Abstract
Antigenic fractions of Coxiella burnetii phase variants were identified with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Immune sera from guinea pigs immunized with Formalin-inactivated phase I or phase II whole cells were used to measure the antigenic activity of whole cells and various soluble and particulate preparations. Phase-specific antigens of C. burnetii whole cells and fractions were compared by dose-response curves at different (antigen and antibody) dilutions. Water-soluble extracts prepared by meta-periodate, ether, and phenol extraction of phase I whole cells yielded antigenic fractions which reacted with anti-phase I antibodies. The extraction of phase I whole cells with dimethyl sulfoxide, trichloracetic acid, and Formalin yielded antigenic fractions which detected antibodies in both anti-phase I and -phase II sera. Interestingly, the trichloracetic acid extract of phase I whole cells also contained a component which bound nonimmune immunoglobulin. The sera of animals immunized with whole cells of the phase II Australian QD strain reacted with lipopolysaccharides of the phase I and phase II Nine Mile strains. Therefore, variations in lipopolysaccharide structure among phase variants of C. burnetii were detected as cross-reactions with immune sera from an interspecific strain. Comparisons of immunofluorescence, microagglutination, and the complement fixation assays with the ELISA indicated greater sensitivity and specificity of the ELISA for the measurement of phase-specific antigens and antibodies.
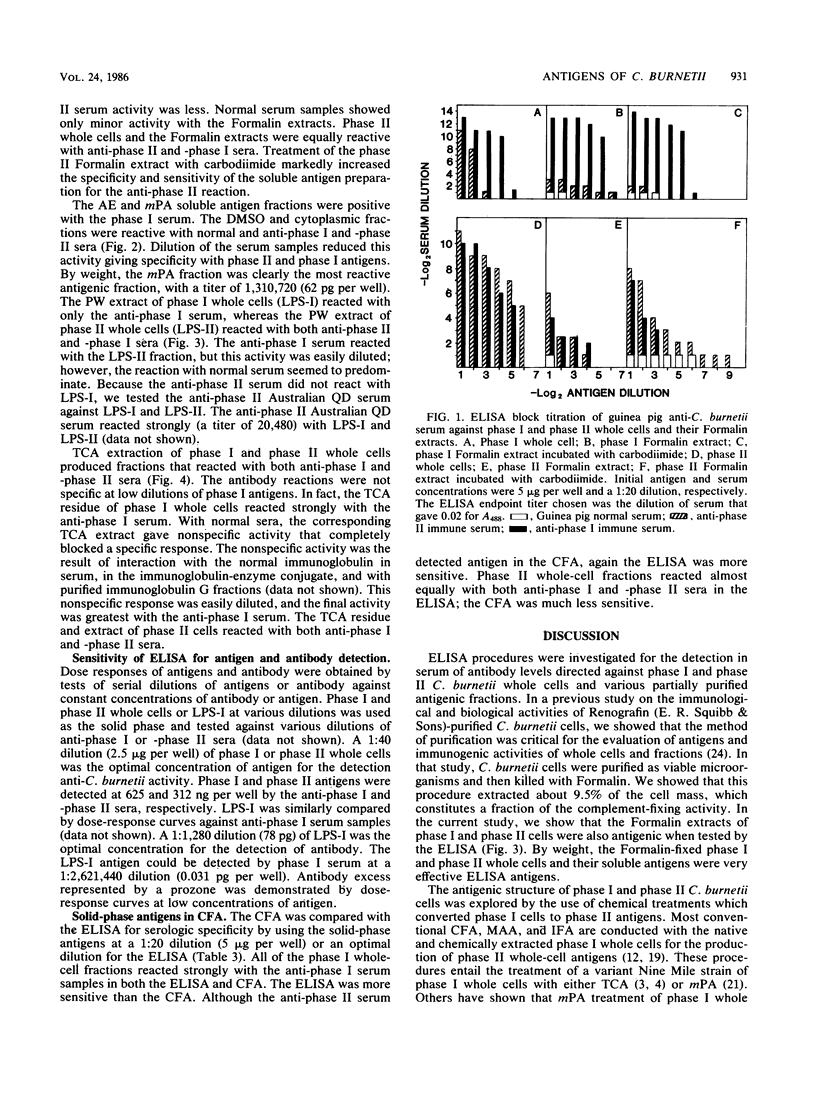
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., HASKINS W. T., LACKMAN D. B., RIBI E., PICKENS E. G. CONVERSION OF THE PHASE I ANTIGEN OF COXIELLA BURNETII TO HAPTEN BY PHENOL TREATMENT. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1165–1170. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1165-1170.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Chemical and immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.994-1002.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLTER J. S., BROWN R. A., BIRD H. H., COX H. R. The preparation of a soluble immunizing antigen from Q-fever rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1956 Apr;76(4):270–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Lindberg A. A., Hammarström S. Titration of antibodies to salmonella O antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):703–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.703-708.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crăcea E., Constantinescu S., Dumitrescu A., Stefănescu M., Szegli G. ELISA in the Q fever diagnosis. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1983 Oct-Dec;42(4):283–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field P. R., Hunt J. G., Murphy A. M. Detection and persistence of specific IgM antibody to Coxiella burnetii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: a comparison with immunofluorescence and complement fixation tests. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):477–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A., Silberman R., Peacock M., Spielman S. H. A microagglutination technique for detection and measurement of rickettsial antibodies. Acta Virol. 1969 Jan;13(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Wike D. A., Pickens E. G., Ormsbee R. A. An antigenic comparison of strains of Coxiella burneti. Acta Virol. 1971 Mar;15(2):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvano R., Boniolo A., Dovis M., Zannino M. ELISA for antibody measurement: aspects related to data expression. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A. A method of purifying Coxiella burnetii and other pathogenic Rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1962 Jan;88:100–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A., BELL E. J., LACKMAN D. B. Antigens of Coxiella burnetii. I. Extraction of antigens with non-aqueous organic solvents. J Immunol. 1962 Jun;88:741–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A., BELL E. J., LACKMAN D. B., TALLENT G. THE INFLUENCE OF PHASE ON THE PROTECTIVE POTENCY OF Q FEVER VACCINE. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:404–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock M. G., Philip R. N., Williams J. C., Faulkner R. S. Serological evaluation of O fever in humans: enhanced phase I titers of immunoglobulins G and A are diagnostic for Q fever endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1089–1098. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1089-1098.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M. G., FISET P. Phase variation of the Nine Mile and other strains of Rickettsia burneti. Can J Microbiol. 1956 May;2(3):310–321. doi: 10.1139/m56-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeer N. Enzymimmuntest (ELISA) zum Nachweis von IgG1-, IgG2- und IgM-Antikörpern bei der Q-Fieber-Infektion des Rindes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Feb;259(1):20–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Brezina R., Urvölgyi J. A new method of preparing diagnostic Q fever antigen. Acta Virol. 1972 Nov;16(6):487–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Johnston M. R., Peacock M. G., Thomas L. A., Stewart S., Portis J. L. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phase variants of Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):421–428. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.421-428.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Peacock M. G., McCaul T. F. Immunological and biological characterization of Coxiella burnetii, phases I and II, separated from host components. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.840-851.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying P. K., Deng R. L., Liu G. Z. Experimental study of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of Q fever antibody. Acta Acad Med Wuhan. 1983;3(3):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF02856646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



