Abstract
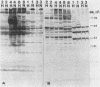
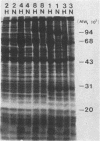
We investigated the antibody response in women with postpartum fever from whom Ureaplasma urealyticum had been isolated from the bloodstream. Acute- and convalescent-phase sera were tested for immunoglobulin G to the polypeptides of five serovars (1, 2, 3, 4, and 8), representing the two genomic clusters of U. urealyticum, by the immunoblotting (Western) method. Convalescent-phase sera from the five patients reacted more intensely and with more (up to 27) polypeptides from each of the five serovars, whereas acute-phase sera reacted weakly and with few polypeptides. Although antibody responses in these women with systemic infection could be detected by the use of any of the five different serovars as antigens, the patterns that were produced differed clearly between the two genetic clusters (serovars 1 and 3 versus serovars 2, 4, and 8). Apparently, a single serovar could be used to detect ureaplasmal antibodies in humans regardless of the serovar of the infecting strain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. B., Cassell G. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Shepard M. C. Measurement of antibody to Ureaplasma urealyticum by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and detection of antibody responses in patients with nongonococcal urethritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):288–295. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.288-295.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Cole B. C. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 8;304(2):80–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101083040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo D., Dupuis K. W., Schmidt N. J., Kenny G. E. Broadly reactive immunofluorescence test for measurement of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies to Ureaplasma urealyticum in infant and adult sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):614–618. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.614-618.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. A., Duffy L., Garrett B., Stephens J., Davis J. K., Cassell G. H. Can group- and serovar-specific proteins be detected in Ureaplasma urealyticum? Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;5(6 Suppl):S325–S331. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198611010-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Huang C. H., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Demonstration of antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae attachment protein in human sera and respiratory secretions. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.437-439.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Cartwright F. D. Effect of urea concentration on growth of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain mycoplasma). J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.144-150.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.510-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamey J. R., Eschenbach D. A., Mitchell S. H., Blumhagen J. M., Foy H. M., Kenny G. E. Isolation of mycoplasmas and bacteria from the blood of postpartum women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 May 1;143(1):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(82)90690-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Kass E. H. Serotypic heterogeneity in isolates of human genital T-mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):499–500. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.499-500.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouches C., Taylor-Robinson D., Stipkovits L., Bove J. M. Comparison of human and animal Ureaplasmas by one- and two-dimensional protein analysis on polyacrylamide slab gel. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Sep-Oct;132B(2):171–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Stemke G. W. Expanded serotyping scheme for Ureaplasma urealyticum strains isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):873–878. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.873-878.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Stemke G. W. Modified metabolic inhibition test for serotyping strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain Mycoplasma). J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):673–676. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.673-676.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., McCormack W. M. The genital mycoplasmas (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1063–1067. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu A. C., Foy H. M., Cartwright F. D., Kenny G. E. The principal protein antigens of isolates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae as measured by levels of immunoglobulin G in human serum are stable in strains collected over a 10-year period. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1830–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1830-1836.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]