Abstract
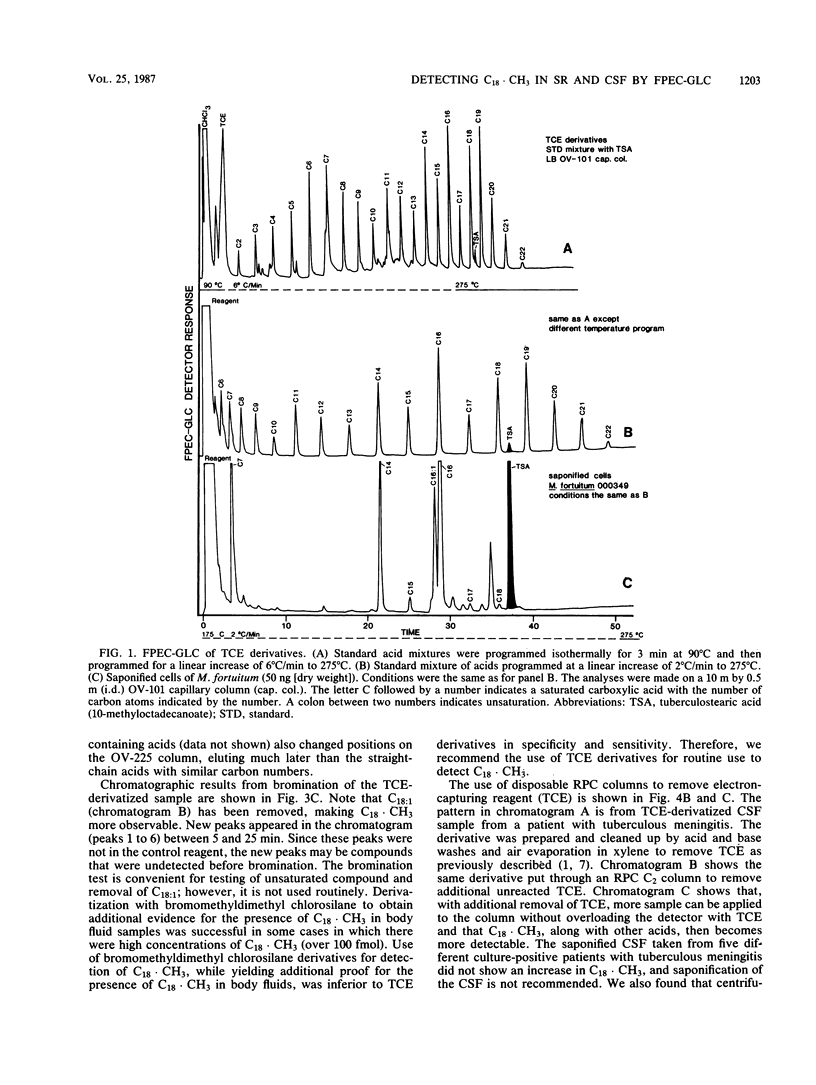
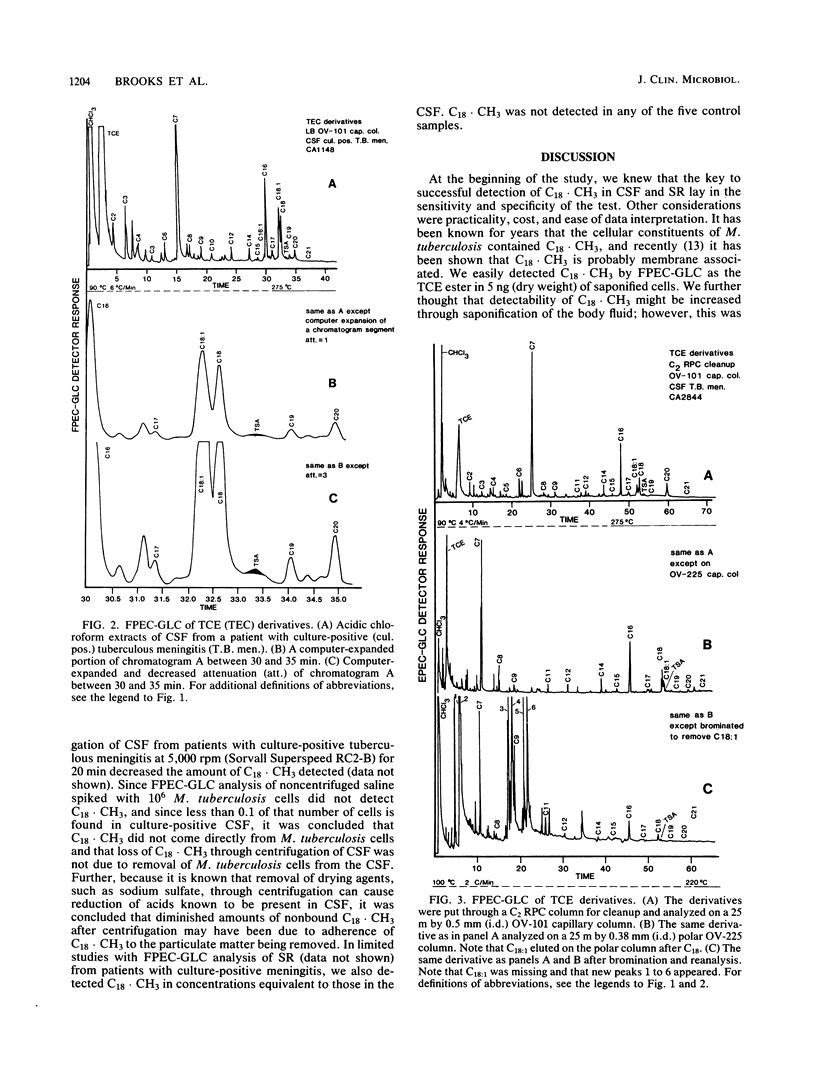
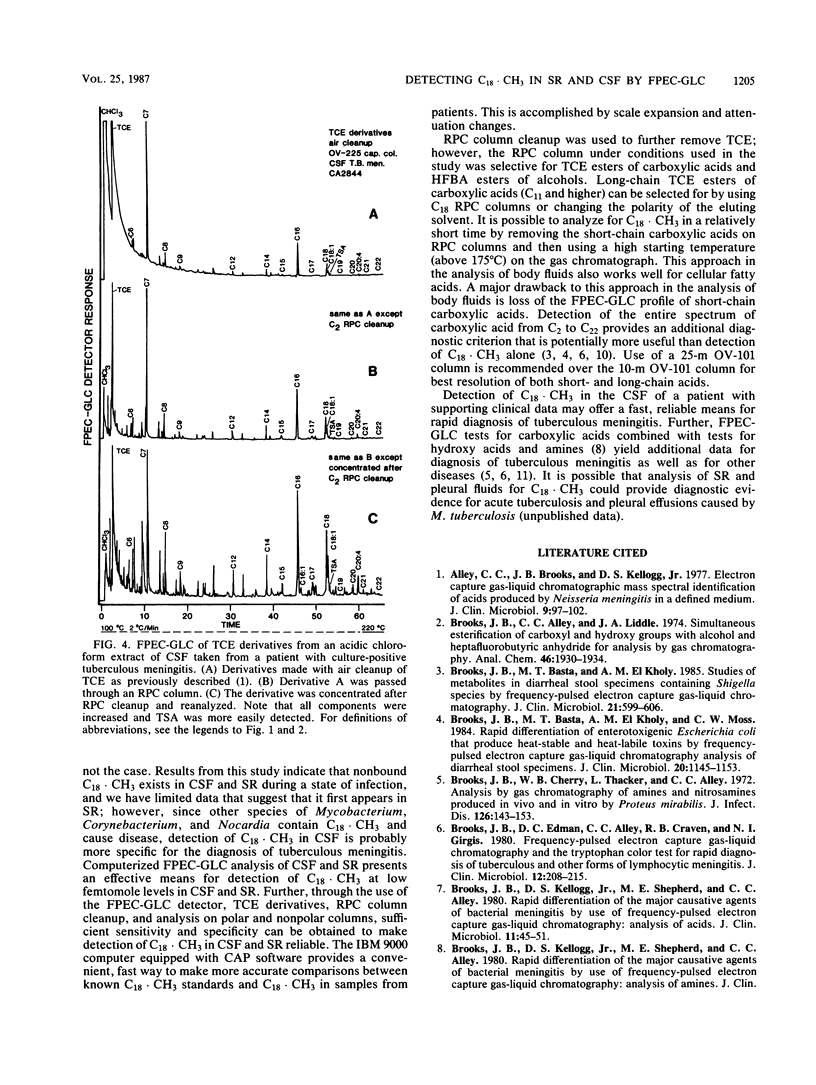
Conditions are described for the detection of tuberculostearic acid (10-methyloctadecanoate; C18 X CH3) in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with tuberculous meningitis. C18 X CH3 was found in both the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with tuberculous meningitis at concentrations of 25 to 50 fmol (10(-15) mol). The necessary specificity and sensitivity for detection of C18 X CH3 were obtained by extraction under acid conditions with organic solvent, specific functional group esterification with trichloroethanol, cleanup with disposable reverse-phase sorption chromatography columns, analysis on high-resolution polar and nonpolar capillary columns, and detection by a frequency-pulsed electron capture detector. Use of an IBM 9000 computer equipped with CAP software significantly aided comparison between known C18 X CH3 standards and C18 X CH3 in clinical specimens. Scale expansion and attenuation changes were the major contributions obtained by use of the computer. The data indicate that detection of C18 X CH3 by frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography may be a valuable aid for early detection of tuberculous meningitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alley C. C., Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr Electron capture gas-liquid chromatographic-mass spectral identification of acids produced by Neisseria meningitidis in a defined medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.97-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Basta M. T., el Kholy A. M., Moss C. W. Rapid differentiation of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli that produce heat-stable and heat-labile toxins by frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography analysis of diarrheal stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1145–1153. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1145-1153.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Basta M. T., el Kholy A. M. Studies of metabolites in diarrheal stool specimens containing Shigella species by frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):599–606. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.599-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Cherry W. B., Thacker L., Alley C. C. Analysis by gas chromatography of amines and nitrosamines produced in vivo and in vitro by Proteus mirabilis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Aug;126(2):143–153. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Edman D. C., Alley C. C., Craven R. B., Girgis N. I. Frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography and the tryptophan color test for rapid diagnosis of tuberculous and other forms of lymphocytic meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):208–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.208-215.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Shepherd M. E., Alley C. C. Rapid differentiation of the major causative agents of bacterial meningitis by use of frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatograph: analysis of acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):45–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.45-51.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Nunez-Montiel O. L., Basta M. T., Hierholzer J. C. Studies of stools from pseudomembranous colitis, rotaviral, and other diarrheal syndromes by frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):549–560. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.549-560.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Gaylord H., Brennan P. J. Structure and antigenicity of the phosphorylated lipopolysaccharide antigens from the leprosy and tubercle bacilli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12345–12351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



