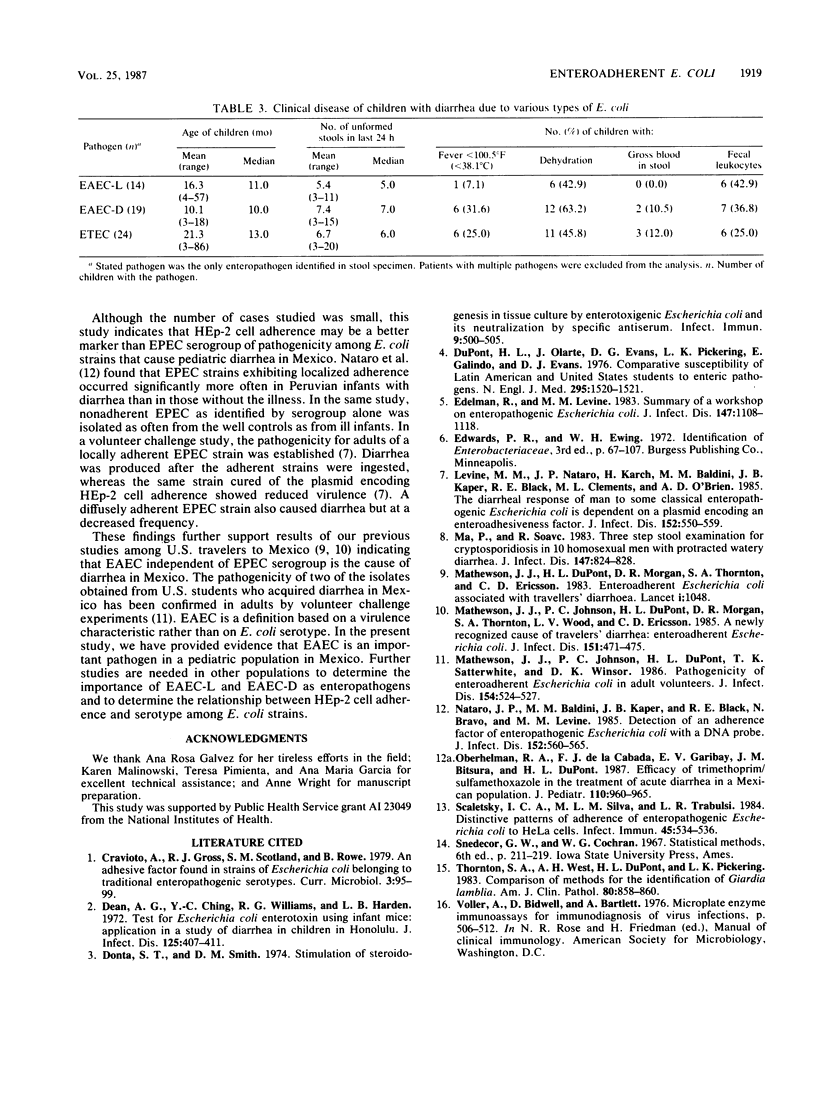
Abstract
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) often exhibits localized adherence or diffuse adherence to HEp-2 cells. We recently provided evidence that HEp-2 cell-adherent or enteroadherent E. coli (EAEC) not belonging to EPEC serogroups was the cause of diarrhea among U.S. travelers to Mexico. In the present study, we looked for EAEC and EPEC in stool specimens from 154 children with acute diarrhea and 137 well children seen at several outpatient clinics in Guadalajara, Mexico. EAEC showing localized adherence (EAEC-L) was isolated from 13.0% of the patients and 0.7% of the controls (P less than 0.0001). EAEC showing diffuse adherence (EAEC-D) was recovered from 20.8% of the patients and 7.3% of the controls (P less than 0.001). EPEC was isolated from 4.5 and 6.7% of the patients and controls, respectively. Among all enteropathogens, only enterotoxigenic E. coli occurred as commonly (21.4%) as EAEC-D and EAEC-L did in children with diarrhea. Of the EAEC-L strains isolated from children with diarrhea, 20% belonged to recognized EPEC serogroups, and 3.1% of EAEC-D strains belonged to recognized EPEC serogroups. This study suggests that EAEC may be an important pediatric enteropathogen in Mexican children with diarrhea and further supports the observation that adherence to HEp-2 cells may be a marker of virulence independent of EPEC serogroup among E. coli strains.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Olarte J., Evans D. G., Pickering L. K., Galindo E., Evans D. J. Comparative susceptibility of latin american and united states students to enteric pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1520–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Levine M. M. From the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Summary of a workshop on enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1108–1118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P., Soave R. Three-step stool examination for cryptosporidiosis in 10 homosexual men with protracted watery diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):824–828. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L., Morgan D. R., Thornton S. A., Ericsson C. D. Enteroadherent Escherichia coli associated with travellers' diarrhoea. Lancet. 1983 May 7;1(8332):1048–1048. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92675-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson J. J., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Morgan D. R., Thornton S. A., Wood L. V., Ericsson C. D. A newly recognized cause of travelers' diarrhea: enteroadherent Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):471–475. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson J. J., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Satterwhite T. K., Winsor D. K. Pathogenicity of enteroadherent Escherichia coli in adult volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):524–527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Bravo N., Levine M. M. Detection of an adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):560–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhelman R. A., Javier de la Cabada F., Vasquez Garibay E., Bitsura J. A., DuPont H. L. Efficacy of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in treatment of acute diarrhea in a Mexican pediatric population. J Pediatr. 1987 Jun;110(6):960–965. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. A., West A. H., DuPont H. L., Pickering L. K. Comparison of methods for identification of Giardia lamblia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Dec;80(6):858–860. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.6.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



