Abstract
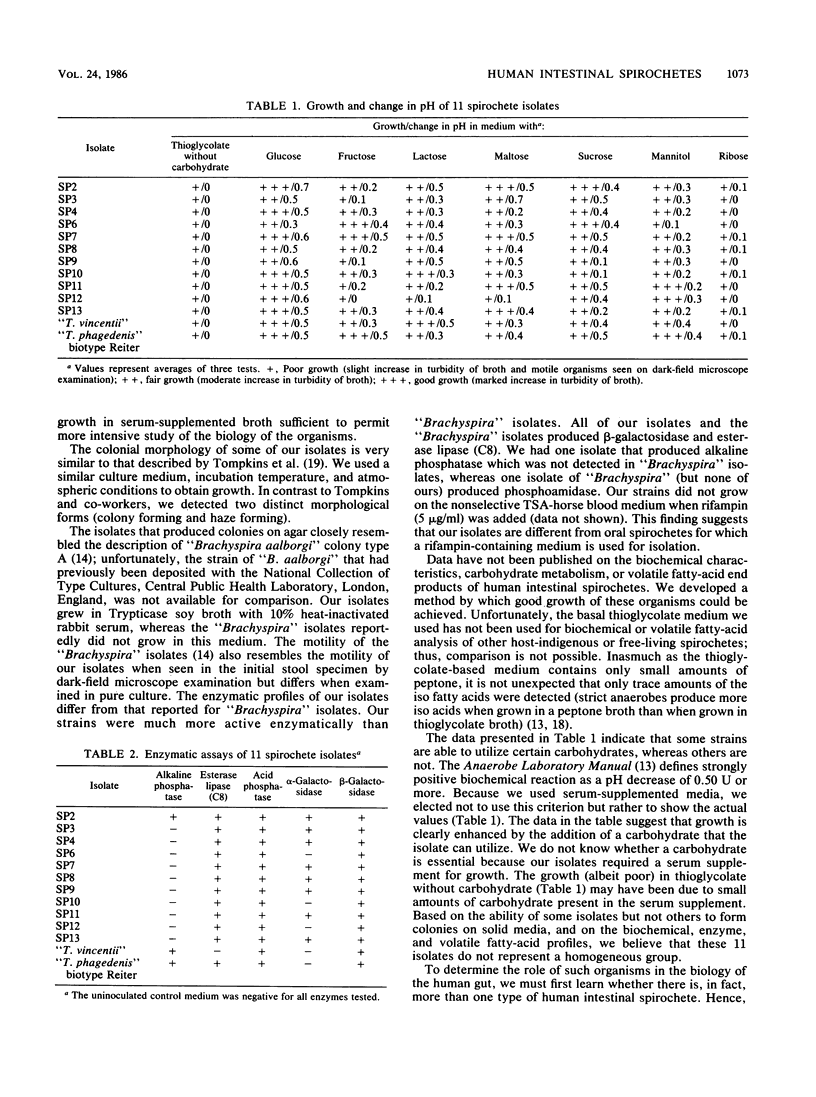
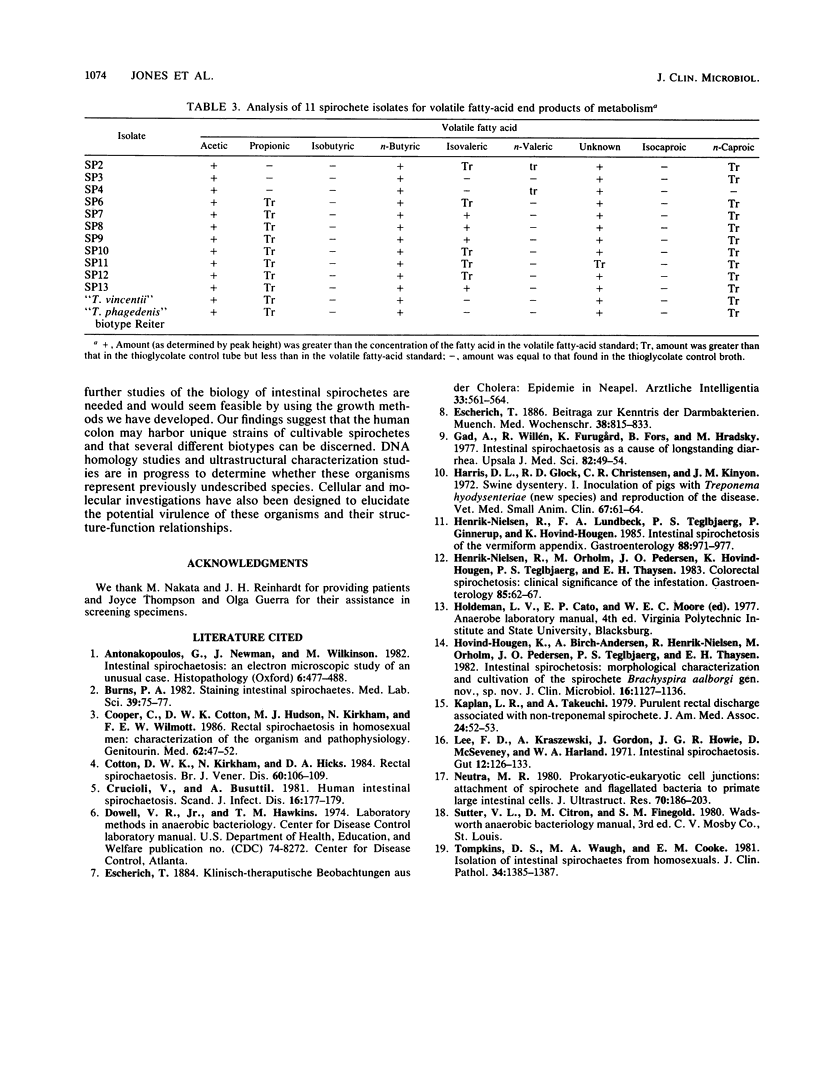
Spirochetes were isolated from the feces of 11 homosexual males who had diarrhea. The anaerobic organisms were isolated from a selective medium that consisted of Trypticase soy agar supplemented with either 5% horse or human blood, 400 micrograms of spectinomycin per ml, and 5 micrograms of polymyxin B per ml. Nonselective media that permitted good growth of these fastidious organisms were developed, and selected biochemical tests were performed. The tests included carbohydrate utilization, detection of certain enzymes, and determination of volatile fatty-acid end products of metabolism. Two growth patterns were noted on solid media, a haze of growth and production of small colonies. Based on the results of biochemical tests, patterns of preformed enzymes, and volatile fatty-acid production, we believe that the 11 isolates represent a heterogeneous group of spirochetes. The data suggest that the human colon may harbor unique strains of cultivable spirochetes; additional study of the taxonomy of the organisms and assessment of their virulence for humans are needed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonakopoulos G., Newman J., Wilkinson M. Intestinal spirochaetosis: an electron microscopic study of an unusual case. Histopathology. 1982 Jul;6(4):477–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1982.tb02744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns P. A. Staining intestinal spirochaetes. Med Lab Sci. 1982 Jan;39(1):75–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C., Cotton D. W., Hudson M. J., Kirkham N., Wilmott F. E. Rectal spirochaetosis in homosexual men: characterisation of the organism and pathophysiology. Genitourin Med. 1986 Feb;62(1):47–52. doi: 10.1136/sti.62.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton D. W., Kirkham N., Hicks D. A. Rectal spirochaetosis. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):106–109. