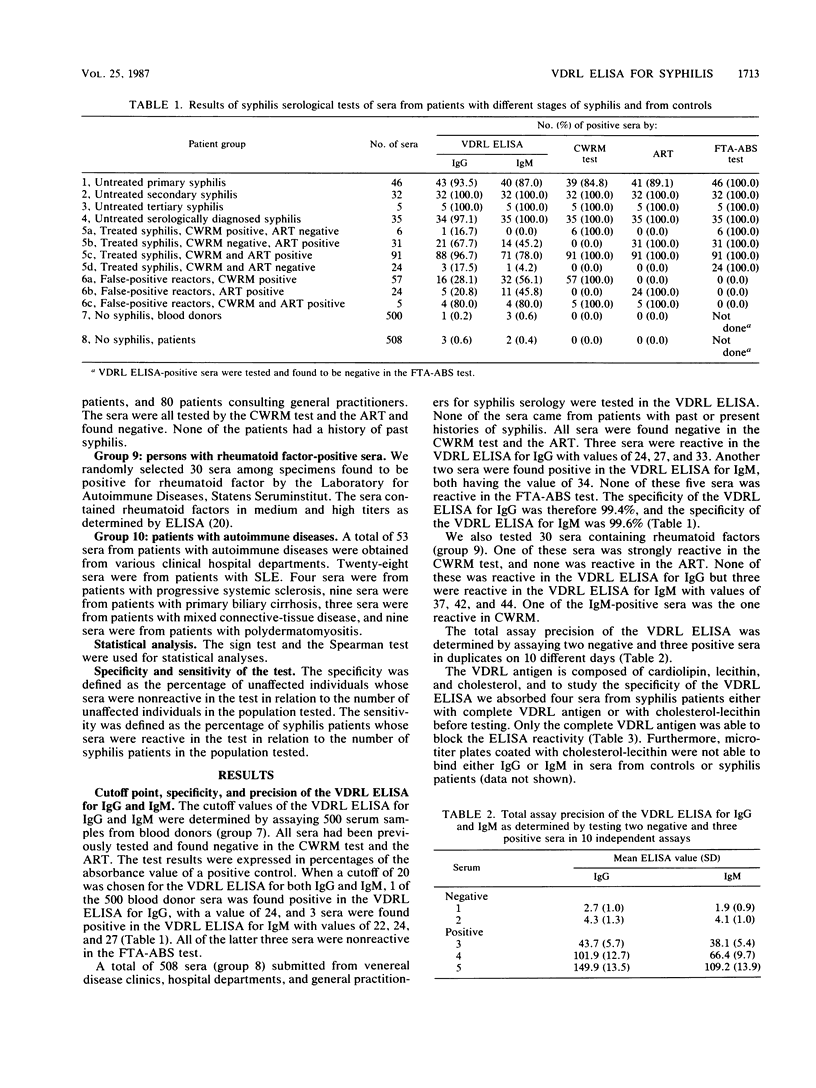
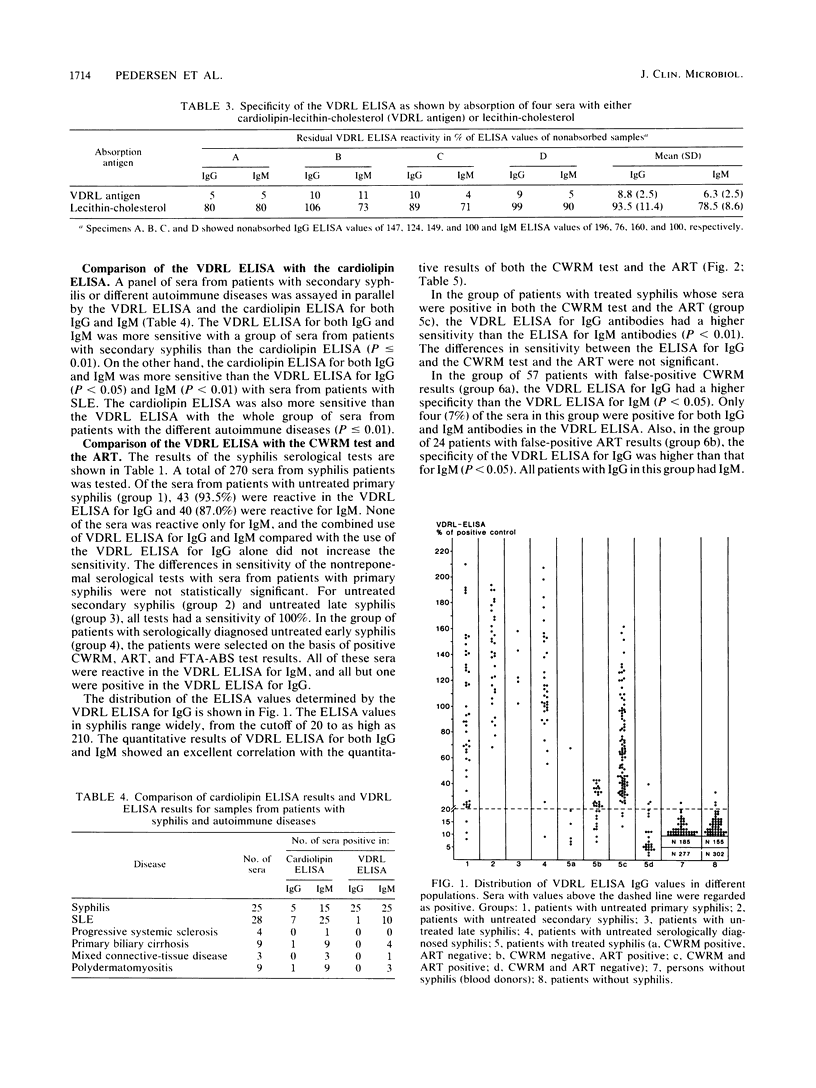
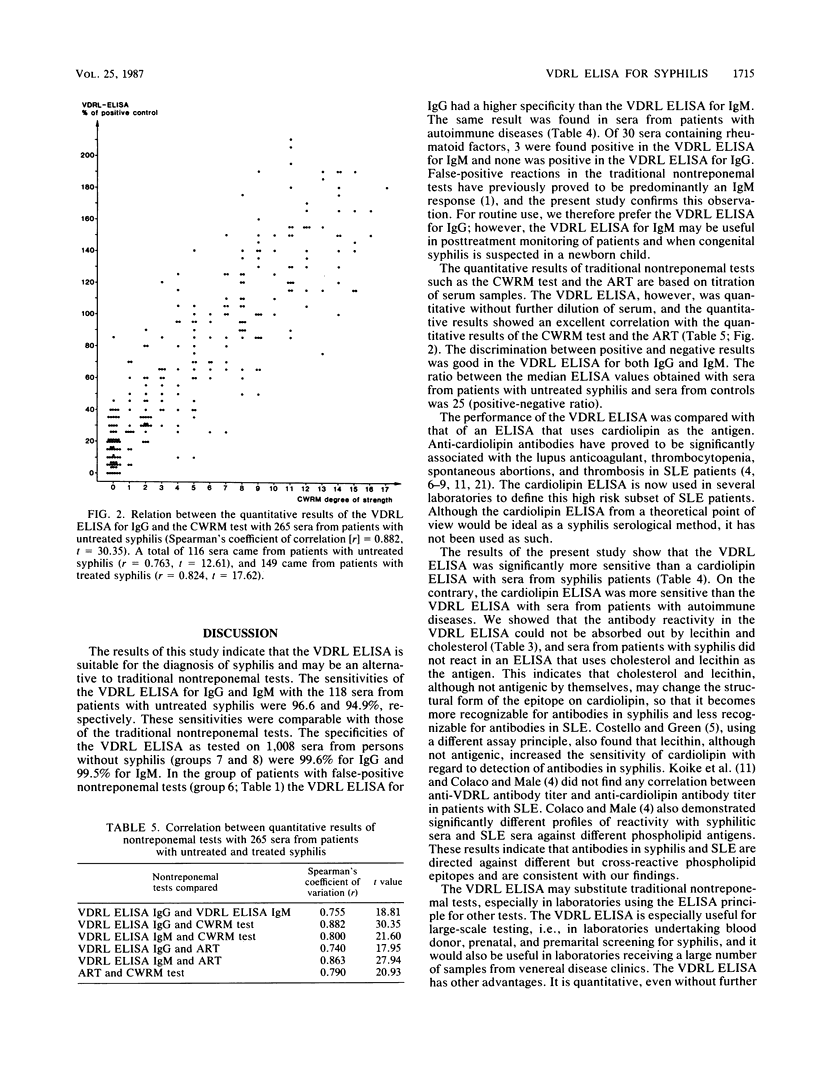
Abstract
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM to cardiolipin, lecithin, and cholesterol (VDRL [Venereal Disease Research Laboratory] ELISA) is described. The specificity of the VDRL ELISA for IgG and IgM was 99.6 and 99.5%, respectively, with sera from 1,008 persons without syphilis. For a group of patients with false-positive results in traditional nontreponemal tests and for patients with autoimmune diseases, the VDRL ELISA for IgG had a higher specificity than the VDRL ELISA for IgM. The sensitivity for IgG and IgM with 118 sera from patients with untreated syphilis was 96.6 and 94.9%, respectively, which was equivalent to the sensitivities of the traditional nontreponemal tests. The performance of the VDRL ELISA was compared with that of an ELISA that uses cardiolipin as the antigen (cardiolipin ELISA). The VDRL ELISA was significantly more sensitive (P less than or equal to 0.01) than the cardiolipin ELISA with 25 sera from syphilis patients but was less sensitive (P less than or equal to 0.01) with 53 sera from patients with autoimmune diseases. The antibody reactivity in the VDRL ELISA could not be absorbed out by lecithin and cholesterol, and the sera from patients with syphilis did not react in an ELISA that uses cholesterol and lecithin as the antigen. This indicates that cholesterol and lecithin, although not antigenic by themselves, may change the structural form of the epitope on cardiolipin so that it becomes more recognizable for antibodies in syphilis and less recognizable for antibodies in autoimmune diseases. The results of the VDRL ELISA were expressed in percentages of the absorbance value of a positive control. The VDRL ELISA gave, without titration of sera, quantitative results that correlated with the quantitative results of the traditional nontreponemal tests obtained by titration. The VDRL ELISA will be well suited for large-scale testing for syphilis and may replace other nontreponemal tests.