Abstract
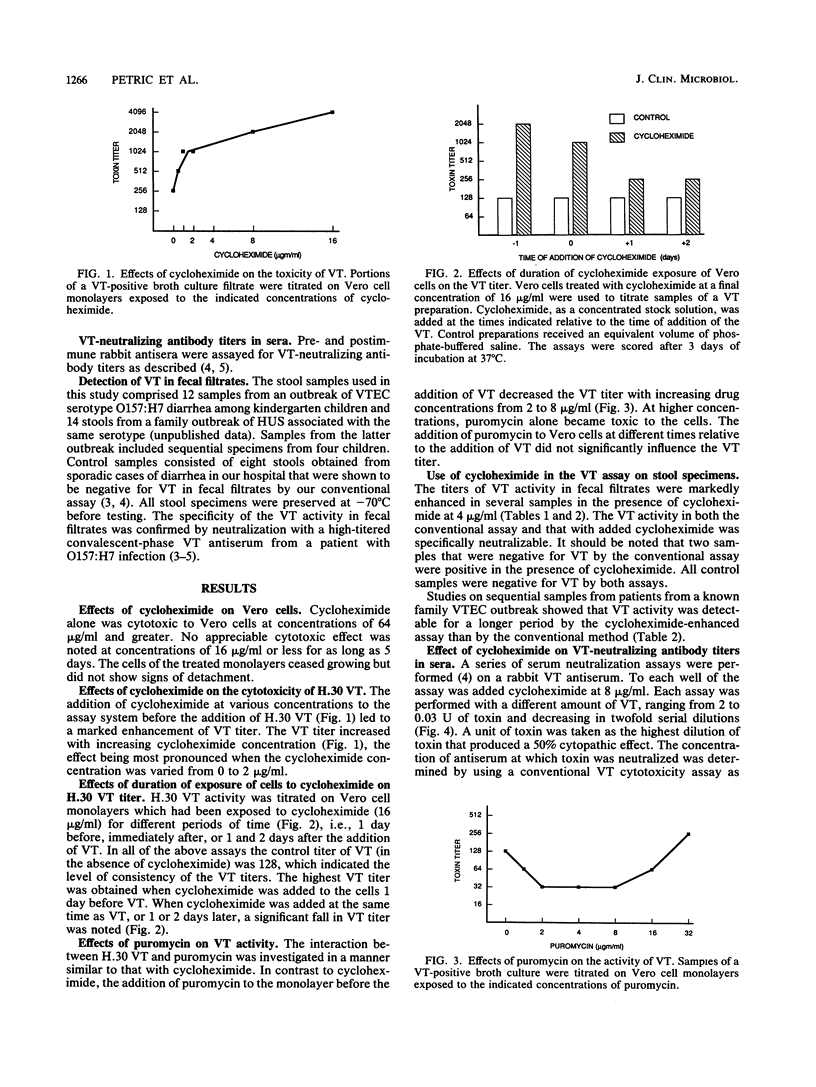
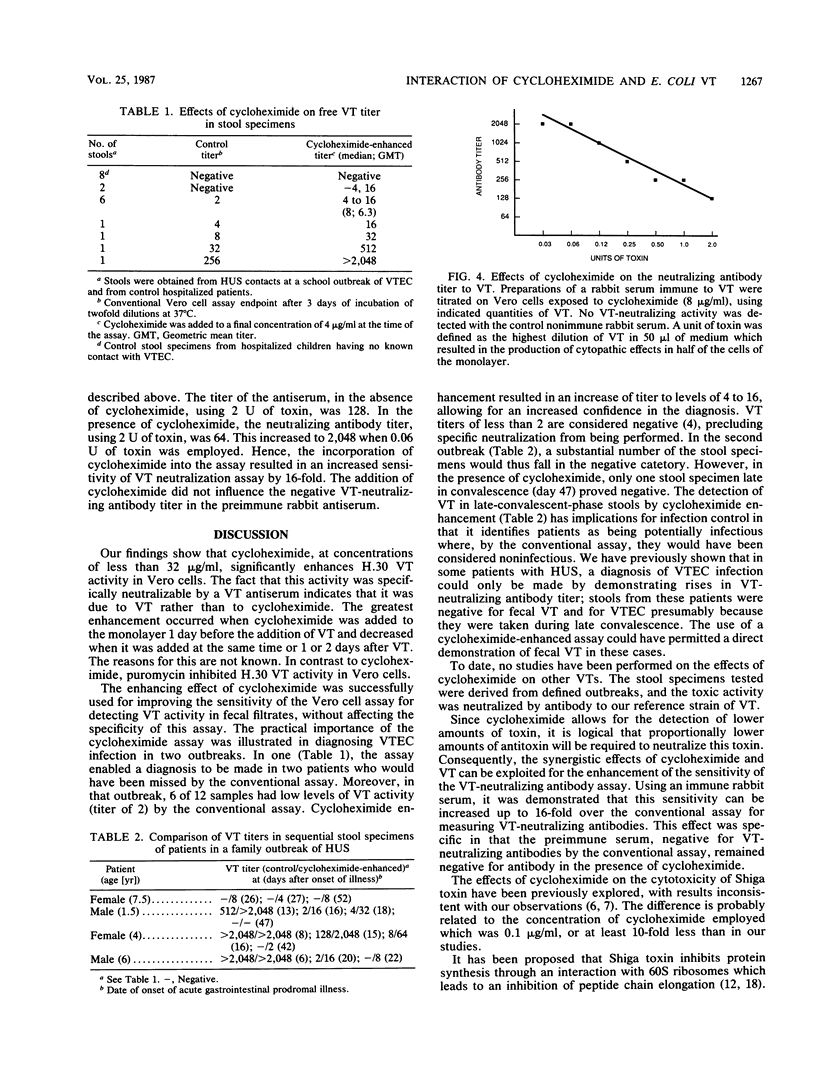
Verocytotoxin (VT)-producing Escherichia coli is closely associated with hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. The diagnosis of this infection requires the demonstration of VT activity in fecal filtrates or the isolation of VT-producing E. coli from stools. To improve the sensitivity of the Vero cell assay for detecting VT, we investigated the interaction between this toxin and cycloheximide and puromycin, agents which, like VT and the related Shiga toxin, are protein synthesis inhibitors. Cycloheximide-treated cells were found to be about eightfold more sensitive to VT, this effect being most pronounced when the drug was added before the toxin. In contrast, puromycin treatment had an antagonistic effect in that it decreased the sensitivity of the cells to VT. In assays of VT in fecal filtrates, the addition of cycloheximide (at 4 to 8 micrograms/ml) increased the sensitivity without affecting the specificity of the assays. Likewise, the use of cycloheximide led to an increase in the sensitivity of the serum VT-neutralizing antibody test by a factor of over eightfold.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. E., Rothman S. W., Doctor B. P. Inhibition of protein synthesis in intact HeLa cells by Shigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):98–107. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.98-107.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Cheung R., Arbus G. S. Sensitive method for detecting low numbers of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in mixed cultures by use of colony sweeps and polymyxin extraction of verotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):614–619. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.614-619.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Louie S., Cheung R. Antigenic heterogeneity of Escherichia coli verotoxins. Lancet. 1986 Jan 18;1(8473):164–165. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M. Shigella toxin(s): description and role in diarrhea and dysentery. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):403–438. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. 3. Effects of shigella enterotoxin in cell culture. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Jan;35(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1973.tb01503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D. Purification and characterization of a Shigella dysenteriae 1-like toxin produced by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):675–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.675-683.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Culp W. J., McKeehan W. L., Hardesty B. The mechanism by which cycloheximide and related glutarimide antibiotics inhibit peptide synthesis on reticulocyte ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):174–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Moran T. P., Colinas R. J. Ribonuclease activity associated with the 60S ribosome-inactivating proteins ricin A, phytolaccin and Shiga toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90498-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Reisbig R., Eiklid K. Subunit structure of Shigella cytotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8732–8738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Peptidyl-puromycin synthesis on polyribosomes from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):624–628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisbig R., Olsnes S., Eiklid K. The cytotoxic activity of Shigella toxin. Evidence for catalytic inactivation of the 60 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8739–8744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Steinberg M. S., Gemski P., Formal S. B., Doctor B. P. Inhibition of in vitro protein synthesis by Shigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90899-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


