Abstract
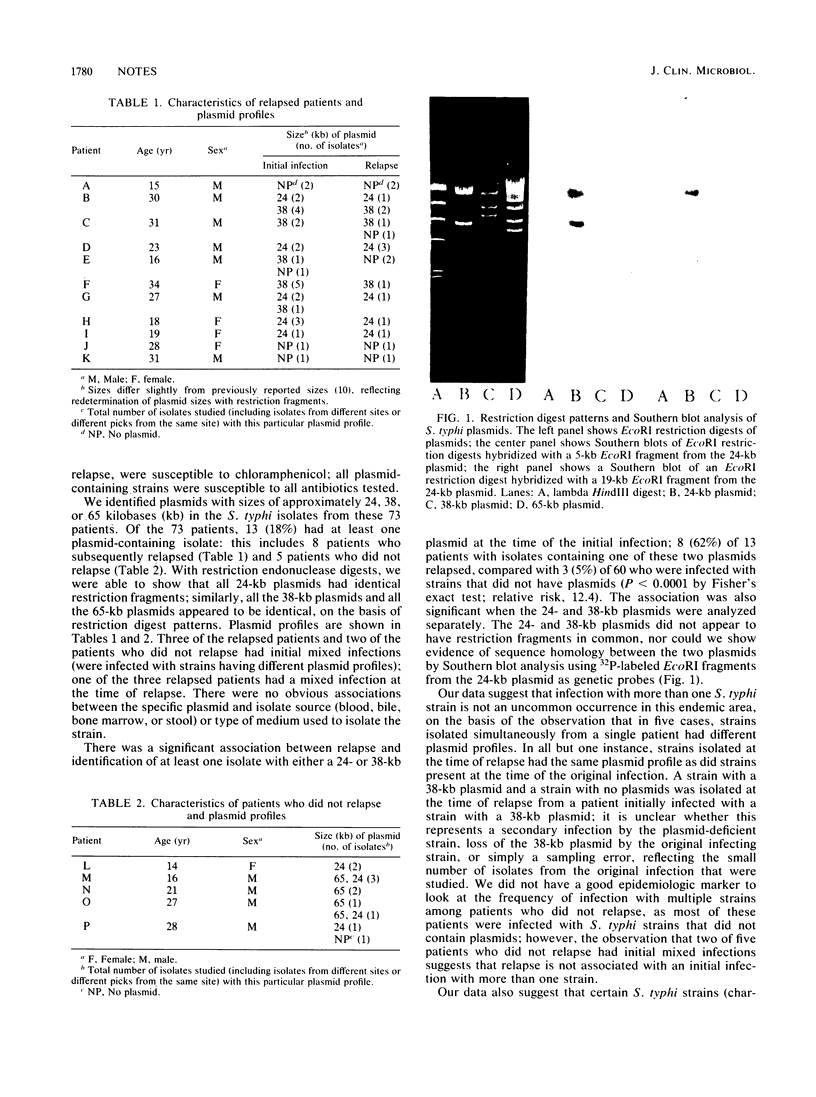
We studied isolates from 73 patients hospitalized with typhoid fever in Lima, Peru. Of these 73 patients, 11 (15%) suffered a clinical relapse, with fever and positive blood cultures, within 3 months of their original illness. Using plasmids as epidemiologic markers, we found that three patients who subsequently relapsed were initially infected with more than one strain of Salmonella typhi. There was a highly significant association between relapse and isolation of a strain containing either a 24- or a 38-kilobase plasmid at the time of the original infection; however, we were unable to show any evidence of homology between these two plasmids. Our data indicate that infection with multiple strains is not uncommon in this endemic area and suggest that relapse may be partly strain dependent.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benavente L., Gotuzzo E., Guerra J., Grados O., Guerra H., Bravo N. Diagnosis of typhoid fever using a string capsule device. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(3):404–406. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerra-Caceres J. G., Gotuzzo-Herencia E., Crosby-Dagnino E., Miro-Quesada M., Carrillo-Parodi C. Diagnostic value of bone marrow culture in typhoid fever. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(6):680–683. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman T. A., Ruiz C. J., Counts G. W., Sachs J. M., Nitzkin J. L. Waterborne typhoid fever in Dade County, Florida. Clinical and therapeutic evaluation of 105 bacteremic patients. Am J Med. 1975 Oct;59(4):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. 2. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):739–746. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 24;283(13):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009242831306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher K. O., Morris J. G., Jr, Gotuzzo E., Ferreccio C., Ward L. R., Benavente L., Black R. E., Rowe B., Levine M. M. Molecular techniques in the study of Salmonella typhi in epidemiologic studies in endemic areas: comparison with Vi phage typing. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jul;35(4):831–835. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Levine M. M., Cordano A. M., D'Ottone K., Jayanetra P., Kopecko D., Pan-Urae R., Prenzel I. Survey of plasmids in Salmonella typhi from Chile and Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):551–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popkiss M. E. Typhoid fever: A report on a point-source outbreak of 69 cases in Cape Town. S Afr Med J. 1980 Mar 1;57(9):325–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. J., Gonzalez O., Palomino C., Music S. I., Hornick R. B., Perroni J., Woodward W. E., Gonzalez C., DuPont H. L., Woodward T. E. Comparative efficacy of chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and co-trimoxazole in the treatment of typhoid fever. Lancet. 1976 Nov 27;2(7996):1155–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91678-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODWARD T. E., SMADEL J. E. MANAGEMENT OF TYPHOID FEVER AND ITS COMPLICATIONS. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Jan;60:144–157. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-1-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]