Abstract
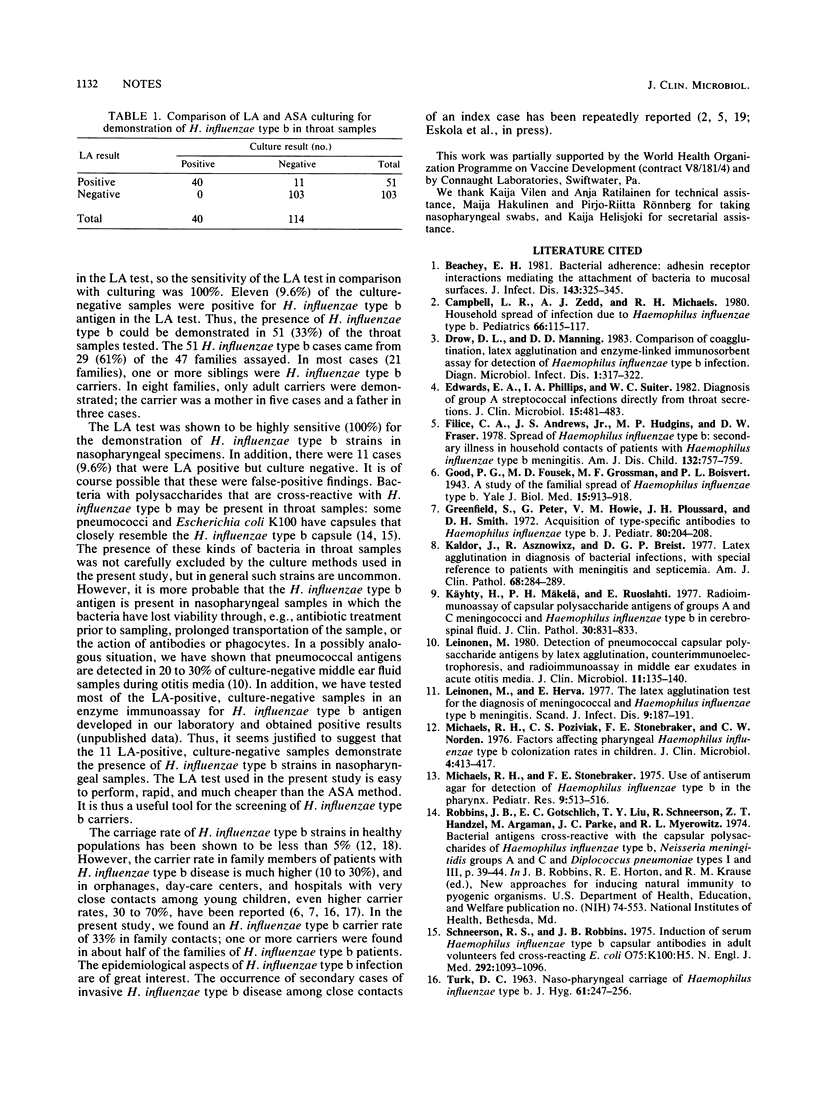
Latex agglutination (LA) for the demonstration of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular antigen in nasopharyngeal swabs was applied to the screening of H. influenzae type b carriers and compared with culturing by the antiserum agar method on Levinthal-bacitracin plates. Altogether, 51 (33%) of the 154 nasopharyngeal specimens collected from the close contacts of patients with invasive H. influenzae type b disease were positive in LA or the antiserum agar method or both. All 40 culture-positive samples were also positive in LA, and in 11 (9.6%) culture-negative samples, H. influenzae type b antigen was demonstrated by LA. LA as used in the present study is cheap, rapid, and easy to perform and is thus an ideal tool for the screening of H. influenzae type b carriers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. R., Zedd A. J., Michaels R. H. Household spread of infection due to Haemophilus influenzae type b. Pediatrics. 1980 Jul;66(1):115–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drow D. L., Manning D. D. Comparison of coagglutination, latex agglutination, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;1(4):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards E. A., Phillips I. A., Suiter W. C. Diagnosis of group A streptococcal infections directly from throat secretions. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):481–483. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.481-483.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G. A., Andrews J. S., Jr, Hudgins M. P., Fraser D. W. Spread of Haemophilus influenzae. Secondary illness in household contacts of patients with H influenzae meningitis. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Aug;132(8):757–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Peter G., Howie V. M., Ploussard J. H., Smith D. H. Acquisition of type-specific antibodies to Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Pediatr. 1972 Feb;80(2):204–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80579-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaldor J., Asznowicz R., Buist D. G. Latex agglutination in diagnosis of bacterial infections, with special reference to patients with meningitis and septicemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Aug;68(2):284–289. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H., Mäkelä P. H., Ruoslahti E. Radioimmunoassay of capsular polysaccharide antigens of groups A and C meningococci and Haemophilus influenzae type b in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Sep;30(9):831–833. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.9.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinonen M. K. Detection of Pneumococcal Capsular polysaccharide antigens by latex agglutination, counterimmunoelectrophoresis, and radioimmunoassay in middle ear exudates in acute otitis media. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):135–140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.135-140.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinonen M., Herva E. The latex agglutination test for the diagnosis of meningococcal and haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1977;9(3):187–191. doi: 10.3109/inf.1977.9.issue-3.06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Poziviak C. S., Stonebraker F. E., Norden C. W. Factors affecting pharyngeal Haemophilus influenzae type b colonization rates in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):413–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.413-417.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Stonebraker F. E., Robbins J. B. Use of antiserum agar for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the pharynx. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):513–516. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of serum Haemophilus influenzae type B capsular antibodies in adult volunteers fed cross-reacting Escherichia coli 075:K100:H5. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 22;292(21):1093–1096. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505222922103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURK D. C. Naso-pharyngeal carriage of Haemophilus influenza type B. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Jun;61:247–256. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D. C. An investigation of the family background of acute Haemophilus infections of children. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Oct;75(2):315–332. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. I., Fraser D. W., Baraff L. J., Plikaytis B. D. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. A national study of secondary spread in household contacts. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 19;301(3):122–126. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907193010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. B., Bass J. W., Yamada S. M. Rapid latex agglutination compared with the throat culture for the detection of group A streptococcal infection. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;5(2):208–212. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198603000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



