Abstract
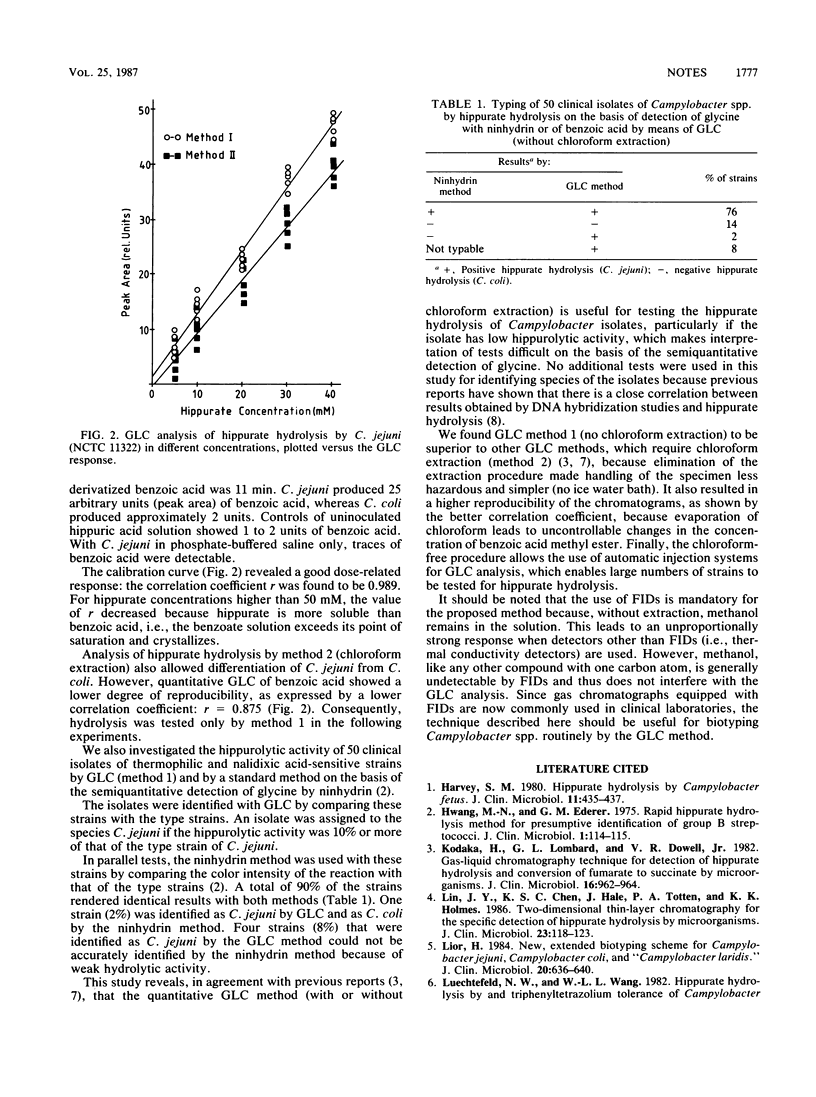
A gas-liquid chromatographic method which requires no chloroform extraction of the split products has been investigated for the detection of hippurate hydrolysis by Campylobacter spp. This technique gave better reproducibility than other tests also used in this study and allows the routine use of the gas-liquid chromatographic method for identification of Campylobacter isolates.
Full text
PDF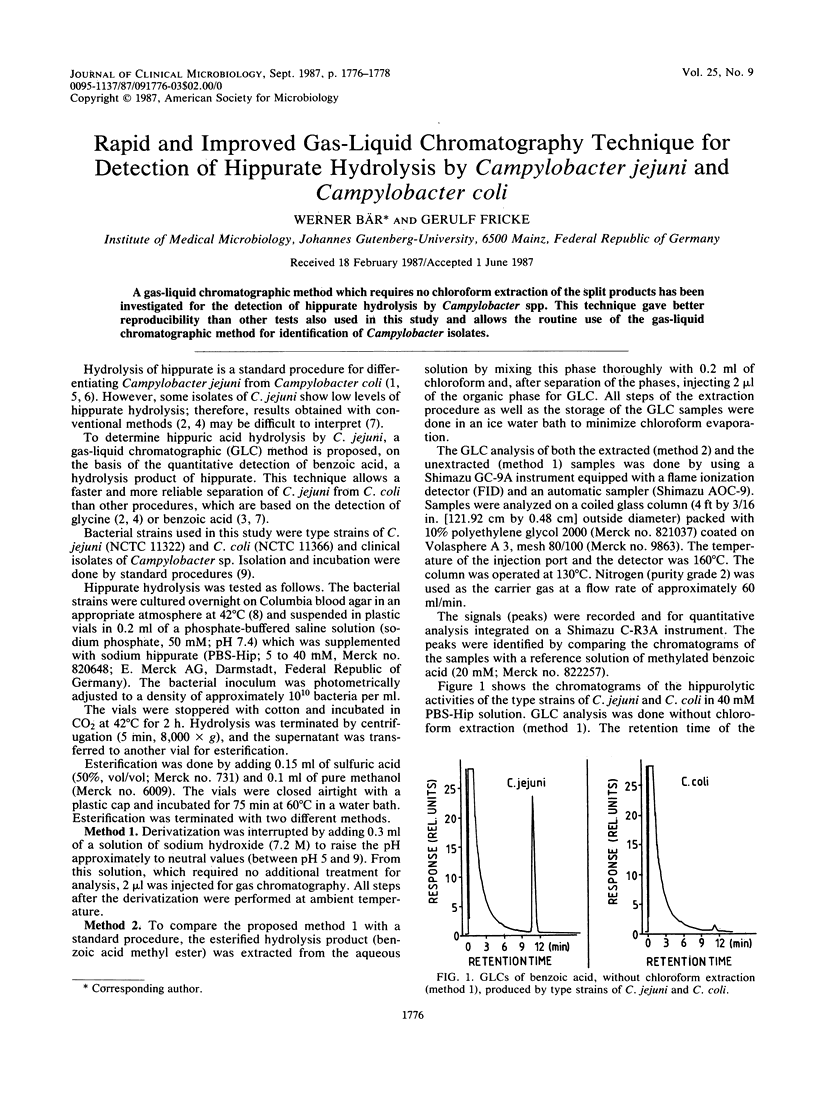

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Harvey S. M. Hippurate hydrolysis by Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.435-437.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaka H., Lombard G. L., Dowell V. R., Jr Gas-liquid chromatography technique for detection of hippurate hydrolysis and conversion of fumarate to succinate by microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):962–964. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.962-964.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Chen K. C., Hale J., Totten P. A., Holmes K. K. Two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography for the specific detection of hippurate hydrolysis by microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):118–123. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.118-123.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., el Sherbeeny M. R., Patton C. M., Kodaka H., Lombard G. L., Edmonds P., Hollis D. G., Brenner D. J. Comparison of four hippurate hydrolysis methods for identification of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):714–718. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.714-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Smibert R. M., Johnson J. L., Krieg N. R. Differential characteristics of catalase-positive campylobacters correlated with DNA homology groups. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jul;30(7):938–951. doi: 10.1139/m84-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


