Abstract
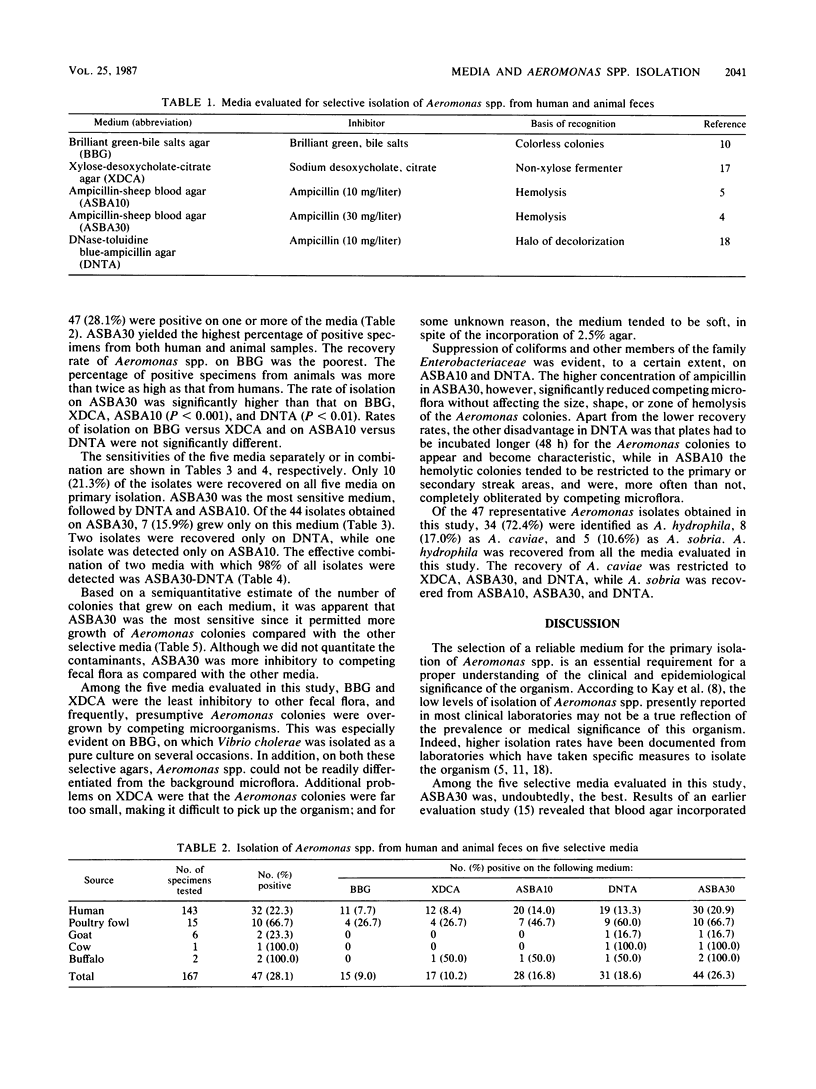
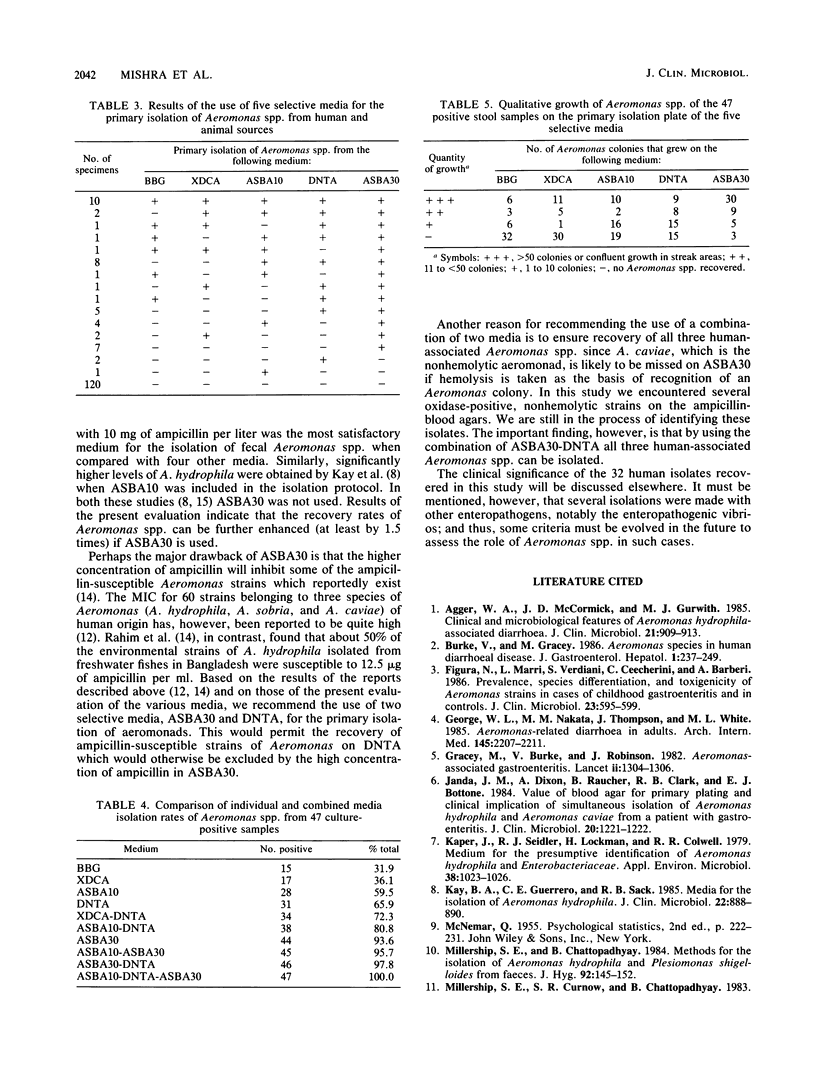
Five selective media were evaluated for their effectiveness in the primary isolation of Aeromonas spp. from human patients with acute diarrhea and from healthy domestic animals. Sheep blood agar with 30 mg of ampicillin per liter (ASBA30) yielded a significantly higher percentage of positive specimens as compared with the four other media. The effective combination of two selective media with which 98% of all isolates were detected and with which all of the three human-associated Aeromonas spp. could be isolated was ASBA30-DNase-toluidine blue agar. ASBA30 was the most sensitive medium since it permitted more growth of Aeromonas colonies and effectively suppressed competing microflora. We recommend the use of ASBA30-DNase-toluidine blue agar for investigations in which an attempt is made to assess the significance of Aeromonas spp. in the etiology of human diarrhea.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agger W. A., McCormick J. D., Gurwith M. J. Clinical and microbiological features of Aeromonas hydrophila-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):909–913. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.909-913.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Marri L., Verdiani S., Ceccherini C., Barberi A. Prevalence, species differentiation, and toxigenicity of Aeromonas strains in cases of childhood gastroenteritis and in controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Nakata M. M., Thompson J., White M. L. Aeromonas-related diarrhea in adults. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Dec;145(12):2207–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Dixon A., Raucher B., Clark R. B., Bottone E. J. Value of blood agar for primary plating and clinical implication of simultaneous isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas caviae from a patient with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1221–1222. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1221-1222.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Seidler R. J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R. Medium for the presumptive identification of Aeromonas hydrophila and Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.1023-1026.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Guerrero C. E., Sack R. B. Media for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):888–890. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.888-890.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millership S. E., Chattopadhyay B. Methods for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides from faeces. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Apr;92(2):145–152. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motyl M. R., McKinley G., Janda J. M. In vitro susceptibilities of Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas sobria, and Aeromonas caviae to 22 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):151–153. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahim Z., Sanyal S. C., Aziz K. M., Huq M. I., Chowdhury A. A. Isolation of enterotoxigenic, hemolytic, and antibiotic-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila strains from infected fish in Bangladesh. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):865–867. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.865-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Burke V., Worthy P. J., Beaman J., Wagener L. Media for isolation of Aeromonas spp. from faeces. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Dec;18(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Zinterhofer L. The detection of Aeromonas hydrophila in stool specimens. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Jul;7(3):124–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


