Abstract
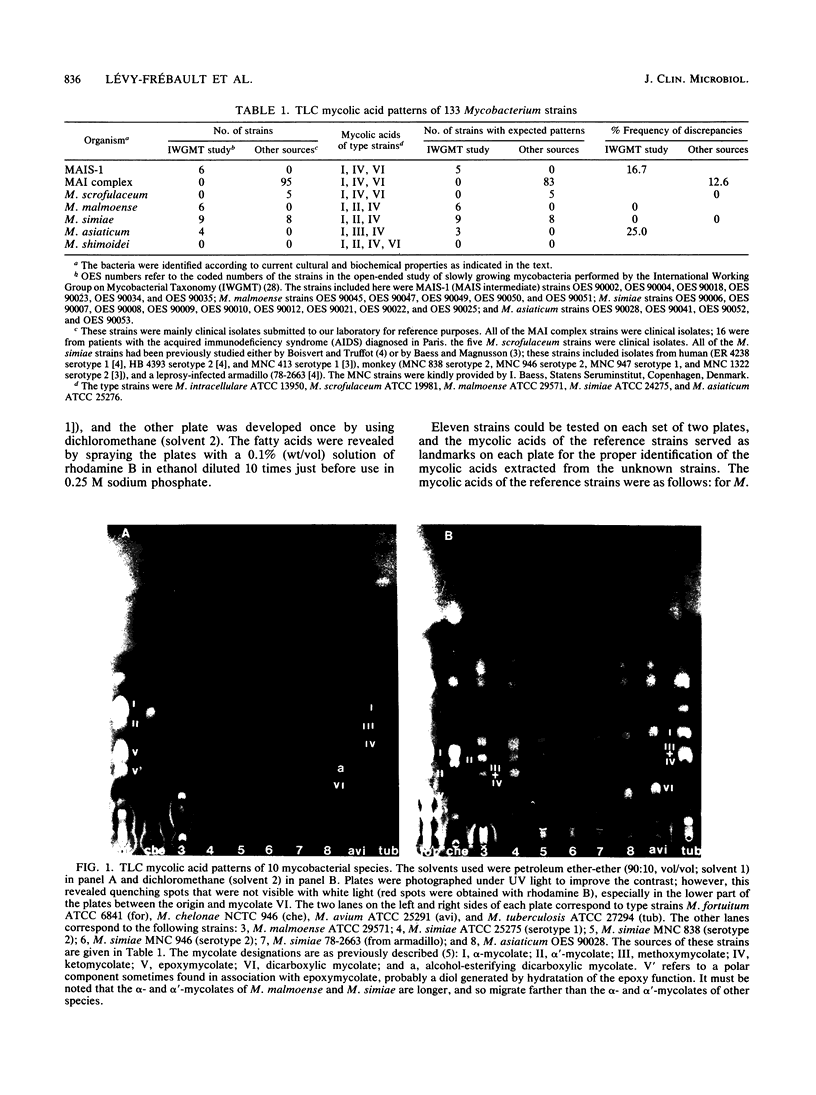
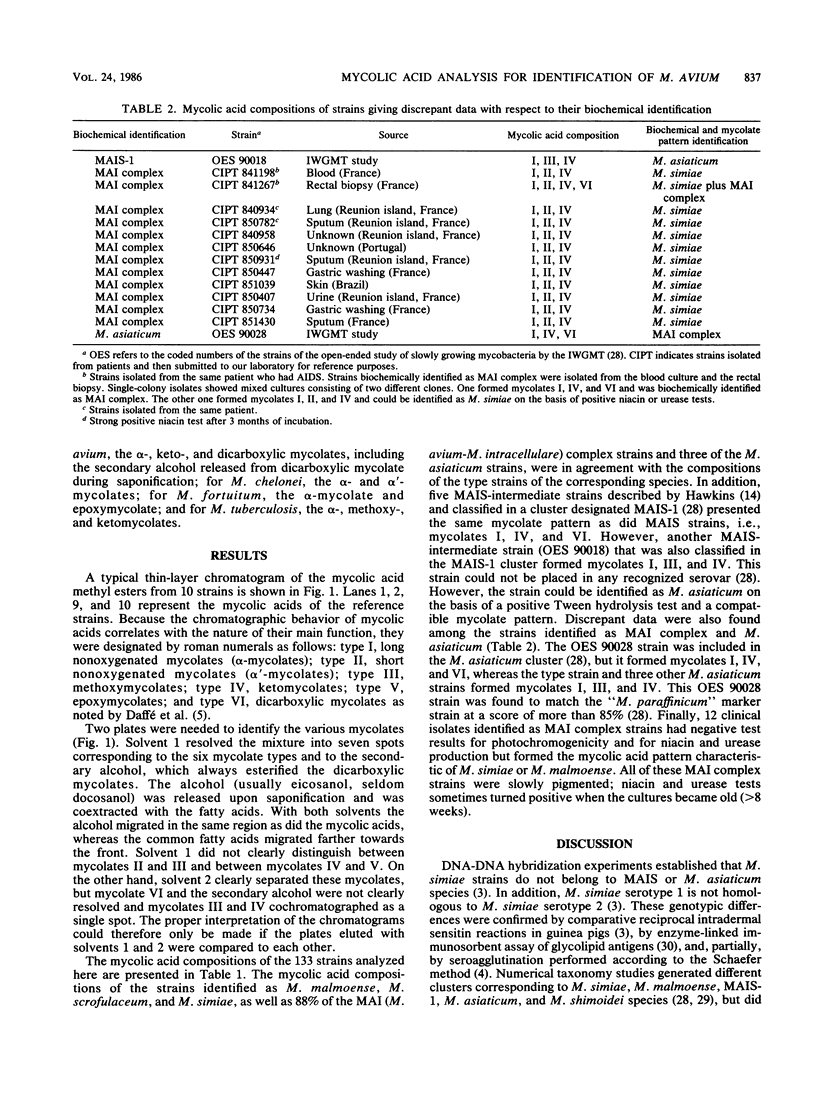
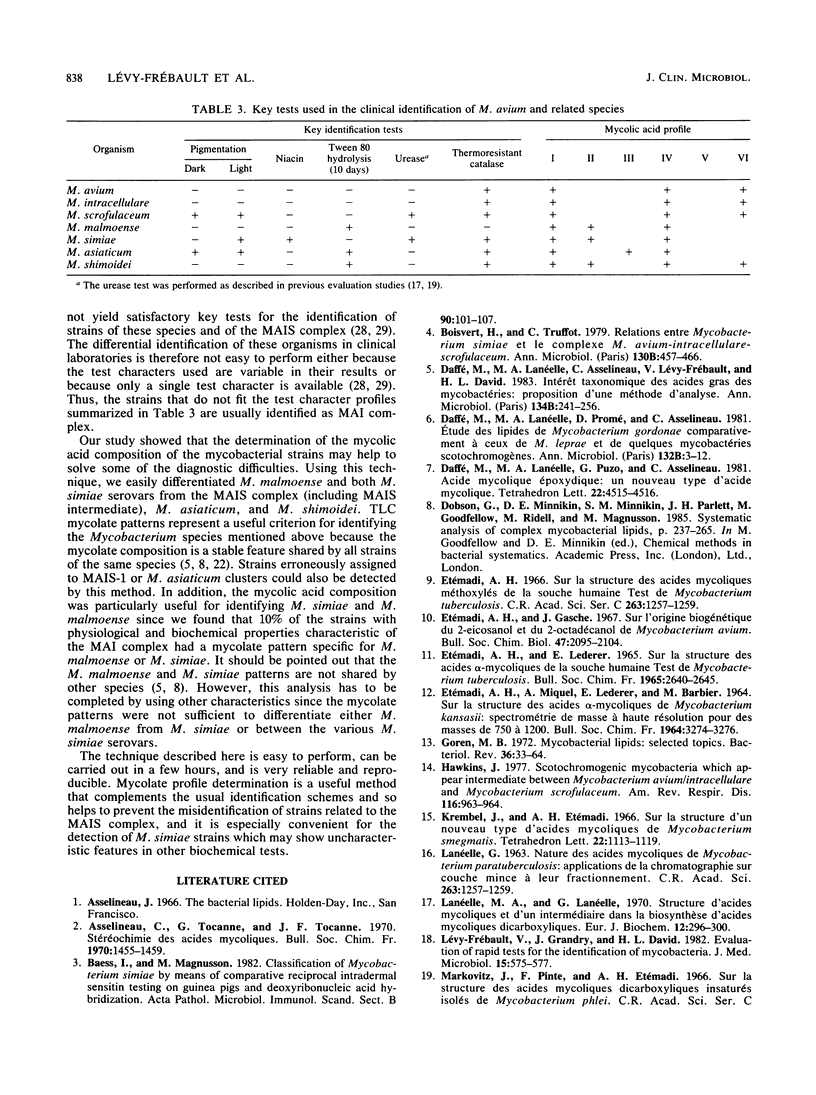
We examined the mycolic acid composition of 133 strains belonging to MAIS complex (Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare-M. scrofulaceum) and MAIS intermediate strains and the related species M. asiaticum, M. malmoense, M. shimoidei, and M. simiae. The analysis revealed that about 10% of the strains identified as M. avium-M. intracellulare complex by conventional cultural and biochemical tests were in fact M. simiae strains according to their mycolate composition. Of 25 strains previously studied by the International Working Group on Mycobacterial Taxonomy, 2 (MAIS intermediate and M. asiaticum) presented patterns incompatible with the clusters to which they had been assigned. M. malmoense and both M. simiae serovars shared the same pattern with alpha-, alpha'-, and ketomycolates. We describe here the method used to identify the mycolic acid profiles in detail. We found it to be highly reproducible and convenient for use in mycobacterial reference laboratories.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baess I., Magnusson M. Classification of Mycobacterium simiae by means of comparative reciprocal intradermal sensitin testing on guinea-pigs and deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Apr;90(2):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boisvert H., Truffot C. Relations entre Mycobacterium simiae et le complexe M. avium-intracellulare-scofulaceum. