Abstract
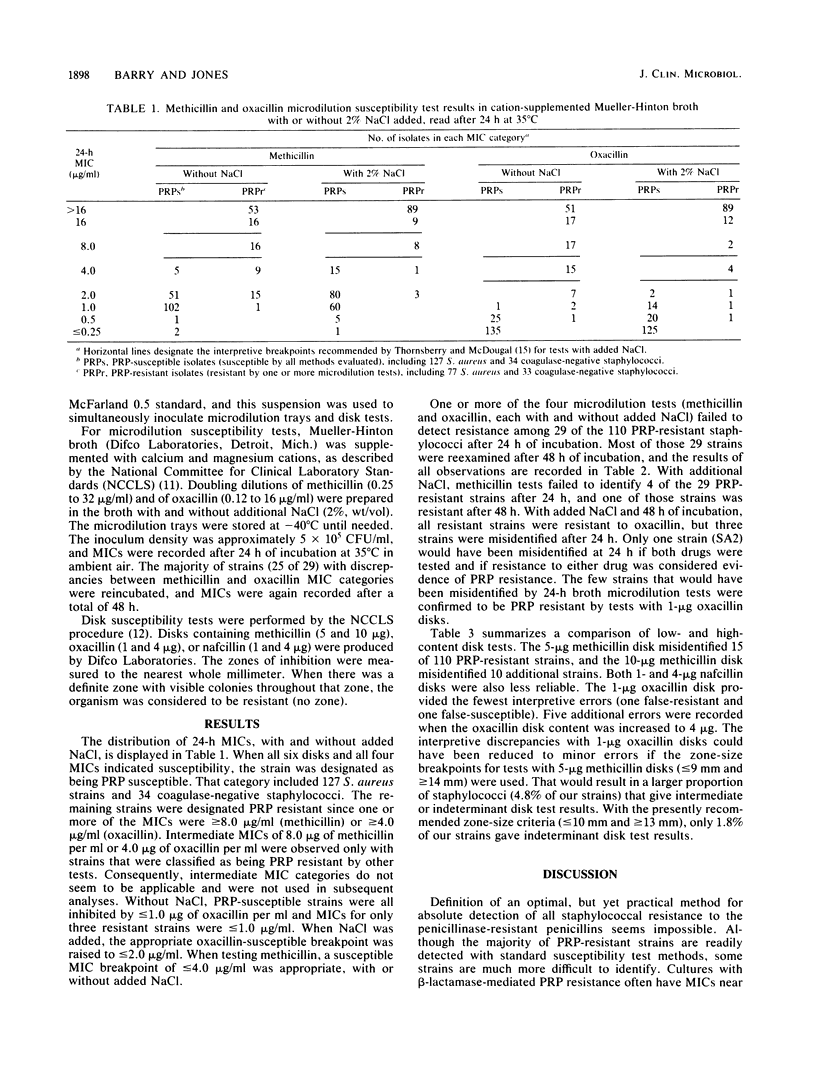
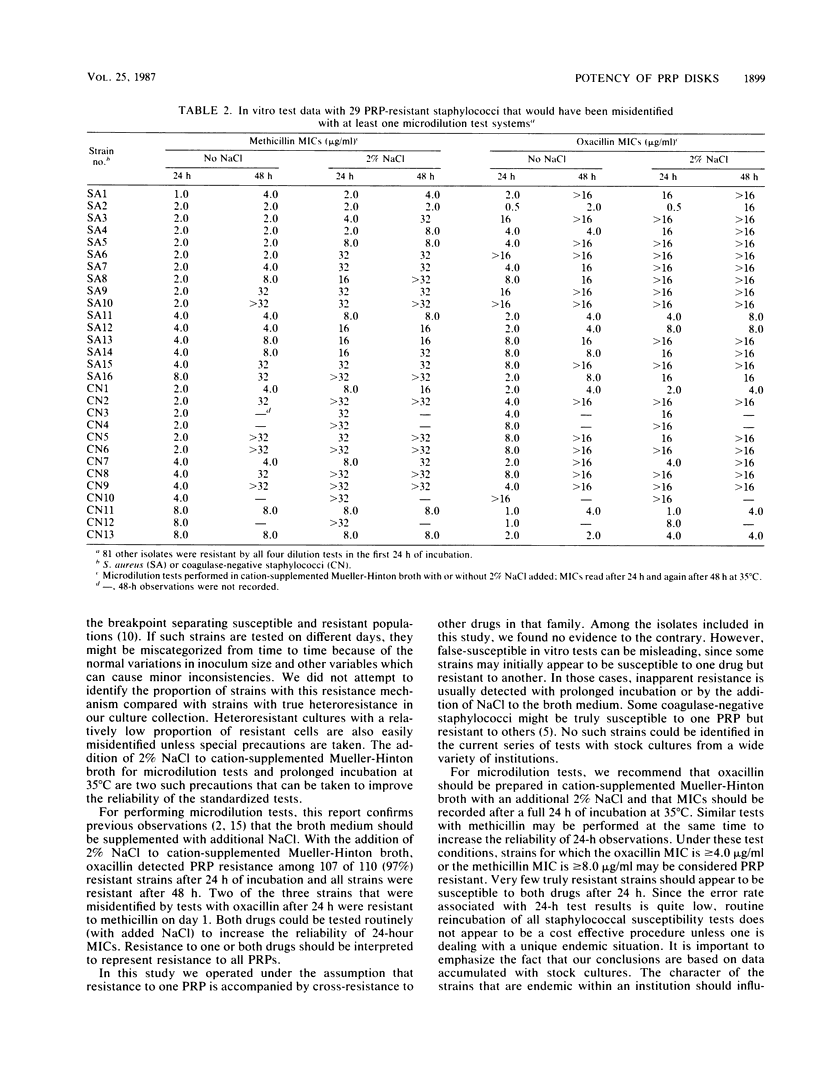
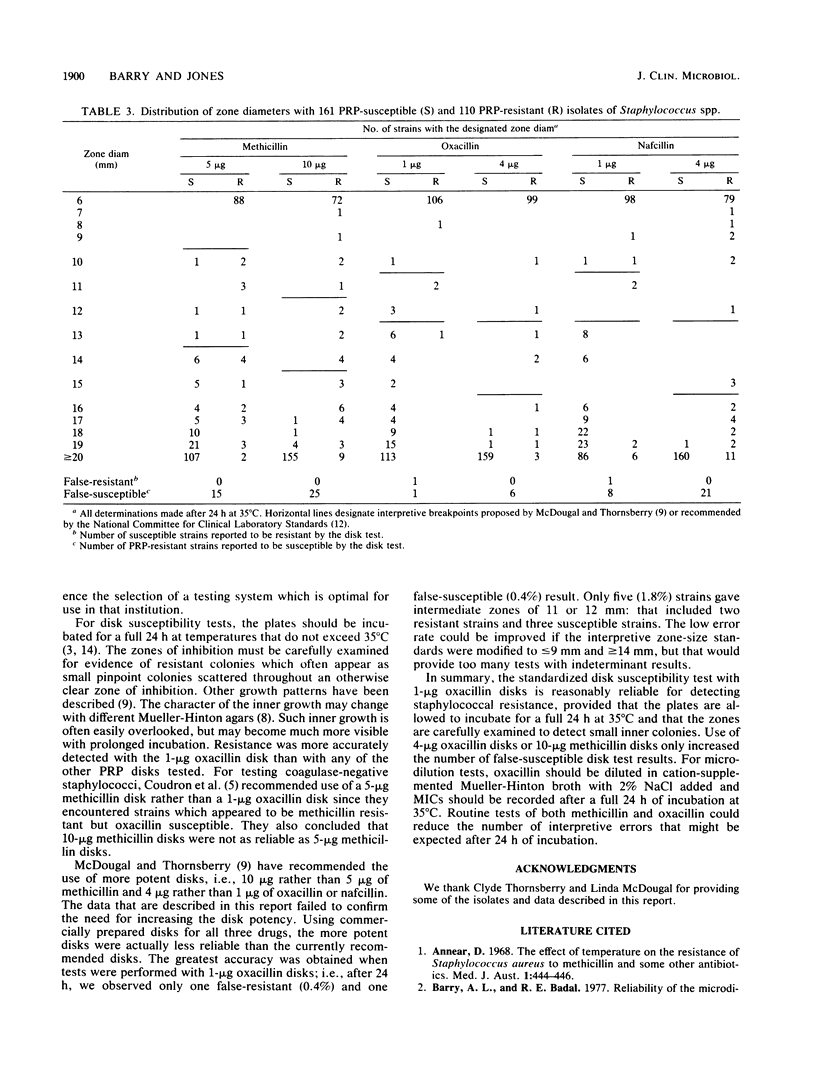
In vitro susceptibility tests were performed with 271 isolates of Staphylococcus species (204 Staphylococcus aureus), including 110 strains resistant to the penicillinase-resistant penicillins. Disks containing 5 or 10 micrograms of methicillin, 1 or 4 micrograms of oxacillin, and 1 or 4 micrograms of nafcillin were evaluated. After a full 24 h of incubation at 35 degrees C, tests with 1-microgram oxacillin disks provided optimal results. Use of the more potent oxacillin, nafcillin, or methicillin disks only increased the number of false-susceptible test results. For broth microdilution tests, 2% NaCl should be added to cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth, and MICs should be recorded after a full 24 h at 35 degrees C. Microdilution tests with oxacillin in broth with 2% NaCl were more reliable than similar tests with methicillin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annear D. I. The effect of temperature on resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and some other antibioics. Med J Aust. 1968 Mar 16;1(11):444–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M. Reevaluation of the ability of the standardized disk diffusion test to detect methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):813–817. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.813-817.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coudron P. E., Jones D. L., Dalton H. P., Archer G. L. Evaluation of laboratory tests for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):764–769. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.764-769.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Barry A. L., O'Toole R., Sherris J. C. Reliability of the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method for detecting methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Aug;24(2):240–247. doi: 10.1128/am.24.2.240-247.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J. H., Coe A. W., Parker M. T. The detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):443–456. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindler J. A., Inderlied C. B. Effect of the source of Mueller-Hinton agar and resistance frequency on the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):205–210. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.205-210.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Thornsberry C. New recommendations for disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.482-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Thornsberry C. The role of beta-lactamase in staphylococcal resistance to penicillinase-resistant penicillins and cephalosporins. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):832–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.832-839.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman S. J. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci: genetics of the minority population. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Feb;42(2):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Caruthers J. Q., Baker C. N. Effect of temperature on the in vitro susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to penicillinase-resistant penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):263–269. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., McDougal L. K. Successful use of broth microdilution in susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1084–1091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1084-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


