Abstract
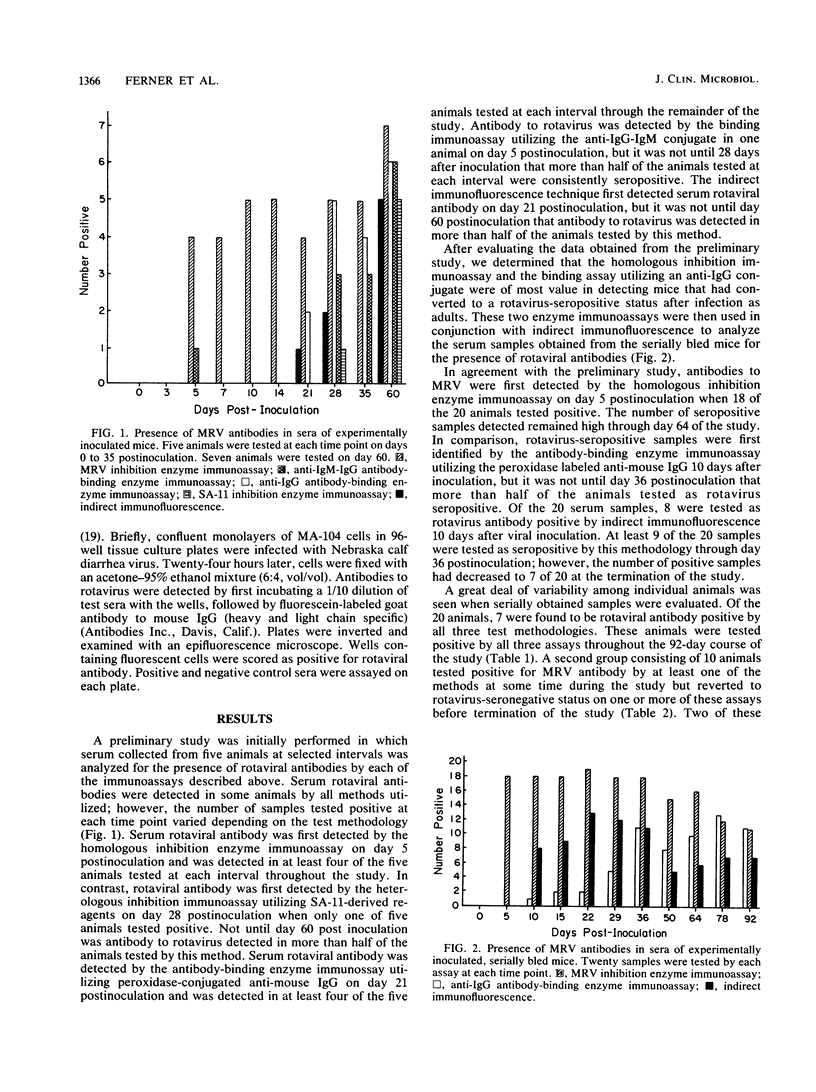
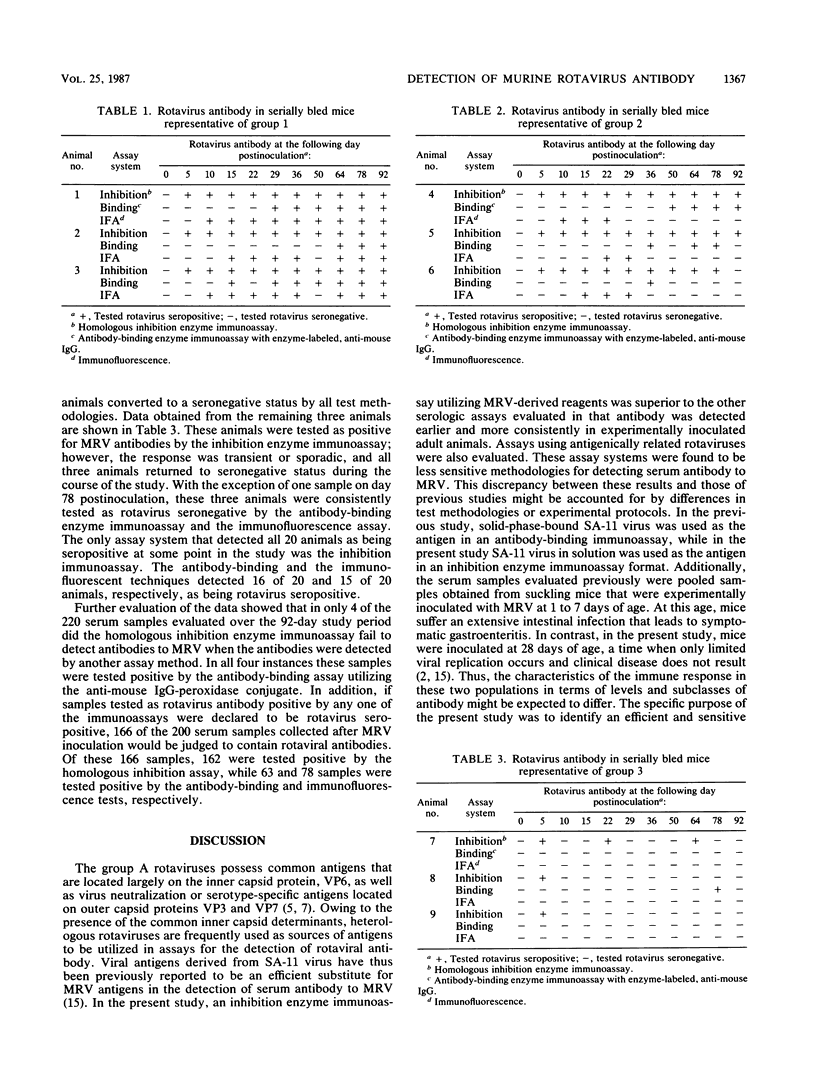
Mice are frequently used as animal models for the study of rotaviral infections. Since natural infection is common in laboratory mice, it is important that rotaviral studies, as well as other studies utilizing suckling mice, employ animals of known immune status to murine rotavirus. A variety of homologous and heterologous enzyme immunoassay systems and an immunofluorescence technique were thus compared to determine the immunoassay that is most effective at detecting adult mice seropositive for rotaviral antibody. It was determined that a homologous enzyme immunoassay inhibition technique utilizing murine rotavirus-derived reagents was the most efficient serologic assay evaluated. A serologic response was consistently detected by this assay by 5 days after experimental rotaviral inoculation of adult mice. A homologous antibody-binding enzyme immunoassay, a heterologous inhibition enzyme immunoassay utilizing antigenically related simian rotavirus (SA-11) reagents, and an immunofluorescence technique utilizing Nebraska calf diarrhea virus antigens were found to be less sensitive for detecting serum antibody to murine rotavirus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eydelloth R. S., Vonderfecht S. L., Sheridan J. F., Enders L. D., Yolken R. H. Kinetics of viral replication and local and systemic immune responses in experimental rotavirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):947–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.947-950.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombold J. L., Ramig R. F. Analysis of reassortment of genome segments in mice mixedly infected with rotaviruses SA11 and RRV. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.110-116.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Vo P. T., Jones R. Cultivation and characterization of three strains of murine rotavirus. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):585–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.585-590.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little L. M., Shadduck J. A. Pathogenesis of rotavirus infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):755–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.755-763.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S. Rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. L., Sidwell R. W., Mahoney A. W., Barnett B. B., Spendlove R. S. Influence of malnutrition and alterations in dietary protein on murine rotaviral disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Jul;173(3):417–426. doi: 10.3181/00379727-173-41665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F., Plotkin S. A. Response of mice to rotaviruses of bovine or primate origin assessed by radioimmunoassay, radioimmunoprecipitation, and plaque reduction neutralization. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):293–300. