Abstract
Secretion of the proinflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18, usually requires two signals. The first, due to microbial products such as lipopolysaccharide, initiates transcription of the cytokine genes and accumulation of the precursor proteins. Cleavage and secretion of the cytokines is mediated by caspase-1, in association with an inflammasome containing Nalp3, which can be activated by binding of extracellular ATP to purinergic receptors. We show that treatment of macrophages with ATP results in production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which stimulate the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway and subsequent Akt and ERK1/2 activation. ROS exerts its effect through glutathionylation of PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted from chromosome 10), whose inactivation would shift the equilibrium in favor of PI3K. ATP-dependent ROS production and PI3K activation also stimulate transcription of genes required for an oxidative stress response. In parallel, ATP-mediated ROS-dependent PI3K is required for activation of caspase-1 and secretion of IL-1β and IL-18. Thus, an increase in ROS levels in ATP-treated macrophages results in activation of a single pathway that promotes both adaptation to subsequent exposure to oxidants or inflammation, and processing and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines.
The inflammatory mediator, extracellular ATP, binds to P2 purinergic receptors that are expressed on a wide spectrum of cell types, including macrophages and epithelial cells (1). The P2 receptors can be classified into two families, the P2X ligand-gated cation channels and the G protein-coupled P2Y receptors. The only known physiological ligand for P2X receptors is extracellular ATP, whereas remaining P2Y receptors can interact with ATP and other nucleotides such as UTP, UDP, and ADP (1).
P2X7 plays a key role in cells from the immune system. Depending on the cell type, treatment with ATP leads to permeabilization of the plasma membrane, cell death, cell proliferation, shedding of cell-adhesion molecules, killing of intracellular pathogens, and secretion of mature IL-1β2 and IL-18 (2–4). Whereas the pathways leading from P2X7 ligation to the different cell responses remain to be characterized in most cases, ATP has been shown to activate various cell signaling mediators, including ERK1/2, PI3K, calcium fluxes, and p38 MAP kinases (5–8).
The proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 play an important role in fever, septic shock, and inflammatory disease (9). In macrophages, their production and secretion are therefore tightly controlled, requiring typically two separate signals (10, 11). Priming of macrophages with pathogen-associated molecular patterns such as LPS is sufficient to stimulate synthesis of pro-IL-1β, but secretion of the mature cytokine requires its cleavage by caspase-1. Caspase-1, in turn, is expressed constitutively as an inactive pro-caspase-1. Cleavage and activation of caspase-1 takes place in association with protein complexes termed inflammasomes, of which there are two types. The inflammasome that is activated after P2X7 ligation contains the adaptor moleculeASC(apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD), cardinal, and the NOD-like receptor family member, Nalp3 (also known as cryopyrin). The Nalp3 inflammasome can be activated by “danger signals” (danger-associated molecular patterns or DAMP) released from stressed or infected eucaryotic cells, such as ATP or uric acid crystals (10, 11), which by themselves do not promote synthesis of the cytokines. LPS priming can increase the efficiency of ATP-mediated caspase-1 activation, but is not required (12, 13). Thus, a pathogen must both express a pathogen-associated molecular pattern capable of driving cytokine synthesis, and be viewed as potentially dangerous to the host organism, for mature IL-1β and IL-18 to be secreted efficiently.
P2X7 ligation can lead to pore formation and cytosolic K+ depletion, and depleting K+ with ionophores without extracellular ATP treatment results in activation of caspase-1 and secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 in macrophages that had been primed with LPS (2, 10). Several pathogens that produce toxins that promote host-cell K+ efflux can also activate the inflammasome, in the absence of a second signal from danger-associated molecular patterns. It was thus proposed that K+ depletion, which may be detected by Nalp3, may be a common mechanism used by different danger-associated molecular patterns and pathogens to activate the inflammasome (11, 14). Nonetheless, K+ effluxes have not been reported in cells stimulated with uric acid crystals, which must be endocytosed to activate the inflammasome (15), and some pathogen-associated molecular patterns such as peptidoglycan and bacterial mRNA may activate the Nalp3 inflammasome after being detected in the cytosol, making it likely that a decrease in cytosolic K+ concentrations may have its effect on Nalp3 indirectly (10), or macrophages may also use other pathways to transmit signals from danger-associated molecular patterns such as ATP to the inflammasome.
We have therefore addressed the possibility that reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced after ATP treatment of primary macrophages may stimulate caspase-1 activation and processing of IL-1β and IL-18. The production of ROS such as H2O2 was long considered as an undesirable consequence of aerobic respiration, being associated with diseases as diverse as aging, cancer, and neurodegenerative disease (16). More recently, however, it has become clear that H2O2 is also a physiological mediator in cell signaling pathways involved in differentiation, proliferation, migration, and cytokine secretion (17, 18). Significantly, an ROS response in psychologically stressed mice leads to caspase-1 activation, secretion of IL-1β, and up-regulation of plasma IL-18 (19).
Given the ability of ROS to activate PI3K and ERK1/2 (20, 21), we also investigated whether ATP-dependent ROS production could activate PI3K and its downstream mediators. We found that in addition to activating PI3K, probably by inactivating PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted from chromosome 10) through glutathionylation, ATP-mediated ROS production can activate ERK1/2 and, subsequently, caspase-1, which is required for IL-1β and IL-18 processing. In parallel, the PI3K pathway is involved in stimulating transcription of genes involved in glutathione synthesis and an oxidative stress response.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Cells and Reagents
ADP, ATP, BzATP, oxATP, UTP, LY-294002, wortmannin, and diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI) were purchased from Sigma, whereas PD98059 was from Calbiochem (La Jolla, CA). Z-YVAD-fmk was from Biovision (Mountain View, CA). The antibodies used for Western blotting were anti-p44/p42 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204), anti-rabbit p44/p42 and anti-p38 (Tyr(P)180/182), pAKT (Thr308), from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA); and Akt1 (C-20), from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). The alveolar macrophages, NR8383, were isolated from Sprague-Dawley rats (22). NR8383 macrophages were maintained in F-12K medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 15% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen), 100 units/ml penicillin, and 100 µg/ml streptomycin at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2.
Measurement of ROS Production by FACS and Fluorescence Microscopy
NR8383 cells were treated with different agonists and inhibitors followed by addition of 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) for 5 min. The samples were analyzed by FACS with a Guava EasyCyte (Hayward, CA) or a Leica epifluorescence microscope (Mannheim, Germany) at 500 nm.
Immunoblotting for Akt and ERK1/2 Phosphorylation
Proteins from lysed cells were analyzed on a SDS-PAGE 4–20% gel (Bio-Rad) and then transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Bio-Rad). Blots were blocked for 1 h with 5% (w/v) nonfat dried milk in TBST. The membrane was incubated over-night at −4 °C with specific antibodies and then incubated again with the corresponding conjugated anti-mouse, anti-rabbit, or anti-goat IgG horseradish peroxidase. Immunoreactive proteins were detected with the ECL Western blotting detection kit (Amersham Biosciences).
Intracellular Staining for ERK1/2 Phosphorylation
NR8383 cells were pretreated with different agonists or inhibitors and centrifuged for 10 min at 600 × g. The pellet was resuspended in ice-cold methanol and then incubated for 30 min at 4 °C. The samples were rinsed with incubation buffer (0.5% bovine serum albumin in phosphate-buffered saline) and then incubated for 1 h at room temperature in incubation buffer with the primary Ab. After rinsing, the samples were treated for 30 min with the secondary fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated Ab (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). The samples were then rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline and analyzed by FACS with the Guava EasyCyte.
