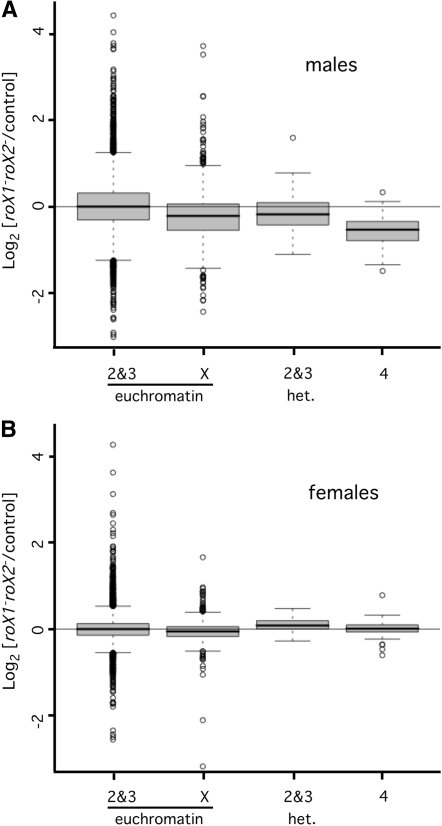
Figure 3.—
Genes situated in proximal heterochromatin require roX RNA for full expression in males. (A) Genes in proximal heterochromatin have reduced expression in roX1SMC17AroX2 male larvae. Box plots were generated using the log2 expression ratios (mutant/control) presented in Figure 1A. The mean expression of genes in proximal heterochromatin on the second and third chromosomes decreases by 0.17 in roX1SMC17AroX2 males (adjusted P-value of 0.003). The mean expression of X-linked genes decreases by 0.24, and expression of fourth-linked genes decreases by 0.58. Changes of the X and fourth chromosome have an adjusted P-value of <6.6 × 10−16. Only genes present in at least 2 out of 3 arrays contributed to this analysis (8347 in second and third euchromatin; 1533 in X euchromatin, 73 in second and third heterochromatin, and 74 on the fourth chromosome). (B) Fourth-linked and heterochromatic genes do not require roX RNA for full expression in females. Box plots were generated using the log2 expression ratios (mutant/control) presented in Figure 1C. The mean change in expression of X-linked genes in roX1SMC17AroX2 females is −0.04. Second and third chromosome heterochromatic genes and fourth- linked genes have a slight average increase (0.06 and 0.01, respectively) that is not statistically significant. Only genes present in at least 2 out of 3 arrays contributed to this analysis (7097 in second and third euchromatin, 1336 in X euchromatin, 57 in second and third heterochromatin, and 69 on the fourth chromosome). Enrichment for heterochromatic genes is described in File S1.