Abstract
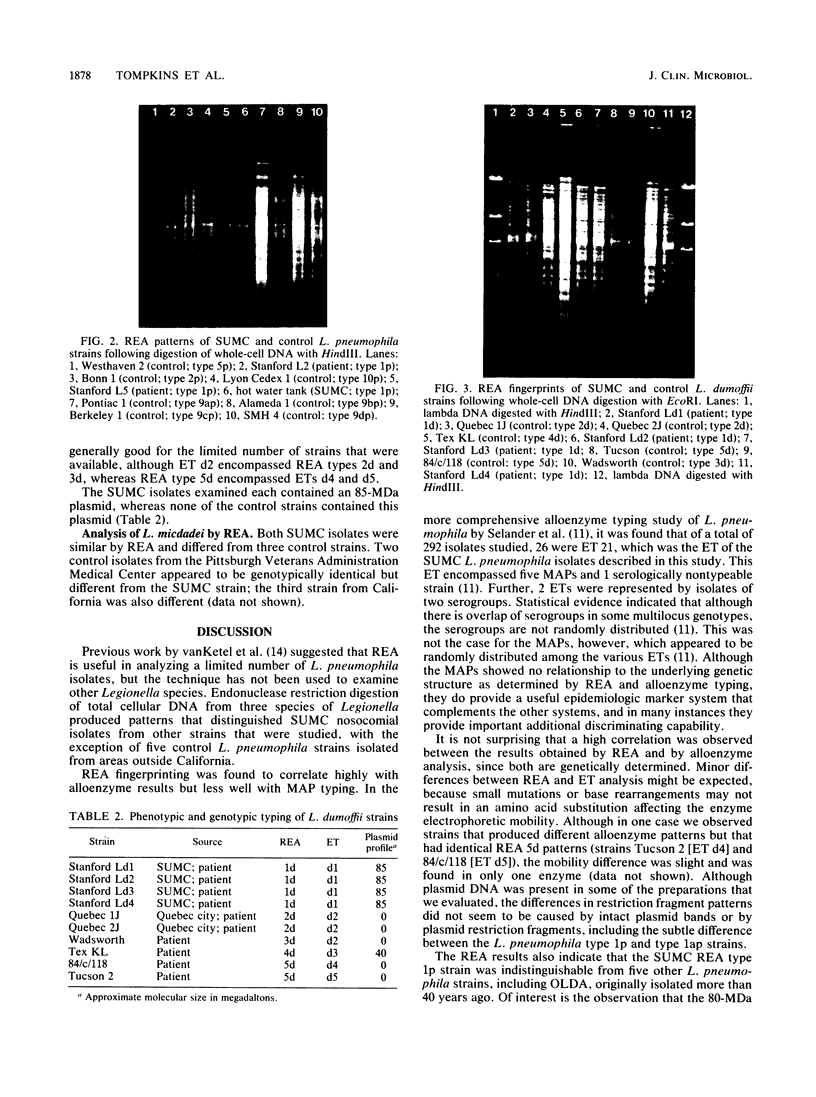
As part of an ongoing investigation into nosocomial Legionella infections at Stanford University Medical Center (SUMC), we applied the technique of restriction endonuclease analysis (REA) to determine strain differences among three species, including Legionella pneumophila, Legionella dumoffii, and Legionella micdadei. A total of 26 human and environmental water isolates from SUMC were selected for REA and compared with control strains that were not epidemiologically linked to SUMC. REA results were compared with results of alloenzyme typing, typing by monoclonal antibodies, and plasmid fingerprinting in all but L. micdadei strains. REA and alloenzyme typing showed that SUMC patient isolates were derived from distinct strains of three species. L. pneumophila strains from SUMC patients were genotypically identical to those isolated from potable water. REA was especially useful in proving that SUMC L. dumoffii patient isolates were derived from a single strain and that patients may have been exposed to a common source(s). REA typing correlated well with alloenzyme typing. These methods complement serologic typing of L. pneumophila and provide discriminating capability between strains of other Legionella species such as L. dumoffii, for which serologic types have not been identified. In addition, REA typing is somewhat easier to perform than alloenzyme typing and can be done in clinical laboratories.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradbury W. C., Pearson A. D., Marko M. A., Congi R. V., Penner J. L. Investigation of a Campylobacter jejuni outbreak by serotyping and chromosomal restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):342–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.342-346.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Vickers R. M., Elder E. M., Lema M., Garrity G. M. Plasmid and surface antigen markers of endemic and epidemic Legionella pneumophila strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):230–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.230-235.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Nakahama C., Tobin J. O., Calarco K., Beer K. B., Joly J. R., Selander R. K. Paleoepidemiologic investigation of Legionnaires disease at Wadsworth Veterans Administration Hospital by using three typing methods for comparison of legionellae from clinical and environmental sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1121–1126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1121-1126.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Bradford H. B., Roberts N. C., Falkow S. Molecular epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae in the U.S. Gulf Coast. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):129–134. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.129-134.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher W. E., Plouffe J. F., Para M. F. Plasmid profiles of clinical and environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1422–1423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1422-1423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F., Para M. F., Maher W. E., Hackman B., Webster L. Subtypes of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 associated with different attack rates. Lancet. 1983 Sep 17;2(8351):649–650. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92531-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel A. F., Chabbert Y. A. Taxonomy and epidemiology of gram-negative bacterial plasmids studied by DNA-DNA filter hybridization in formamide. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):269–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Moseley S. L., Kingscote B. New method for classification of leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroup pomona by restriction endonuclease analysis: serovar kennewicki. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.585-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N., Labigne-Roussel A., Cohen M. L. Cloned, random chromosomal sequences as probes to identify Salmonella species. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):156–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J., ter Schegget J., Zanen H. C. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):362–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.362-364.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]