Abstract
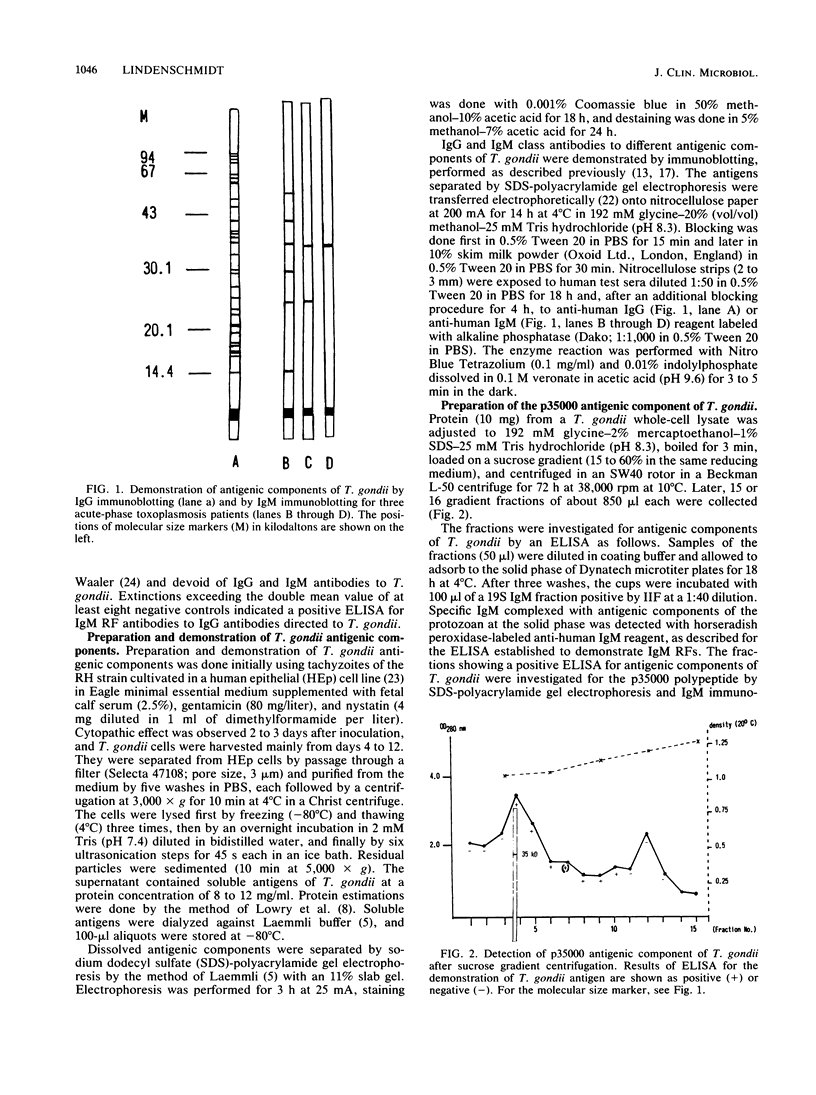
On the basis that 89% of 48 acute-phase toxoplasmosis patients showed immunoglobulin M (IgM) class antibodies to the 35,000-molecular-weight antigenic component (p35000) of Toxoplasma gondii, as demonstrated by IgM immunoblotting, the antigen was purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation and enzyme labeled for use in an enzyme-linked antigen immunosorbent assay (ELA) for the demonstration of IgM class antibodies to the p35000 component. The ELA showed a specificity of 96% with 139 serum specimens at a serum dilution of only 1:5. The test serologically detected 73 symptomatic acute-phase toxoplasmosis patients; 64 were positive in the 19S IgM indirect immunofluorescent-antibody test, and 9 were negative, although they showed IgM antibodies to p35000, as demonstrated by IgM immunoblotting. Also, the ELA turned out to be independent of IgM rheumatoid factors in six acute-phase toxoplasmosis serum specimens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Franco E. L., Walls K. W., Sulzer A. J., Soto J. C. Diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis with the enzyme-labelled antigen reversed immunoassay for immunoglobulin M antibodies. J Immunoassay. 1983;4(4):373–393. doi: 10.1080/15321818308057016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. Relation to allergy. N Y State J Med. 1968 Feb 1;68(3):411–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Goding J. W., Remington J. S. Detection and characterization of membrane antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2578–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde B., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for differentiation of nonspecific from specfic toxoplasma IgM fluorescent antibodies in patients with rheumatoid factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Apr;148(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper L. H., Crabb J. H., Pfefferkorn E. R. Purification of a major membrane protein of Toxoplasma gondii by immunoabsorption with a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenschmidt E. G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of soluble Toxoplasma gondii antigen in acute-phase toxoplasmosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;4(5):488–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02014430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenschmidt E. G. Rheumafaktoraktivität als Störfaktor bei der serologischen Diagnostik spezifischer IgM-Antikörper. Immun Infekt. 1984 Apr;12(2):94–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Remington J. S. The diagnosis and treatment of toxoplasmosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):95–104. doi: 10.1007/BF02001573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for avoiding false-positive results occurring in immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays due to presence of both rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.73-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Sproul P., Baker L., Rubinstein P., Stevens C. E., Taylor P., Gallo R. C., Gold J. W., Lee Y. S. Radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunoassay of antibodies to the core protein (P24) of human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV III). J Virol Methods. 1985 May;11(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Turunen H. J., Paasivuo R. T., Leinikki P. O. Immunoblot analysis of Toxoplasma gondii antigens by human immunoglobulins G, M, and A antibodies at different stages of infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):133–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.133-135.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Turunen H. J., Paasivuo R., Forsblom E., Suni J., Leinikki P. O. Identification of antigenic components of Toxoplasma gondii by an immunoblotting technique. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 25;158(2):252–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80589-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez C., Afchain D., Capron A., Dissous C., Santoro F. Major surface protein of Toxoplasma gondii (p30) contains an immunodominant region with repetitive epitopes. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):747–749. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., von Deimling U., Flehmig B. Detection of IgM antibodies to cytomegalovirus (CMV) using an enzyme-labelled antigen (ELA). J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Mullenax J., Araujo F. G., Erlich H. A., Remington J. S. Western Blot analysis of the antigens of Toxoplasma gondii recognized by human IgM and IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodaria P. V., Fraser K. B., Stanford F. Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-IgM. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jan;32(1):53–57. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Remington J. S. Comparison of methods for quantitating antigen-specific immunoglobulin M antibody with a reverse enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.63-70.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer A. J., Franco E. L., Takafuji E., Benenson M., Walls K. W., Greenup R. L. An oocyst-transmitted outbreak of toxoplasmosis: patterns of immunoglobulin G and M over one year. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Mar;35(2):290–296. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasheva B., Dessev G. Artifacts in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis due to 2-mercaptoethanol. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van der Veen J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of toxoplasma antibodies in human sera. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;33(7):635–639. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