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.293-300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Shaw R. D., Greenberg H. B. Passive protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea by monoclonal antibodies to surface proteins vp3 and vp7. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.700-703.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Lee P. C., Carmody P. J., Barrett H. J., Ogra P. L. Age-dependent rotavirus-enterocyte interactions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jun;170(2):146–154. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Offor E., Klossner K., Kowalski E., Carmody P. J., Ogra P. L. Effect of age and malnutrition on rotavirus infection in mice. Pediatr Res. 1985 Dec;19(12):1250–1253. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198512000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. F., Eydelloth R. S., Vonderfecht S. L., Aurelian L. Virus-specific immunity in neonatal and adult mouse rotavirus infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):917–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.917-927.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Knudson D. L., Sheridan J. F., Paturzo F. X. Detection of antibody to epizootic diarrhea of infant mice (EDIM) virus. Lab Anim Sci. 1983 Oct;33(5):442–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Taniguchi K. Sequential passages of human rotavirus in MA-104 cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(10):1025–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderfecht S. L., Osburn B. I. Detection of anti-rotavirus antibody-producing cells in paraffin-embedded tissue sections. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Feb;43(2):356–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Dambrauskas R., Trier J. S. Susceptibility of mice to rotavirus infection: effects of age and administration of corticosteroids. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):565–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.565-574.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Barbour B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identification of rotaviruses from different animal species. Science. 1978 Jul 21;201(4352):259–262. doi: 10.1126/science.208150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Barbour B. A., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Measurement of rotavirus antibody by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay blocking assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):283–287. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.283-287.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Zissis G., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Kim H. W., Parrott R. H., Urrutia J. J., Mata L., Greenberg H. B. Epidemiology of human rotavirus Types 1 and 2 as studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 23;299(21):1156–1161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811232992103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