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1979 Nov-Dec;130B(4):457–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffé M., Lanéelle M. A., Asselineau C., Lévy-Frébault V., David H. Intérêt taxonomique des acides gras des mycobactéries: proposition d'une méthode d'analyse. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Sep-Oct;134B(2):241–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffé M., Lanéelle M. A., Promé D., Asselineau C. Etude des lipides de Mycobacterium gordonae comparativement à ceux de M. leprae et de quelques mycobactéries scotochromogènes. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Jul-Aug;132B(1):3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etemadi A. H., Gasche J. Sur l'origine biogénétique du 2-eicosanol et du 2-octadécanol de Mycobacterium avium. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47(11):2095–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etemadi A. H., Lederer E. Sur la structure des acides alpha-mycoliques de la souche humaine test de Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bull Soc Chim Fr. 1965 Sep;9:2640–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B. Mycobacterial lipids: selected topics. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Mar;36(1):33–64. doi: 10.1128/br.36.1.33-64.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. E. Scotochromogenic mycobacteria which appear intermediate between Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Nov;116(5):963–964. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.5.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanéelle M. A., Lanéelle G. Structure d'acides mycoliques et d'un intermediaire dans la biosynthèse d'acides mycoliques dicarboxyliques. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):296–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy-Frébault V., Grandry J., David H. L. Evaluation of rapid tests for the identification of mycobacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):575–577. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer L., David H. L. Evaluation de l'activité uréase et de l'activité beta-glucosidase pour l'identification pratique des mycobactéries. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1979 Oct;130B(3):323–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Minnikin S. M., Parlett J. H., Goodfellow M., Magnusson M. Mycolic acid patterns of some species of Mycobacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Oct;139(2-3):225–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00402005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G. The "atypical" mycobacteria: recognition and disease association. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(3):185–222. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara D. L., Barr V. L., Knisley C. V., Tsang A. Y., McClatchy J. K., Brennan P. J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of glycolipid antigens for identification of mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):569–574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.569-574.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



