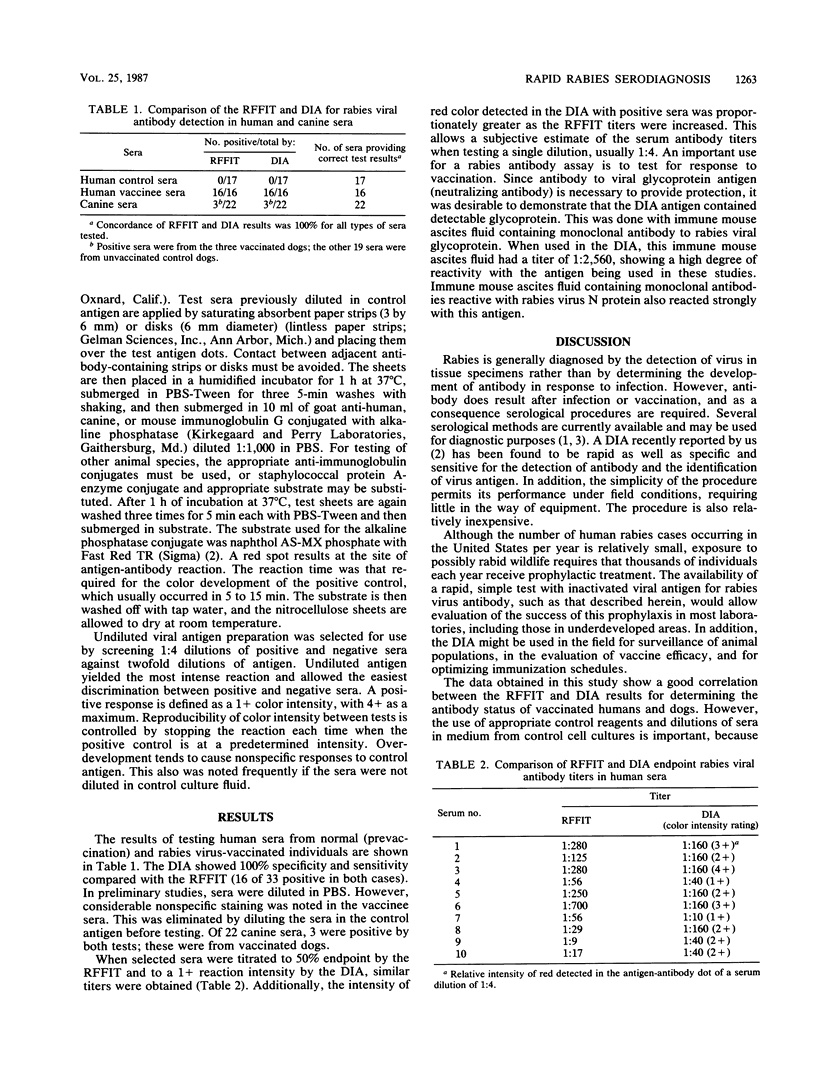
Abstract
A dot immunobinding assay that uses inactivated antigen for the detection of rabies viral antibodies was compared with the rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test. Results of testing pre- and postvaccination sera from humans (n = 33) and canines (n = 22) were identical for both tests. Endpoint titers of positive sera also were approximately the same by both methods. When a mouse monoclonal antibody was used, the dot immunobinding assay antigen was shown to possess detectable rabies virus glycoprotein and core antigens.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Heberling R. L., Kalter S. S. Rapid dot-immunobinding assay on nitrocellulose for viral antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):109–113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.109-113.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Yager P. A., Baer G. M. A rapid reproducible test for determining rabies neutralizing antibody. Bull World Health Organ. 1973 May;48(5):535–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