Immunoprecipitation for PTEN Glutathionylation
Ten million NR8383 cells were lysed for 30 min on ice with a lysis buffer containing 50 mm Hepes, 150 mmNaCl, 50 mm β-glycerophosphate, 1 mm sodium orthovanadate, 10 mm sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mm EGTA, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 100 mm sodium fluoride, 5 mm GSH, 10 µm diethylenetri-aminepentaacetic acid, 0.5% Nonidet-40, 1% Triton X-100, 10% glycerol, 10 ng/ml leupeptin, and 10 ng/ml aprotinin, pH 7.4. The lysates were then centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min and the proteins were collected. Five hundred micrograms of protein was incubated with anti-PTEN Ab overnight at −4 °C. The bond complex was washed with cold lysis buffer, and 40 µl of the immunoprecipitated complex was loaded on a 4–20% SDSPAGE gel (Bio-Rad). After electrophoresis, the proteins were revealed with Ab against PTEN (Santa Cruz; dilution 1:1000) or GSH-protein complexes (Virogen, Watertown, MA).
Measurement of gcl and Cytokine Gene Expression
NR8383 cells were cultured in 60-mm Petri dishes and pretreated for 30 min with PD98059 (10 µm), LY294002 (50 µm), or wortmannin (100 nm), followed by ATP (3 mm), BzATP (1 mm), UTP (1 mm), ADP (0.4 mm), or control buffer for 5 min. The cells were then centrifuged at 600 × g at 4 °C for 10 min. When the cells were pretreated with oxATP (0.3 mm), the time of incubation was 2 h.
After centrifuging the cells, the RNA extraction was performed with RNEasy Minikit (250) from Qiagen (Valencia, CA), following the manufacturer’s instructions, with an additional step where 1 unit/µl of RNase-free DNase (Fisher, Lafayette, CO) was added for 15 min after cell lysis. The reverse transcriptase assay was performed using TaqMan-Reverse Transcription Reagents (Applied Biosystem, Foster City, CA) with a final volume of 40 µl. The reaction cycle was performed on a Eppendorf Termocycler for 45 min (25 °C for 10 min; 48 °C for 30 min; 95 °C for 5 min). Approximately 1 µg of cDNA was used for a real-time PCR using primers specific for gclc and gclm. The reaction was performed using SYBR Green Jump Start™, Taq Ready Mix™ for quantitative PCR (Sigma). The reverse transcriptase-PCR was performed on a ×3000 Stratagene Thermo-cycler with a pre-heating cycle for 10 min at 95 °C and 50 cycles, then 95 °C for 25 s, 60 °C for 40 s, and 70 °C for 40 s.
The sequences of the gclc primers were: 5′-ATGGAGGTACAGTTGACAGAC-3′, sense; and 5′-ACGGCGTTGCCACCTTTGCA-3′, antisense. For gclm, the primers were: 5′-GCTGTACCAGTGGGCACAG-3′, sense; and 5′-GGCTTCAATGTCAGGGATGC-3′, antisense. The il-18 primers were: 5′-ATATCGACCGAACAGCCAAC-3′, sense; and 3′-TAGGGTCACAGCCAGTCCTC-5′, antisense. As a control gene, we used gapdh: 5′-ACCCCCAATGTATCCGTTGT-3′, sense; and 5′-TACTCCTTGGAGGCCATGT-3′, antisense.
Measurement of Caspase-1 Activity by FACS
Caspase-1 activity was measured in NR8383 cells using a caspase assay kit, carboxyfluorescein Flica (Immunochemistry Technologies, Bloomington, MN). In brief, 106 cells were incubated with different agonists or inhibitors followed by addition of the caspase-1 fluorigenic substrate, FAM-VAD-fmk (20 µm). As a control for specificity, cells were also incubated with the caspase-1 inhibitor, Z-YVAD-fmk, before adding FAM-VAD-fmk. Fluorescence was measured using the Guava EasyCite.
Quantification of Cytokine Release
Ten million NR8383 cells were primed with 1 µg/ml LPS for 2 h at 37 °C, and then treated with 2 µm DPI for 10 min, 50 µm Z-YVAD-fmk for 30 min, or LY294002 for 10 min. Finally, the cells were stimulated with 3 mm ATP or control buffer for 6 h. The cells were then spun down and the supernatant collected. The ELISA analysis of the supernatant was performed following the manufacturer’s protocol for IL-18 (BIOSOURCE, Carlsbad, CA) and IL-1β (Pierce Biotechnology).
Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Ins Tat software (GraphPad Software Inc., version 4.0) by Tukey test and was considered significant at p < 0.05.
RESULTS
Extracellular ATP Induces ROS Production in Primary Macrophages
Stimulation of primary rat microglia with the P2X7 agonist, BzATP, leads to release of large amounts of superoxide (23). To determine whether stimulation of primary alveolar macrophages with ATP may also result in production of ROS, macrophages were preincubated with the ROS-sensitive dye, DCF, before treating with 3 mm ATP for 5 min. ATP treatment caused the fluorescence of DCF to increase dramatically, as measured by FACS, compared with background controls (Fig. 1A). A comparable increase in fluorescence was achieved by treating macrophages with 1 mM H2O2, and the ATP-induced increase in ROS levels could be inhibited by N-acetylcysteine (NAC) (Fig. 1A).
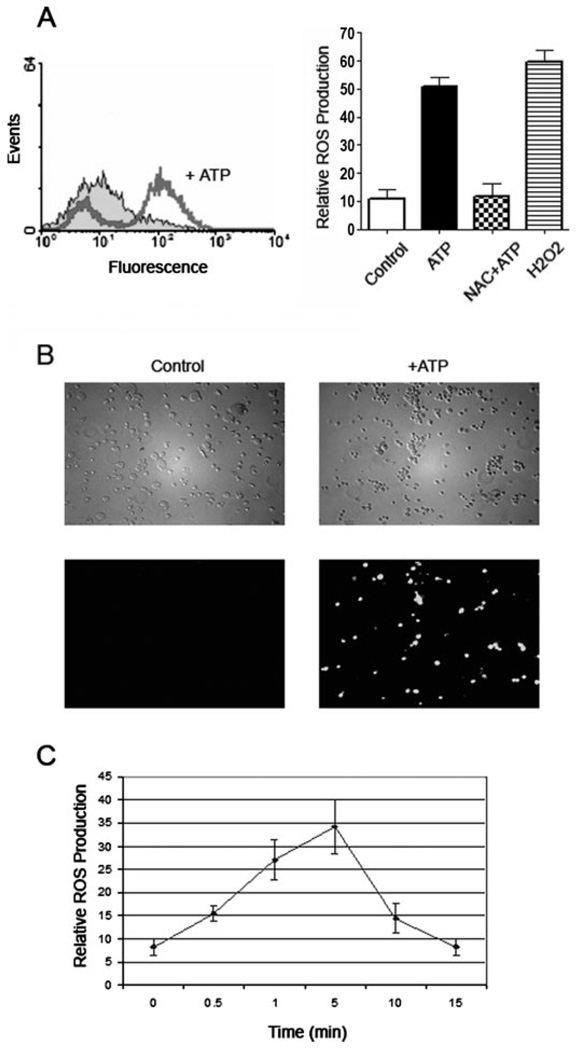
FIGURE 1. ATP induces ROS production in macrophages.
