Abstract
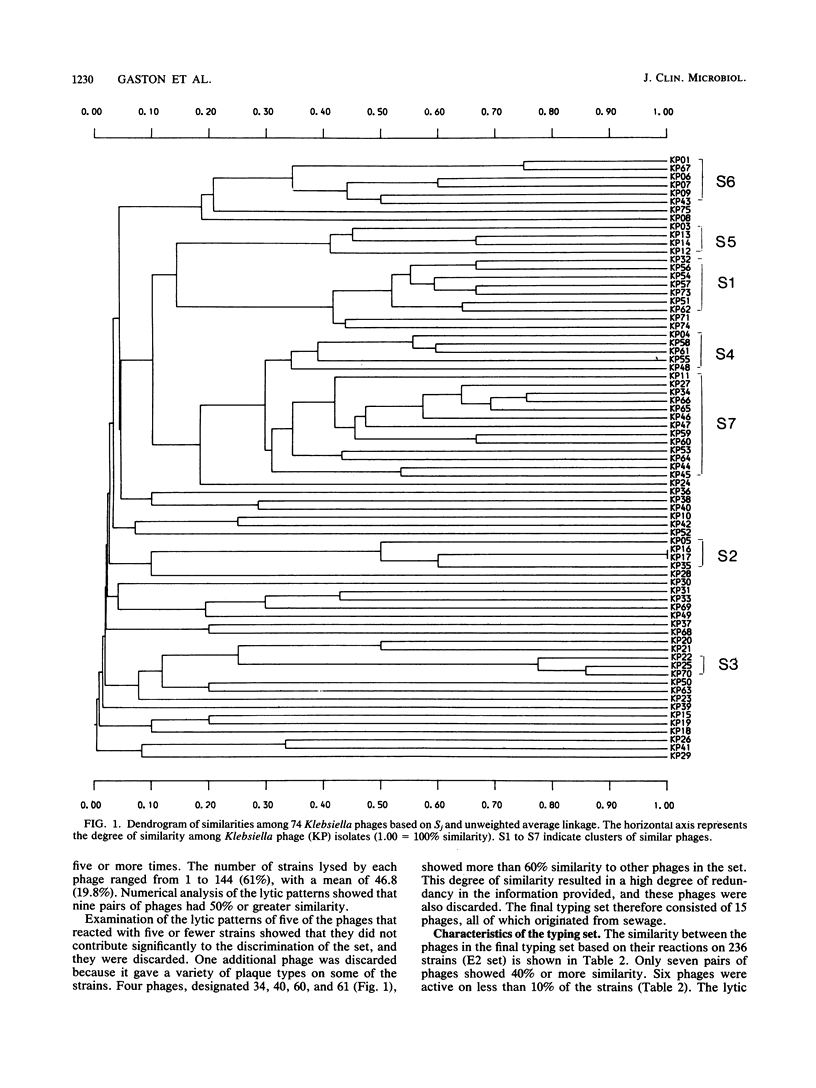
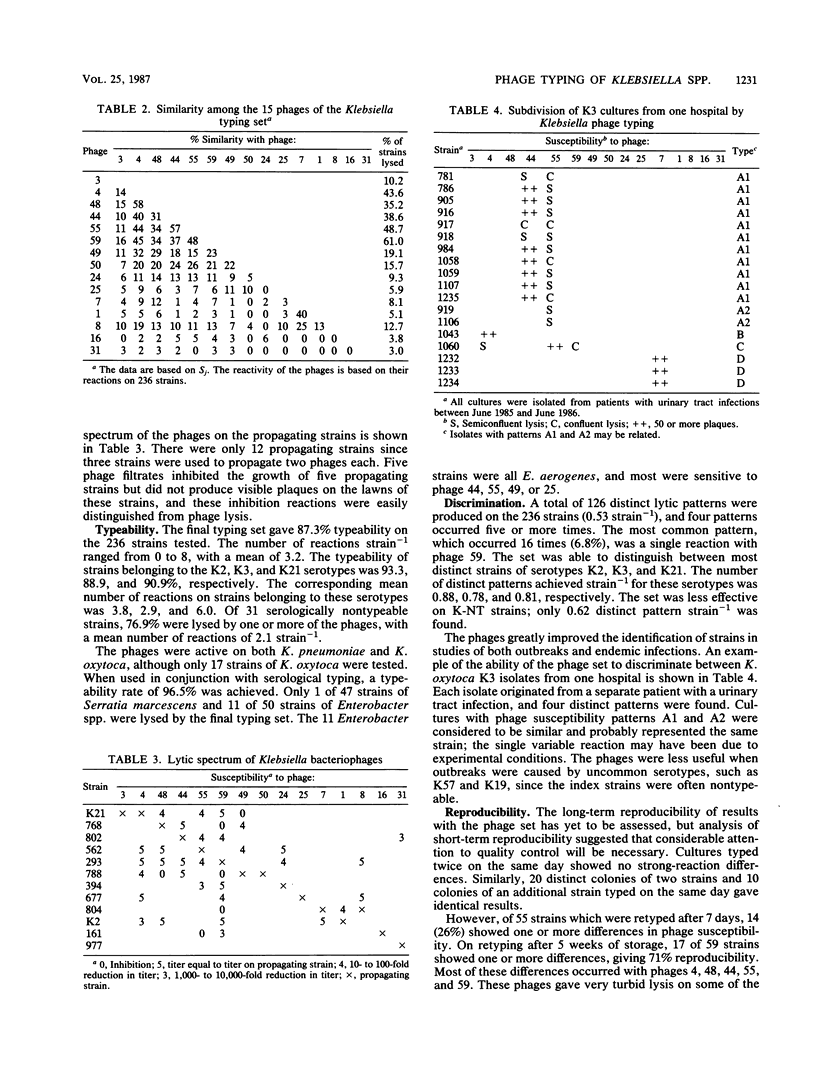
A bacteriophage typing scheme for hospital isolates of Klebsiella spp. was developed. The scheme was designed specifically as a secondary typing method to discriminate between strains of serotypes K2, K3, and K21 but proved to be an efficient general typing method for strains of most serotypes. The set of 15 phages gave 87.3% typeability on 236 strains of more than 70 different serotypes. Typeability within the K2, K3, and K21 strains was 93, 89, and 91%, respectively. There was a mean of 3.2 reactions strain-1 for all phage-typeable strains. Of the serologically nontypeable strains, 76.7% were susceptible to one or more phages. The most common pattern accounted for only 7% of the strains. The lytic patterns were reproducible if strains were typed on the same day, but differences were observed if strains were stored for 1 week or more before retyping. A total of 96.5% of the strains were typeable by a combination of capsular serology and phage typing.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C., Schneider R. Bacteriocins as tools in analysis of nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):15–19. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.15-19.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffenmyer C. L., Rycheck R. R., Yee R. B. Bacteriocin (klebocin) sensitivity typing of klebsiella. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):239–244. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.239-244.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casewell M. W., Phillips I. Aspects of the plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance and epidemiology of Klebsiella species. Am J Med. 1981 Feb;70(2):459–462. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90788-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curie K., Speller D. C., Simpson R. A., Stephens M., Cooke D. I. A hospital epidemic caused by gentamicin-resistant Klebsiella aerogenes. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Feb;80(1):115–123. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson A. S., Cooke E. M. The development and assessment of a bacteriocin typing method for Klebsiella. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Apr;82(2):207–223. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall F. A. Bacteriocine typing of Klebsiella spp. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Nov;24(8):712–716. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.8.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israil A. M. The significance of bacteriocin typing of Klebsiella strans. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981;250(1-2):63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDWELL O. M. Apparatus for phagetyping of Staphylococcus aureus. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1959 Mar;18:49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILCH H., DEAK S. STUDIES ON KLEBSIELLA INFECTIONS BY PHAGE DETECTION AND PHAGE TYPING. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1964;11:251–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfreyman J. M. Klebsiella serotyping by counter-current immunoelectrophoresis. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):219–225. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przondo-Hessek A., Slopek S. Typing of Klebsiella bacilli by means of Klebsiella bacteriophages from the collection of Przondo-Hessek. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1967;15(4):563–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Duncan I. B. Combined biochemical and serological typing of clinical isolates of Klebsiella. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):534–539. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.534-539.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Nord C. E., Sjoberg L., Duncan I. B. Comparison of bacteriophage typing, serotyping, and biotyping as aids in epidemiological surveillance of Klebsiella infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):638–642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.638-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser E., Noone P., Bonnet M. L. A new serotyping method for Klebsiella species: evaluation of the technique. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Apr;29(4):305–308. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.4.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Lee S., Wang W. L., Bennett J. V., Eickhoff T. C. Nosocomial klebsiella infections: intestinal colonization as a reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1971 May;74(5):657–664. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoons-Smit A. M., Verweij-Van Vught A. M., Kanis I. Y., MacLaren D. M. Biochemical and serological investigations on clinical isolates of klebsiella. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):265–276. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slopek S., Maresz-Babczyszyn J. A working scheme for typing Klebsiella bacilli by means of pneumocins. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1967;15(4):525–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slopek S., Przondo-Hessek A., Milch H., Deák S. A working scheme for bacteriophage typing of Klebsiella bacilli. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1967;15(4):589–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