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crucioli V., Busuttil A. Human intestinal spirochaetosis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1981;70:177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrik-Nielsen R., Lundbeck F. A., Teglbjaerg P. S., Ginnerup P., Hovind-Hougen K. Intestinal spirochetosis of the vermiform appendix. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):971–977. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K., Birch-Andersen A., Henrik-Nielsen R., Orholm M., Pedersen J. O., Teglbjaerg P. S., Thaysen E. H. Intestinal spirochetosis: morphological characterization and cultivation of the spirochete Brachyspira aalborgi gen. nov., sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1127–1136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1127-1136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. R., Takeuchi A. Purulent rectal discharge associated with a nontreponemal spirochete. JAMA. 1979 Jan 5;241(1):52–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. D., Kraszewski A., Gordon J., Howie J. G., McSeveney D., Harland W. A. Intestinal spirochaetosis. Gut. 1971 Feb;12(2):126–133. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neutra M. R. Prokaryotic-eukaryotic cell junctions: attachment of spirochetes and flagellated bacteria to primate large intestinal cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 Feb;70(2):186–203. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. H., Orholm M., Pedersen J. O., Hovind-Hougen K., Teglbjaerg P. S., Thaysen E. H. Colorectal spirochetosis: clinical significance of the infestation. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jul;85(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins D. S., Waugh M. A., Cooke E. M. Isolation of intestinal spirochaetes from homosexuals. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Dec;34(12):1385–1387. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.12.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