A, left, alveolar macrophages were preincubated with an ROS-sensitive dye, DCF (5 µm), for 5 min, before treating with 3 mm ATP for another 5 min at 37 °C. Enhancement in DCF fluorescence was measured immediately in a FACS, which showed a large increase in fluorescence in ATP-treated macrophages, compared with DCF-labeled untreated controls. A, right, DCF fluorescence was quantified as the mean fluorescence measured by FACS. Preincubation of macrophages with 25 mm NAC for 5 min before ATP treatment abrogated the increase in ROS production. As a positive control, maximal ROS production was measured when untreated macrophages were incubated with 1 mm H2O2for 5 min. p < 0.001 for cells treated with ATP, compared with cells treated with control buffer, or cells treated with ATP with NAC. B, macrophages were preincubated with DCF and then treated with control buffer (left) or 3 mm ATP (right) for 5 min, and visualized immediately with a fluorescence microscope. Phase-contrast microscopy (top panels) does not show obvious morphological changes in macrophages due to ATP treatment. Green fluorescence (bottom panels) was emitted from cells that had been treated with ATP (right, bottom) but not from untreated controls (left, bottom). C, ROS production was maximal after a 5-min incubation with 3 mm ATP, and returned to basal levels within 15 min, as measured by FACS of DCF-labeled cells. All experiments were performed in triplicate at least 3 times on separate days. The values show averages and S.D. from 3 samples of a representative experiment.
ATP-induced ROS production was also confirmed by viewing ATP-treated macrophages by fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, the increase in ROS levels was transient. By FACS, ROS production was detectable within 0.5 min of ATP stimulation, rose to maximal levels within 5 min, and sub-sided to basal levels by 15 min (Fig. 1C).
Ligation of P2X7 and Other Purinergic Receptors Leads to ROS Production
Besides expressing the purinergic receptor, P2X7, rat alveolar macrophages express other purinergic receptors, which can be stimulated by ATP, ADP, and UTP (24, 25). All of these nucleotides, including UDP, can promote high levels of ROS production (Fig. 2A). At least part of the ATP-mediated response is due to the P2X7 receptor, as it can be blocked partially by pretreatment with the irreversible P2X7 antagonist, oxATP, and can be stimulated with the P2X7 agonist, BzATP (26) (Fig. 2, B and C). As incubation with extracellular ADP, UDP, and UTP can also induce ROS production, these results suggest that ligation of P2X7 ligation and other purinergic receptors, possibly P2X4, P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y6, or P2Y12 (24), can all lead to activation of enzymes that result in ROS production.
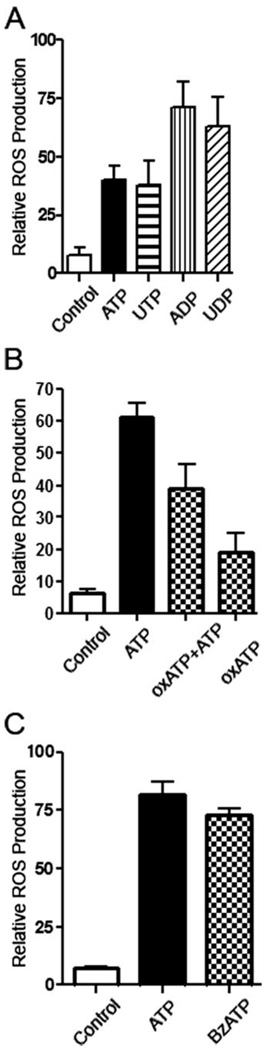
FIGURE 2. Ligation of several purinergic receptors can stimulate ROS production in macrophages.
A, incubation of DCF-labeled macrophages with 3 mm ATP, 3 mm UTP, 0.4 mm ADP, or 0.1 mm UDP results in an increase in ROS levels in macrophages, as measured by FACS of DCF-stained macrophages. p < 0.01 for cells treated with ATP, compared with cells treated with control buffer. B, preincubation of macrophages with 0.3 mm of the P2X7 antagonist, oxATP, for 2 h inhibits partially ATP-mediated ROS production due to treatment with 3 mm ATP for 5 min. p < %0.05 for cells treated with oxATP and ATP, compared with cells treated with ATP. C, incubation with 1 mm of the P2X7 agonist, BzATP, for 5 min induces as much ROS production as 3 mm ATP. p < 0.001 for cells treated with BzATP, compared with cells treated with control buffer. The values show averages and S.D. from 3 samples of a representative experiment, and represent results obtained from at least three representative experiments.
Ligation of Purinergic Receptors Leads to Activation of the PI3K Pathway
Extracellular ATP can activate PI3K in macrophages and other cell types (6, 8, 27). In many cell types, PI3K phosphorylates and activates the downstream Ser/Thr kinase, Akt/PKB, which promotes survival or controls metabolism through phosphorylation of multiple targets (28). Although oxidants are known to stimulate the PI3K/Akt pathway (29, 30), the mechanism linking P2 receptor ligation with PI3K activation had not been elucidated. We therefore explored the possibility that ATP-mediated ROS production could activate the PI3K pathway in alveolar macrophages, by measuring phosphorylation of Akt by immunoblots using Ab against a phosphorylated residue of Akt (residue Thr308) that leads to Akt activation in different cell types. As shown in Fig. 3, a short incubation of macrophages with ATP caused Akt phosphorylation to increase significantly, consistent with previous reports in macrophages and astrocytes (8, 27). The increase in Akt phosphorylation could be inhibited by co-treatment of macrophages with NAC (Fig. 3, lane 3), suggesting that ATP-induced ROS production leads to Akt phosphorylation. In addition, ATP-induced Akt phosphorylation was blocked almost completely by pre-treatment of macrophages with the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002 (Fig. 3, lane 4), implying that ATP-mediated ROS production results in PI3K activation and subsequently to Akt phosphorylation/activation.
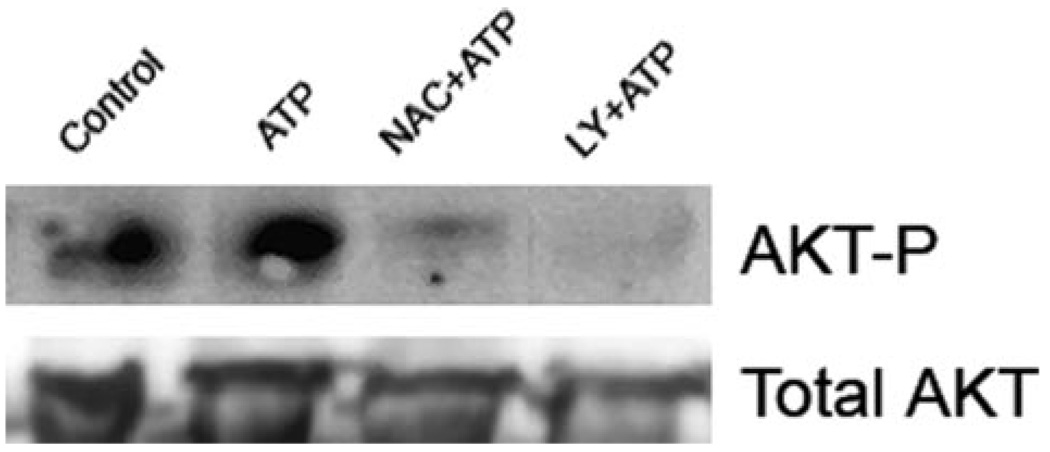
FIGURE 3. Treatment of macrophages with ATP results in ROS-dependent PI3K activation and Akt phosphorylation.
Macrophages were pretreated for 5 min with 25 mm NAC or 50 µM of the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, for 5 min, and incubated for 5 min with 3 mm ATP. Akt phosphorylation was determined by Western blot, using an Ab recognizing Akt phosphorylated on residue Thr308. The Western blot is representative of three experiments performed on separate days.
