patient sera is suggested. Similar epitopes may exist on various forms of Leishmania or Trypanosoma protozoa.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila J. L., Bretaña A., Casanova M. A., Avila A., Rodríguez F. Trypanosoma cruzi: defined medium for continuous cultivation of virulent parasites. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Aug;48(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Rieber M. Antibodies to laminin in American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.402-406.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretaña A., Avila J. L., Arias-Flores M., Contreras M., Tapia F. J. Trypanosoma cruzi and American Leishmania spp: immunocytochemical localization of a laminin-like protein in the plasma membrane. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Apr;61(2):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess Q., Acosta A. M., Sethi J. K., Santos-Buch C. A. Reversible acquisition of a host cell surface membrane antigen by Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):299–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.299-302.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossio P. M., Diez C., Szarfman A., Kreutzer E., Candiolo B., Arana R. M. Chagasic cardiopathy. Demonstration of a serum gamma globulin factor which reacts with endocardium and vascular structures. Circulation. 1974 Jan;49(1):13–21. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.49.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAS E., LARANJA F. S., MIRANDA A., NOBREGA G. Chagas' disease; a clinical, epidemiologic, and pathologic study. Circulation. 1956 Dec;14(6):1035–1060. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.14.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjeux P., Santoro F., Afchain D., Loyens M., Capron A. Circulating immune complexes and anti-IgG antibodies in mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Mar;29(2):195–198. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. T., Vickerman K., Coombs G. H. A quick, simple method for purifying Leishmania mexicana amastigotes in large numbers. Parasitology. 1981 Jun;82(Pt 3):345–355. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000066889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Buch C. A. American trypanosomiasis: Chagas' disease. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1979;19:63–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Cossio P. M., Schmuñis G. A., Arana R. M. The EVI antibody in acute Chagaś disease. J Parasitol. 1977 Feb;63(1):149–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Terranova V. P., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., de Fatima Lima M., Scheinman J. I., Martin G. R. Antibodies to laminin in Chagas' disease. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1161–1171. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R. Antibodies to collagens and procollagens. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):472–498. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Dziadek M., Fujiwara S., Nowack H., Wick G. Nidogen: a new, self-aggregating basement membrane protein. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):455–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark H., Aumailley M., Wick G., Fleischmajer R., Timpl R. Immunochemistry, genuine size and tissue localization of collagen VI. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;142(3):493–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


