Abstract
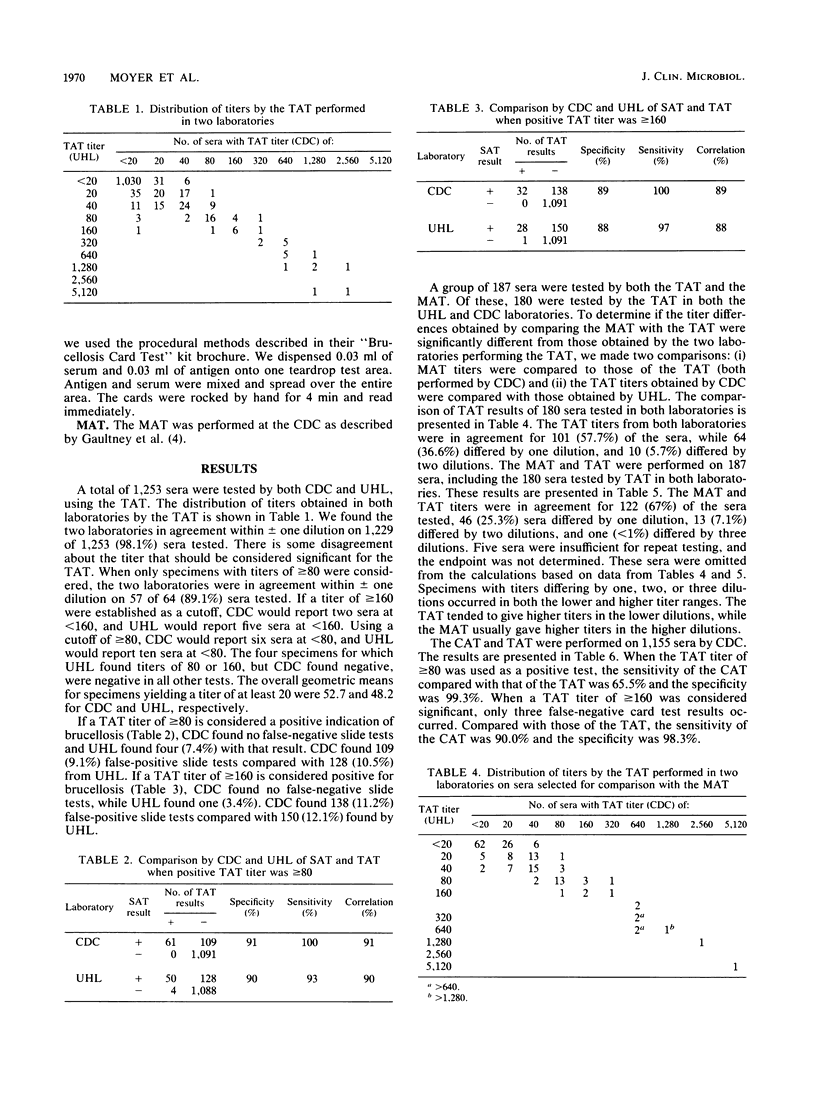
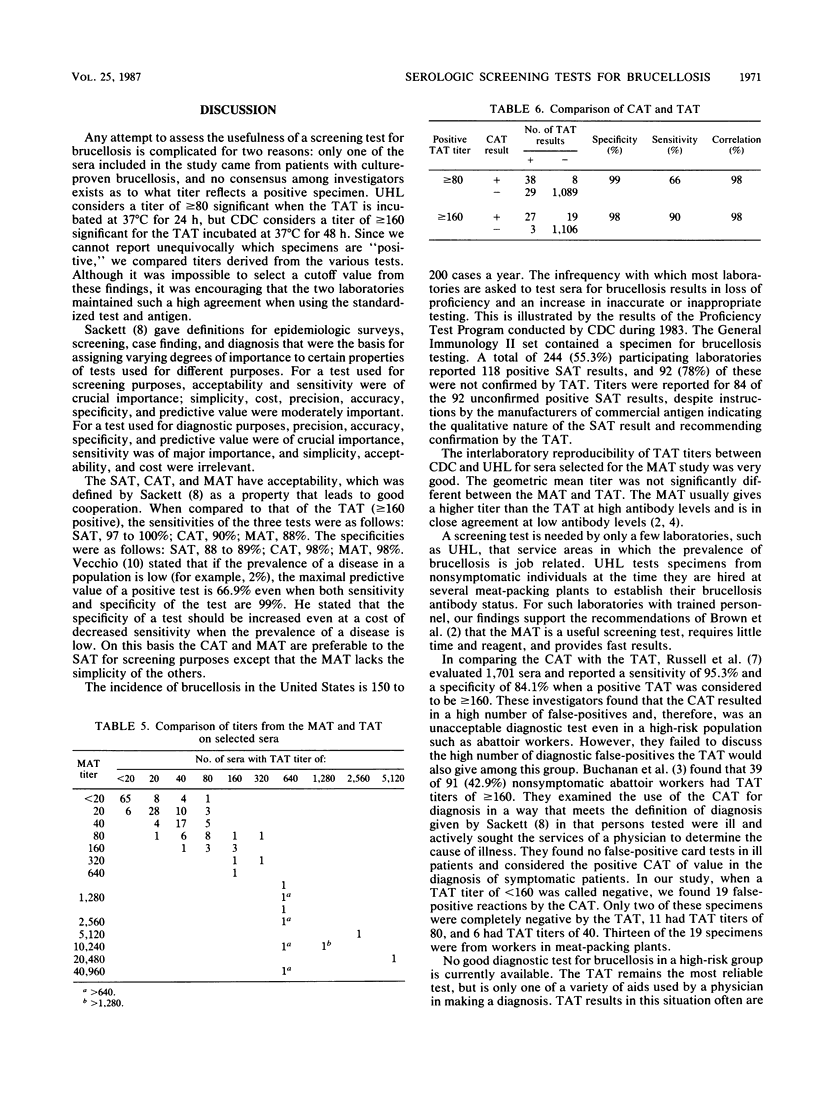
The slide agglutination test (SAT), microagglutination test (MAT), and card agglutination test (CAT) were compared with each other, using the tube agglutination test (TAT) as the standard method, by two reference laboratories to determine effectiveness as screening tests for human brucellosis. TAT titers of 1,253 sera tested in both laboratories were compared. In one laboratory, 1,270 sera were tested by the TAT and SAT, while the other laboratory tested 1,261 sera by both methods. Of these sera, 1,155 were tested in one laboratory by the CAT and 187 sera were tested by the MAT. Compared with that of the TAT (greater than or equal to 160 positive), the sensitivities were 97 to 100% (SAT), 90% (CAT), and 88% (MAT). The specificities were 88 to 89% (SAT), 98% (CAT), and 88% (MAT). For populations with a low prevalence of disease, increased specificity offers higher predictive value, so the CAT and MAT are preferable for screening purposes and the choice between tests depends on the number and frequency of tests performed. All sera reactive in the CAT and MAT should be retested with the TAT.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown S. L., Klein G. C., McKinney F. T., Jones W. L. Safranin O-stained antigen microagglutination test for detection of brucella antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):398–400. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.398-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Sulzer C. R., Frix M. K., Feldman R. A. Brucellosis in the United States, 1960-1972. An abattoir-associated disease. Part II. Diagnostic aspects. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Nov;53(6):415–425. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197411000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaultney J. B., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Microagglutination procedures for febrile agglutination tests. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):635–640. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.635-640.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. O., Patton C. M., Kaufmann A. F. Evaluation of the card test for diagnosis of human brucellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):454–458. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.454-458.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPINK W. W., McCULLOUGH N. B., HUTCHINGS L. M., MINGLE C. K. A standardized antigen and agglutination technic for human brucellosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1954 Apr;24(4):496–498. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/24.4_ts.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L., Holland W. W. Controversy in the detection of disease. Lancet. 1975 Aug 23;2(7930):357–359. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio T. J. Predictive value of a single diagnostic test in unselected populations. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 26;274(21):1171–1173. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605262742104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