ROS-dependent PI3K Activation Leads to ERK1/2 Phosphorylation
Recent studies have shown that ATP treatment of thymocytes and macrophages results in phosphorylation of ERK1/2, which is downstream from PI3K activation (6, 8). To investigate whether ROS-dependent PI3K activation can in turn lead to ERK1/2 activation, we stimulated alveolar macrophages with ATP in the presence of antioxidants or PI3K inhibitors, and measured ERK1/2 phosphorylation by immunoblot, using Ab against phosphorylated residues of ERK1/2 (residues Thr202 and Tyr204) that lead to ERK1/2 activation (31). Thus, ATP stimulation of macrophages led to ERK1/2 phosphorylation within 1 min, consistent with the time course of ROS production after ATP treatment (Fig. 1C), which could be inhibited by NAC and the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056 (Fig. 4A). Interestingly, the time course of ERK1/2 phosphorylation was also similar to Akt phosphorylation (Fig. 4A), although Akt phosphorylation subsided after 10 min, as observed for ATP-induced ROS production (Fig. 1C). ERK1/2 phosphorylation was confirmed by measuring staining with Ab against phosphorylated ERK1/2 by FACS. Short ATP treatment led to ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which could be inhibited partially by the PI3K inhibitors, wortmannin (Fig. 4, B and C) or LY294002 (Fig. 4C), or the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056 (Fig. 4, B and C). Again, ERK1/2 phosphorylation was inhibited by co-treatment with NAC (not shown). Taken together, the results imply that ATP treatment leads to ROS production, which activates PI3K, and PI3K in turn activates Akt and ERK1/2.
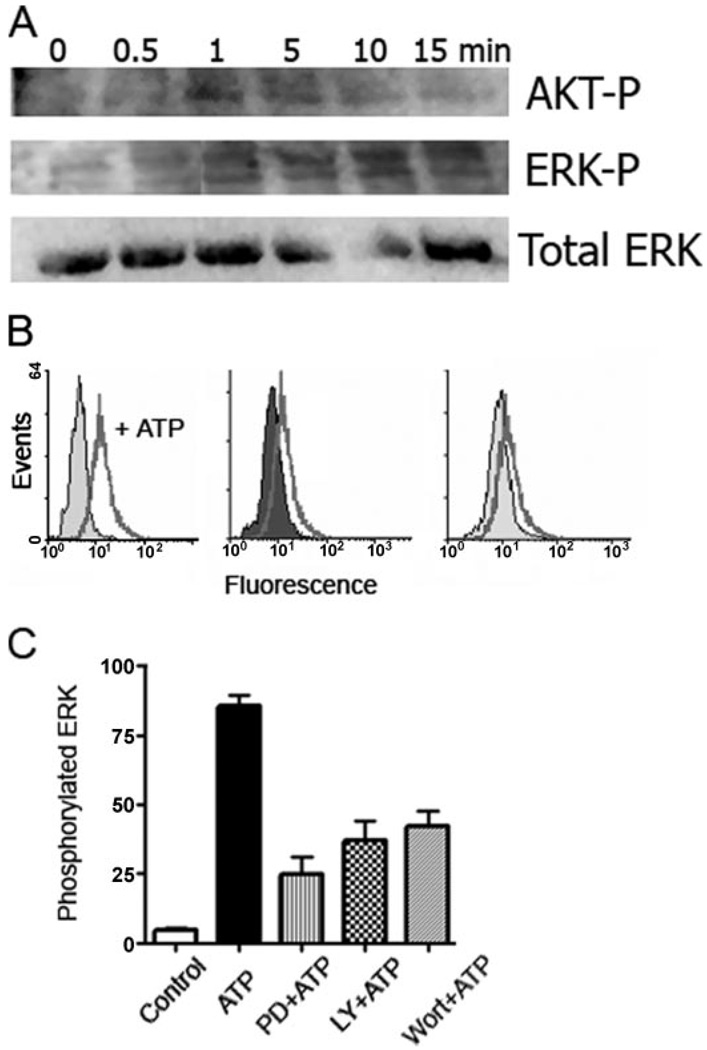
FIGURE 4. ATP-dependent ROS production and PI3K activation are upstream from ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
A, macrophages were incubated with 3 mm ATP, and cells were lysed at different times after the addition of ATP. ERK1/2 phosphorylation was determined by Western blot, probing with an Ab recognizing ERK1/2 phosphorylated on residues Thr202 and Tyr204. Akt phosphorylation was measured with an Ab recognizing Akt phosphorylated on residue Thr308. The Western blot is representative of three experiments performed on separate days. B, ERK1/2 phosphorylation was confirmed by FACS. Macrophages were pretreated for 5 min with control buffer (left panel), 1 µm of the PI3K inhibitor, wortmannin (middle panel), or 10 µm of the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056 (right panel), for 5 min, and incubated for 5 min with 3 mm ATP. ERK1/2 phosphorylation was measured by FACS, after incubating per-meabilized cells with the Ab recognizing phosphorylated ERK1/2. C, ERK1/2 phosphorylation was quantified as the mean fluorescence measured by FACS. Preincubation of macrophages with the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056, or the PI3K inhibitors, wortmannin or LY294002, for 5 min before ATP treatment decreased significantly the extent of ERK1/2 phosphorylation. p < 0.001 for cells treated with wortmannin and ATP, compared with cells treated with ATP. The results are representative of at least two experiments performed on separate days.
ATP-mediated Glutathionylation of PTEN Correlates with Activation of the PI3K Pathway
The phosphatase, PTEN, removes the 3′-phosphate of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate, thus inhibiting PI3K signaling. Previous studies have revealed that PTEN can be inhibited reversibly by H2O2 (32, 33). Moreover, oxidized cysteines can then form a disulfide bond with glutathione (GSH), the main antioxidant present in the cell cytosol. A number of signaling proteins have recently been shown to undergo glutathionylation, including protein-tyrosine phosphatases and transcription factors (34–38). But as there are no known examples for activating kinases through glutathionylation, we reasoned that inactivation of PTEN through glutathionylation could result in de facto activation of the PI3K pathway.
To test this hypothesis, macrophages were treated with ATP, lysed in a GSH-rich lysis buffer, and proteins were then immunoprecipitated with PTEN-conjugated beads and submitted to electrophoresis. Immunoblotting with an Ab against GSH revealed that a sizable fraction of PTEN exists in a monomeric form that can be recognized by the anti-GSH Ab even in untreated macrophages, with a smaller fraction of PTEN being found in a high molecular weight complex (Fig. 5A). But the amount of PTEN in both the monomeric glutathionylated form and in the high molecular weight complex increased significantly after a 3-min incubation with ATP (Fig. 5A). Treatment of the immunoprecipitate with the reducing agent, dithiothreitol, before electrophoresis resulted in disappearance of both the monomeric and multimeric PTEN (Fig. 5A), demonstrating that the Ab recognized only the glutathionylated form of PTEN.