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K. Studies of syphilitic antibodies. II. Substances responsible for biological false positive sero-reactions. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Mar;44(1):49–54. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. T., Zaidi A., Larsen S. A., Reynolds G. H. Serological response to syphilis treatment. A new analysis of old data. JAMA. 1985 Mar 1;253(9):1296–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaço C. B., Male D. K. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in syphilis and a thrombotic subset of SLE: distinct profiles of epitope specificity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):449–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello P. B., Green F. A. Reactivity patterns of human anticardiolipin and other antiphospholipid antibodies in syphilitic sera. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):771–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englert H. J., Hawkes C. H., Boey M. L., Derue G. J., Loizou S., Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hull R. G., Hughes G. R. Degos' disease: association with anticardiolipin antibodies and the lupus anticoagulant. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Sep 8;289(6445):576–576. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6445.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Asherson R. A., Boey M. L., Hughes G. R. Cerebral infarction in systemic lupus: association with anticardiolipin antibodies. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1984 Jan-Mar;2(1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hegde U., Derue G., Morgan S. H., Englert H., Chan J. K., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies in autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1985 Feb;59(2):231–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. Syphilis tests in diagnostic and therapeutic decision making. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Mar;104(3):368–376. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-3-368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Sueishi M., Funaki H., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Anti-phospholipid antibodies and biological false positive serological test for syphilis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. R. A simple chromatographic method for purification of egg lecithin. Lipids. 1980 Jun;15(6):481–484. doi: 10.1007/BF02534078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. S. Biological false positive reactions in treponemal serological tests used to diagnose syphilis. Genitourin Med. 1986 Oct;62(5):356–356. doi: 10.1136/sti.62.5.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. S., Jørgensen B. B., Pedersen N. S. Treatment of early infectious syphilis in Denmark. A retrospective serological study. Dan Med Bull. 1984 Feb;31(1):70–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathlev T. Haemagglutination test utilizing pathogenic Treponema pallidum for the sero-diagnosis of syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1967 Sep;43(3):181–185. doi: 10.1136/sti.43.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT H. Cardiolipin antigen. I. A qualitative examination of sensitivity and specificity. Br J Vener Dis. 1951 Mar;27(1):23–33. doi: 10.1136/sti.27.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPANGLER A. S., JACKSON J. H., FIUMARA N. J., WARTHIN T. A. SYPHILIS WITH A NEGATIVE BLOOD TEST REACTION. JAMA. 1964 Jul 13;189:87–90. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070020015003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejtorp M., Høier-Madsen M., Halberg P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determination of IgM rheumatoid factor. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979;8(2):65–70. doi: 10.3109/03009747909105338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr Cerebral infarction in systemic lupus: association with anticardiolipin antibodies. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1984 Jan-Mar;2(1):3–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