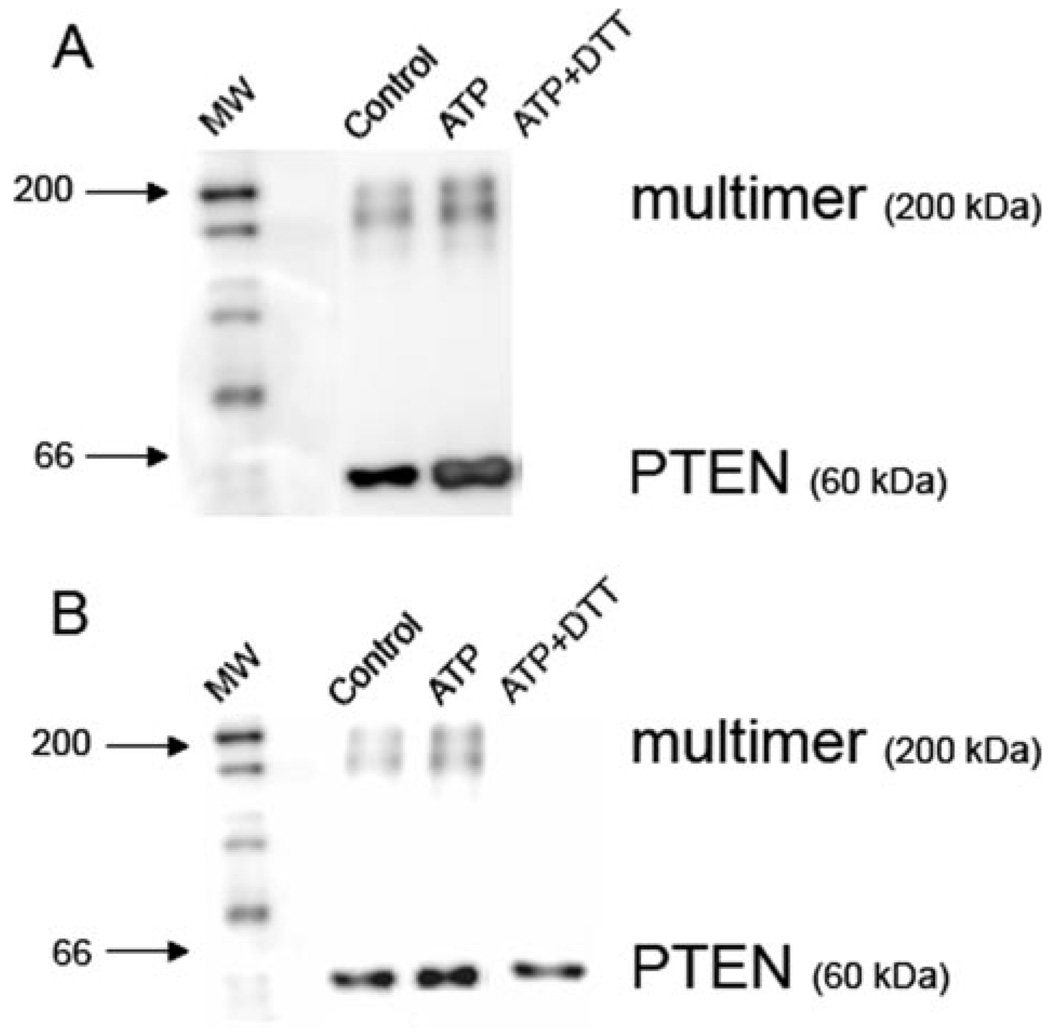
FIGURE 5. ATP-dependent ROS production induces glutathionylation of PTEN.
Macrophages were pretreated for 5 min with control buffer or 3 mm ATP for 1 min. Cells were lysed, and the proteins were immunoprecipitated overnight with PTEN-conjugated beads. A, the extent of glutathionylation was determined by Western blot, using an Ab recognizing GSH. The anti-GSH Ab revealed the presence of immunoprecipitated protein both as a monomer corresponding to the molecular mass of PTEN (60 kDa) or a larger complex (200 kDa). The level of glutathionylation of PTEN in both monomeric and multimeric forms increases after ATP stimulation of macrophages. Treatment of the immunoprecipitate with the reducing agent dithiothreitol before electrophoresis dissociates GSH from all proteins. B, the results were confirmed by reprobing the same membrane with an Ab recognizing total PTEN. The anti-PTEN Ab also revealed the presence of PTEN in monomers and a larger complex. Macrophage stimulation with ATP causes the amount of PTEN in the larger complex to increase slightly. Treatment with the reducing agent dithiothreitol causes PTEN to dissociate from the larger complex. The Western blots are representative of two experiments performed on separate days.
Reprobing the same membrane with an Ab against PTEN verified the presence of PTEN (60 kDa) in both the treated and untreated macrophages (Fig. 5B). The anti-PTEN Ab also con-firmed the presence of PTEN in the high molecular weight complex, whose levels increased after the 3-min incubation with ATP (Fig. 5B). As expected, dithiothreitol dissociated PTEN from the multimeric complex, without affecting the presence of the monomeric PTEN (Fig. 5B). Thus, ATP-dependent glutathionylation of PTEN correlates with ATP-dependent activation of PI3K and is likely to contribute to activation of the PI3K pathway.
ROS Production Results in a PI3K-dependent Redox Response through Expression of Genes Involved in GSH Synthesis
GSH is the most abundant intracellular nonprotein thiol and most important antioxidant in the cytosol. GSH is synthesized through the sequential action of glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL) and glutathione synthase (GS) (39, 40). The rate-limiting enzyme in GSH synthesis, GCL, is composed of two subunits, the catalytic (GCLC) and modulatory (GCLM) subunits, which are encoded by separate genes, gclc and gclm, that are regulated independently in response of oxidative stress.
As GCL plays a key role in resistance to ROS-mediated oxidative stress (41, 42), we determined whether ATP treatment of macrophages may affect gcl expression by real-time PCR, using primers specific for gclc and gclm. Thus, short incubation of macrophages with ATP led to significant up-regulation of both the gclc and gclm genes, whereas smaller up-regulation was observed when macrophages were stimulated with UTP or ADP (Fig. 6A). Incubation with the P2X7 agonist, BzATP, also resulted in a large increase in gclc and gclm expression, whereas the antagonist oxATP inhibited ATP-induced gclm and gclc up-regulation (not shown), suggesting that ligation of several purinergic receptors, including P2X7, may stimulate gcl up-regulation. The expression of gcl was similar to control levels when ATP-treated macrophages were also treated with catalase (not shown), which converts H2O2 produced on the outside of cells into water and oxygen, implying that ATP-mediated H2O2 production is responsible for regulation of gclc and gclm expression.
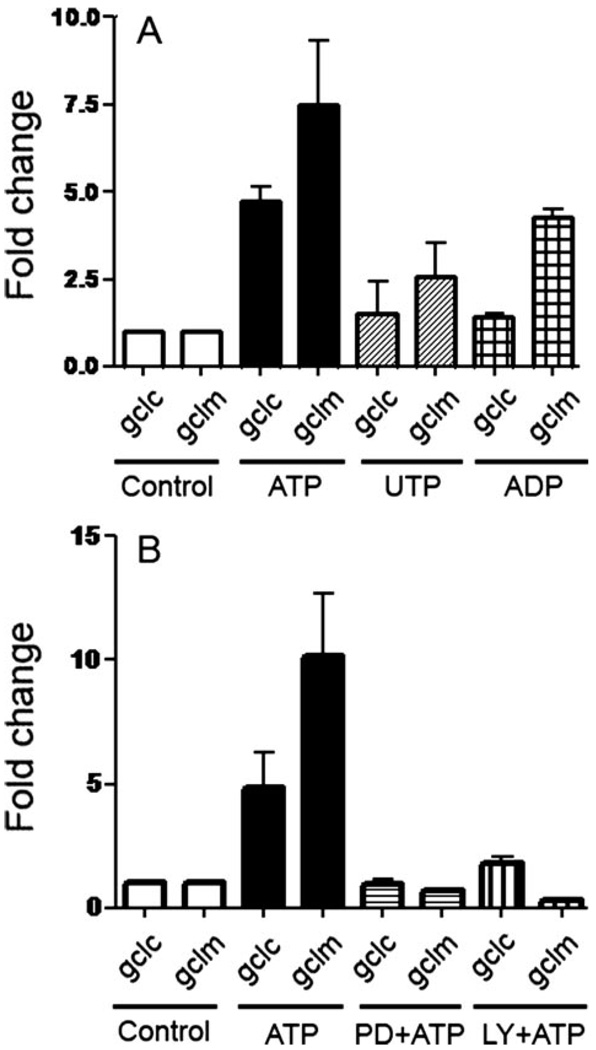
FIGURE 6. Stimulation of macrophages with ATP results in PI3K- and ERK1/2-dependent up-regulation of genes involved in GSH synthesis.
A, incubation of macrophages with 3 mm ATP, 3 mm UTP, or 0.4 mm ADP for 20min, followed by an additional 6 h in the absence of nucleotides results in an increased expression of gclc and gclm, as measured by real-time PCR. p < 0.001 for gclm of cells treated with ATP, compared with cells treated with control buffer; and p < 0.01 for gclm of cells treated with ADP, compared with cells treated with control buffer. B, macrophages were pretreated for 5 min with the PI3K inhibitors, LY294002 (50 µm), or the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056 (10 µm), for 5 min, and then incubated for 5 min with 3 mm ATP. Expression of gclm and gclc was measured by real-time PCR. p < 0.001 for gclm of cells treated with ATP, compared with cells treated with ATP or either LY294002 or PD98056. The results are representative of at least three experiments performed on separate days.
Given the effect of ATP-mediated ROS production on PI3K activation, we then investigated whether the PI3K pathway may influence gcl expression. Both the PI3K inhibitors, LY294002 and wortmannin (shown for LY294002 in Fig. 6B), and the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056 (Fig. 6B), blocked ATP-dependent gcl up-regulation. Taken together, these results suggest that ATP ligation of P2X7 results in an increase in ROS levels, which activate PI3K and subsequently ERK1/2, which in turn regulates the oxidative stress response of the cell.
Extracellular ATP Leads to Cytokine Secretion through a Path-way Involving ERK1/2-dependent Caspase-1 Activation
Extracellular ATP stimulates secretion of the key proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and IL-18, through a pathway requiring the presence of P2X7 (2). P2X7 ligation by itself does not lead to IL-1β or IL-18 transcription or translation, but after macro-phage stimulation of receptors such as the TLR, P2X7 ligation by ATP results in activation of caspase-1 and secretion of the mature form of both cytokines. Recently it was shown that an inflammasome is required for ATP-dependent IL-1β and IL-18 secretion (10), but a molecular pathway linking P2X7 ligation and the inflammasome was not identified. We therefore explored the possibility that ATP-mediated ROS production may play a role in caspase-1 activation and cytokine secretion.
Caspase-1 activation was quantified by measuring binding to cells of a fluorescently labeled caspase inhibitor by FACS. As measured by real-time PCR, ATP treatment, in the absence of TLR ligands, had no effect on transcription for IL-18 (not shown), in agreement with previous studies on the lack of effect of ATP alone on IL-1β transcription (2). However, ATP treatment by itself results in caspase activation (Fig. 7A). Caspase activation was also inhibited by pretreating the cells with the irreversible caspase-1 inhibitor, Z-YVAD-fmk, before incubation with ATP (not shown), confirming that caspase-1 was activated by ATP. Importantly, ATP-mediated caspase-1 activation was inhibited strongly when macrophages were co-incubated with DPI (Fig. 7A), a flavoprotein inhibitor of NADPH oxidase, consistent with the conclusion that ATP-dependent ROS production is responsible for caspase-1 activation.
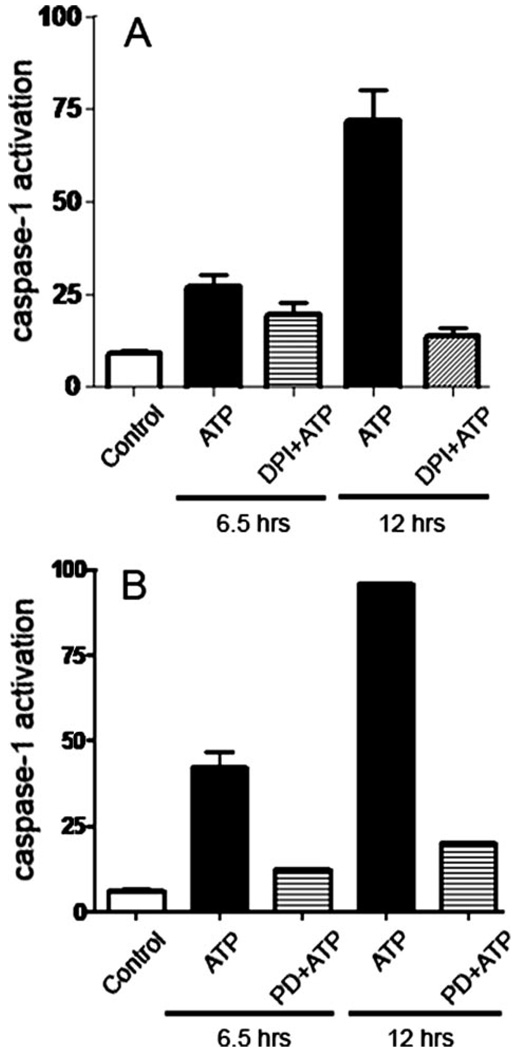
FIGURE 7. ATP-dependent ROS production and ERK1/2 activation are upstream from caspase-1 activation.
A, macrophages were stained with the fluorescent caspase substrate, FAM-VAD-fmk, pretreated for 10 min with the redox inhibitor, DPI (2 µm), and then incubated for 6.5 or 12 h with 3 mm ATP. Caspase-1 was measured by FACS. The specificity of caspase-1 activation was verified by pretreating the stained cells with the irreversible caspase-1 inhibitor, Z-YVAD-fmk. p < 0.001 for cells treated with DPI and ATP for 12 h, compared with cells treated with ATP for 12 h. B, stained macrophages were pretreated for 5 min with 10 µm of the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056, for 5 min, before incubation for 5 min with 3 mm ATP. p < 0.001 for cells treated with PD98056 and ATP for 6.5 or 12 h, compared with cells treated with ATP alone. The values show averages and S.D. from experiments performed in triplicate, and represent results obtained from at least two representative experiments.
To determine whether ROS production is sufficient for caspase-1 activation, we then evaluated whether the PI3K pathway may be involved. To examine the role of a downstream mediator in the pathway, we measured the effect of the ERK1/2 inhibitor on caspase-1 activation. The ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98056, blocked essentially all of the ATP-mediated caspase-1 activation (Fig. 7B). Conversely, the irreversible caspase-1 inhibitor had no effect on ATP-dependent ROS production (not shown). These results demonstrate that ATP-mediated ROS production leads to ERK1/2 activation, which in turn regulates activation of the inflammasome.
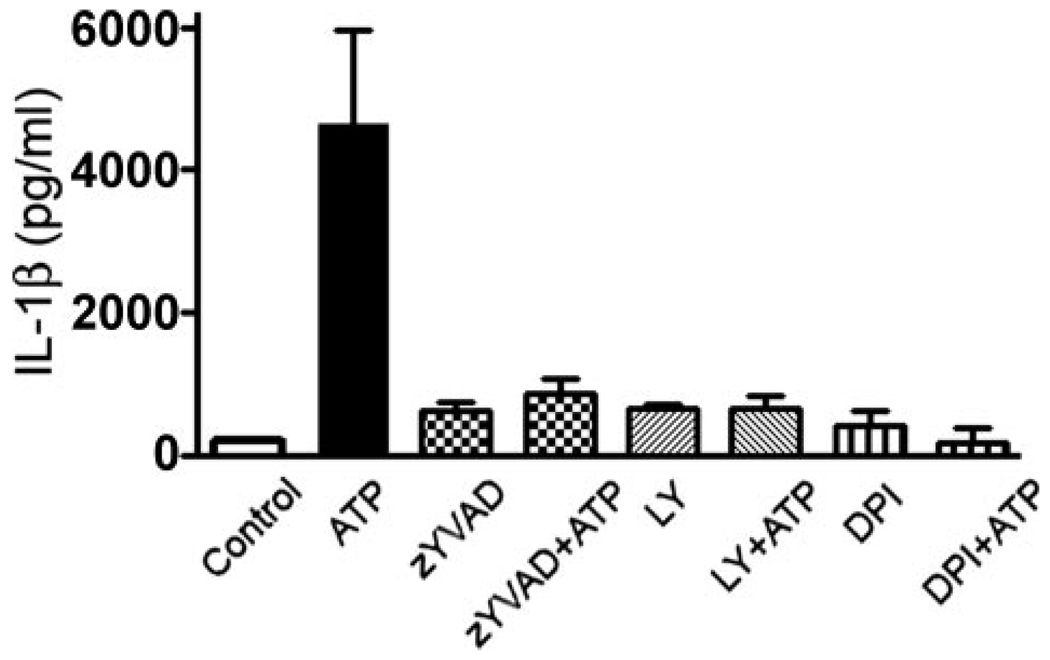
Because ATP alone cannot induce synthesis of cytokines (2), the role of ROS production and caspase-1 activation in cytokine secretion was then addressed using macrophages that had been primed with the TLR4 ligand, LPS, before stimulating the macrophages with ATP. IL-1β and IL-18 secretion was quantified by ELISA. Incubation of primed macrophages with ATP led to secretion of both IL-1β and IL-18, which in both cases could be inhibited by pretreatment with DPI (shown for IL-1β in Fig. 8), consistent with our observations that DPI blocks caspase-1 activation (Fig. 7A). Cytokine secretion was also inhibited by preincubation with the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or the caspase-1 inhibitor, Z-YVAD-fmk (Fig. 8). Thus, ATP-mediated ROS production in LPS-primed macrophages leads to ERK1/2 activation, which is upstream from caspase-1 activation and cytokine secretion.
FIGURE 8. ATP stimulation of macrophages leads to IL-1β secretion through a pathway requiring ROS production and PI3K activation.
Macrophages were primed with 1 µg/ml LPS for 2 h at 37 °C, before treating the macrophages with the caspase-1 inhibitor, Z-YVAD-fmk (50 µm) for 30 min, DPI (2 µm) for 10 min, or LY294002 (50 µm) for 10 min. The cells were then stimulated with 3 mm ATP for 6 h. Secretion of IL-1β was measured by ELISA. p < 0.001 for cells treated with ATP and Z-YVAD-fmk, DPI, or LY294002, compared with cells treated with ATP alone. The experiment was performed twice in duplicate, and the results represent the average and S.D.
DISCUSSION
Until recently, the production of H2O2 was studied primarily in macrophages and neutrophils. These cells use the NADPH oxidase complex (Nox2) in the plasma membrane to generate H2O2. The primary purpose of the respiratory burst in neutrophils is to kill internalized pathogens; however, in alveolar macrophages, a signaling role for H2O2 produced by the respiratory burst may be more important (18). In phagocytes, activation of the immune cells by pathogens leads to assembly of the Nox complex at the plasma membrane, which releases superoxide into the phagosome. Superoxide dismutation then results in production of H2O2. Nonphagocytic cells also express the functional homologues of the Nox catalytic subunit (43), and can generate H2O2 at the plasma membrane following stimulation with cytokines and growth factors (44).
We show here that stimulation of alveolar macrophages with ATP and other extracellular nucleotides leads to transient production of high levels of ROS. The effects of the agonist BzATP and the antagonist oxATP suggest that P2X7 ligation is responsible for much of the activity. Although the pathway coupling purinergic receptor ligation with ROS generation remains unknown, it is likely that the Nox complex is activated at the level of the plasma membrane. Localized Nox assembly has previously been reported in lipid rafts in activated microglia and HL-60 cells and in focal complexes in migrating endothelial cells (45, 46), and could also take place near ligated P2X7, which has been found to localize in lipid rafts in T cells and cells from submandibular glands (47, 48).
What could be the trigger for Nox assembly? Potassium depletion due to ionophore or ATP treatment leads to an influx of Ca2+ and the activation of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and calcium-independent and -dependent phospholipase A2 (PLA2) (49, 50). Calcium-independent PLA2 (iPLA2) stimulates the colocalization of caspase-1 and pro-IL-1β in secretory lysosomes, which could favor caspase-1 activation and pro-IL-1β cleavage and perhaps its subsequent shedding (10, 51). It has been proposed that Nalp3 may also respond to cytosolic lipids such as arachidonic acid and lyso-phospholipids generated by iPLA2 (10). Phospholipase-generated signals in ATP-treated macrophages may also synergize with elevated cytosolic Ca2+ in stimulating ROS production, as Ca2+ levels or iPLA2 activity in various cell types can modulate ROS production (52–54). Conversely, elevated ROS levels can activate iPLA2 or trigger Ca2+ fluxes (55, 56), suggesting that P2X7-dependent inflammasome activation could conceivably involve a cooperative loop between ROS generation, Ca2+ fluxes, and iPLA2 activation.
ROS is involved in diverse receptor systems, including tumor necrosis factor-α, epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, the T and B cell receptors, and insulin (17, 52, 57–60). Signal activation is often thought to occur through ROS-mediated inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatases, which shifts the equilibrium in favor of kinase activation. An essential cysteine in the active site of protein-tyrosine phosphatases has been identified as target for oxidation by H2O2, which can then undergo reversible glutathionylation (35–37). Previous studies have shown that oxidative inactivation of phosphatases leads to sustained activation of the corresponding kinases (44). As activation of kinases through glutathionylation has not been reported, we investigated the possibility that the cognate phosphatase, PTEN, could be inactivated. In fact, PTEN is glutathionylated soon after ATP stimulation of macrophages. ROS production and PTEN glutathionylation in ATP-stimulated macrophages could thereby shift the balance in favor of PI3K, which leads in turn to phosphorylation of Akt. In agreement with previous studies (5, 6), we find that ERK1/2 is also activated in ATP-treated cells, although the mechanism for activation of the PI3K pathway was not identified.
An important feature of any signaling pathway is reversibility. For ROS to regulate PTEN reversibly, it is critical to prevent oxidation of the active site Cys of PTEN beyond sulfenic acid (S-OH). The enzyme is protected against further, irreversible oxidation by reaction with GSH to form the mixed disulfide (44). Glutathionylation of PTEN leads to formation of high molecular weight oligomers, which can be reversed in lysed cells by incubation with a reducing agent. Treatment of cells with oxidants or the proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α and IL-1β, causes an initial depletion of GSH, followed by recovery and increased synthesis of GSH (39). The rate-limiting enzyme in GSH synthesis is GCL, and its expression is regulated by several transcription factor binding sites, such as AP-1 and antioxidant response elements, in response to oxidants and inflammatory stimuli (39), thus providing an adaptive mechanism to protect the cells during subsequent proinflammatory or oxidant stress. Similarly, we find that gcl expression increases following treatment of macrophages with the proinflammatory mediator, ATP. The up-regulation requires both ROS production and activation of the PI3K pathway.
Unexpectedly, we found that ATP-mediated, ROS-dependent PI3K activation is also involved in activation of caspase-1 and processing of IL-1β and IL-18. The Nalp3 inflammasome can be activated by stimuli as diverse as ATP, K+ ionophores, bacterial toxins, and uric acid crystals (10, 11). It will be intriguing to determine whether any of the cell signaling pathways initiated by stimuli other than ATP may also converge on the inflammasome via ROS.
Footnotes
This work was supported by a fellowship from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Technologico do Brasil (CNPq), the University of California, and National Institutes of Health Grant HL37556.
The abbreviations used are: IL, interleukin; BzATP, 2′,3′-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)-ATP; DCF, 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein; DPI, diphenyleneiodonium chloride; iPLA2, calcium-independent phospholipase A2; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; Nox, NADPH oxidase complex; oxATP, periodate-oxidized ATP; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted from chromosome 10; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Z, benzyloxycarbonyl; fmk, fluoromethyl ketone; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Ab, antibody; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GCL, glutamate cysteine ligase; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorter; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.
REFERENCES
- 1.Burnstock G, Knight GE. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2004;240:31–304. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(04)40002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ferrari D, Pizzirani C, Adinolfi E, Lemoli RM, Curti A, Idzko M, Panther E, Di Virgilio F. J. Immunol. 2006;176:3877–3883. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.3877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Coutinho-Silva R, Stahl L, Raymond MN, Jungas T, Verbeke P, Burnstock G, Darville T, Ojcius DM. Immunity. 2003;19:403–412. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lammas DA, Stober C, Harvey CJ, Kendrick N, Panchalingam S, Kumararatne DS. Immunity. 1997;7:433–444. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gendron FP, Neary JT, Theiss PM, Sun GY, Gonzalez FA, Weisman GA. Am. J. Physiol. 2003;284:C571–C581. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00286.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Auger R, Motta I, Benihoud K, Ojcius DM, Kanellopoulos JM. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:28142–28151. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501290200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pfeiffer ZA, Aga M, Prabhu U, Watters JJ, Hall DJ, Bertics PJ. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2004;75:1173–1182. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1203648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.da Cruz CM, Ventura AL, Schachter J, Costa-Junior HM, da Silva Souza HA, Gomes FR, Coutinho-Silva R, Ojcius DM, Persechini PM. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006;147:324–334. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dinarello CA. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006;83:447S–455S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/83.2.447S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lich JD, Arthur JC, Ting JP-Y. Immunity. 2006;24:241–243. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Meylan E, Tschopp J, Karin M. Nature. 2006;442:39–44. doi: 10.1038/nature04946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yamamoto M, Yaginuma K, Tsutsui H, Sagara J, Guan X, Seki E, Yasuda K, Yamamoto M, Akira S, Nakanishi K, Noda T, Taniguchi S. Genes Cells. 2004;9:1055–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2004.00789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mariathasan S, Newton K, Monack DM, Vucic D, French DM, Lee WP, Roose-Girma M, Erickson S, Dixit VM. Nature. 2004;430:213–218. doi: 10.1038/nature02664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mariathasan S, Weiss DS, Newton K, McBride J, O’Rourke K, Roose-Girma M, Lee WP, Weinrauch Y, Monack DM, Dixit VM. Nature. 2006;440:228–232. doi: 10.1038/nature04515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martinon F, Petrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. Nature. 2006;440:237–241. doi: 10.1038/nature04516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tabner BJ, El-Agnaf OM, German MJ, Fullwood NJ, Allsop D. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005;33:1082–1086. doi: 10.1042/BST20051082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rhee SG. Science. 2006;312:1882–1883. doi: 10.1126/science.1130481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Forman HJ, Torres M. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002;166:S4–S8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2206007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sekiyama A, Ueda H, Kashiwamura S.-i, Sekiyama R, Takeda M, Rokutan K, Okamura H. Immunity. 2005;22:669–677. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Qin S, Chock PB. Biochemistry. 2003;42:2995–3003. doi: 10.1021/bi0205911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee SB, Cho ES, Yang HS, Kim H, Um HD. Cell. Signal. 2005;17:197–204. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Helmke RJ, Boyd RL, German VF, Mangos JA. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 1987;23:567–574. doi: 10.1007/BF02620974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parvathenani LK, Tertyshnikova S, Greco CR, Roberts SB, Robertson B, Posmantur R. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:13309–13317. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209478200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bowler JW, Bailey RJ, North RA, Surprenant A. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003;140:567–575. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang GH, Helmke RJ, Mork AC, Martinez JR. J. Leukocyte Biol. 1997;62:341–348. doi: 10.1002/jlb.62.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.North RA. Physiol. Rev. 2002;82:1013–1067. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jacques-Silva MC, Rodnight R, Lenz G, Liao Z, Kong Q, Tran M, Kang Y, Gonzalez FA, Weisman GA, Neary JT. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004;141:1106–1117. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Brazil DP, Park J, Hemmings BA. Cell. 2002;111:293–303. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhuang S, Kochevar IE. Photochem. Photobiol. 2003;78:361–371. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2003)078<0361:soaopk>2.0.co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Klotz LO, Schieke SM, Sies H, Holbrook NJ. Biochem. J. 2000;352:219–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Monteiro HP, Rocha Oliveira CJ, Curcio MF, Moraes MS, Arai RJ. Methods Enzymol. 2005;396:350–358. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)96029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Leslie NR, Bennett D, Lindsay YE, Stewart H, Gray A, Downes CP. EMBO J. 2003;22:5501–5510. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee SR, Yang KS, Kwon J, Lee C, Jeong W, Rhee SG. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:20336–20342. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111899200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kil IS, Park JW. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:10846–10854. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411306200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee SR, Kwon KS, Kim SR, Rhee SG. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:15366–15372. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.25.15366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Barrett WC, DeGnore JP, Konig S, Fales Hm, Keng YF, Zhang ZY, Yim MB, Chock PB. Biochemistry. 1999;38:6699–6705. doi: 10.1021/bi990240v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rinna A, Torres M, Forman HJ. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006;41:86–91. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fratelli M, Goodwin LO, Orom UA, Lombardi S, Tonelli R, Mengozzi M, Ghezzi P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005;102:13998–14003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504398102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rahman I. Mutat. Res. 2005;579:58–80. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Forman HJ, Dickinson DA, Iles KE. Mol. Aspects Med. 2003;24:189–194. doi: 10.1016/s0098-2997(03)00013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ridnour LA, Sim JE, Choi J, Dickinson DA, Forman HJ, Ahmad IM, Coleman MC, Hunt CR, Goswami PC, Spitz DR. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005;38:1361–1371. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Moellering DR, Levonen AL, Go YM, Patel RP, Dickinson DA, Forman HJ, Darley-Usmar VM. Biochem. J. 2002;362:51–59. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3620051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lambeth JD. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004;4:181–189. doi: 10.1038/nri1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tonks NK. Cell. 2005;121:667–670. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Vilhardt F, van Deurs B. EMBO J. 2004;23:739–748. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wu RF, Xu YC, Ma Z, Nwariaku FE, Sarosi GA, Jr, Terada LS. J. Cell Biol. 2005;171:893–904. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200507004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bannas P, Adriouch S, Kahl S, Braasch F, Haag F, Koch-Nolte F. Blood. 2005;105:3663–3670. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-08-3325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Garcia-Marcos M, Perez-Andres E, Tandel S, Fontanils U, Kumps A, Kabre E, Gomez-Munoz A, Marino A, Dehaye JP, Pochet S. J. Lipid Res. 2006;47:705–714. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M500408-JLR200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Andrei C, Margiocco P, Poggi A, Lotti LV, Torrisi MR, Rubartelli A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004;101:9745–9750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308558101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Duke RC, Witter RZ, Nash PB, Young JD, Ojcius DM. FASEB J. 1994;8:237–246. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.2.8119494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.MacKenzie A, Wilson HL, Kiss-Toth E, Dower SK, North RA, Surprenant A. Immunity. 2001;15:825–834. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kumar Singh D, Kumar D, Siddiqui Z, Kumar Basu S, Kumar V, Rao KV. Cell. 2005;121:281–293. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gong MC, Arbogast S, Guo Z, Mathenia J, Su W, Reid MB. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006;100:399–405. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00873.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Colston JT, de la Rosa SD, Strader JR, Anderson MA, Freeman GL. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:2533–2540. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.03.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bogeski I, Bozem M, Sternfeld L, Hofer HW, Schulz I. Cell Calcium. 2006;40:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zima AV, Blatter LA. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006;71:310–321. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.02.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kamata H, Honda S-i, Maeda S-i, Chang L, Hirata H, Karin M. Cell. 2005;120:649–661. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Meng TC, Fukada T, Tonks NK. Mol. Cell. 2002;9:387–399. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00445-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Finkel T. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003;15:247–254. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(03)00002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nathan C. J. Clin. Investig. 2003;111:769–778. doi: 10.1172/JCI18174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]