Abstract
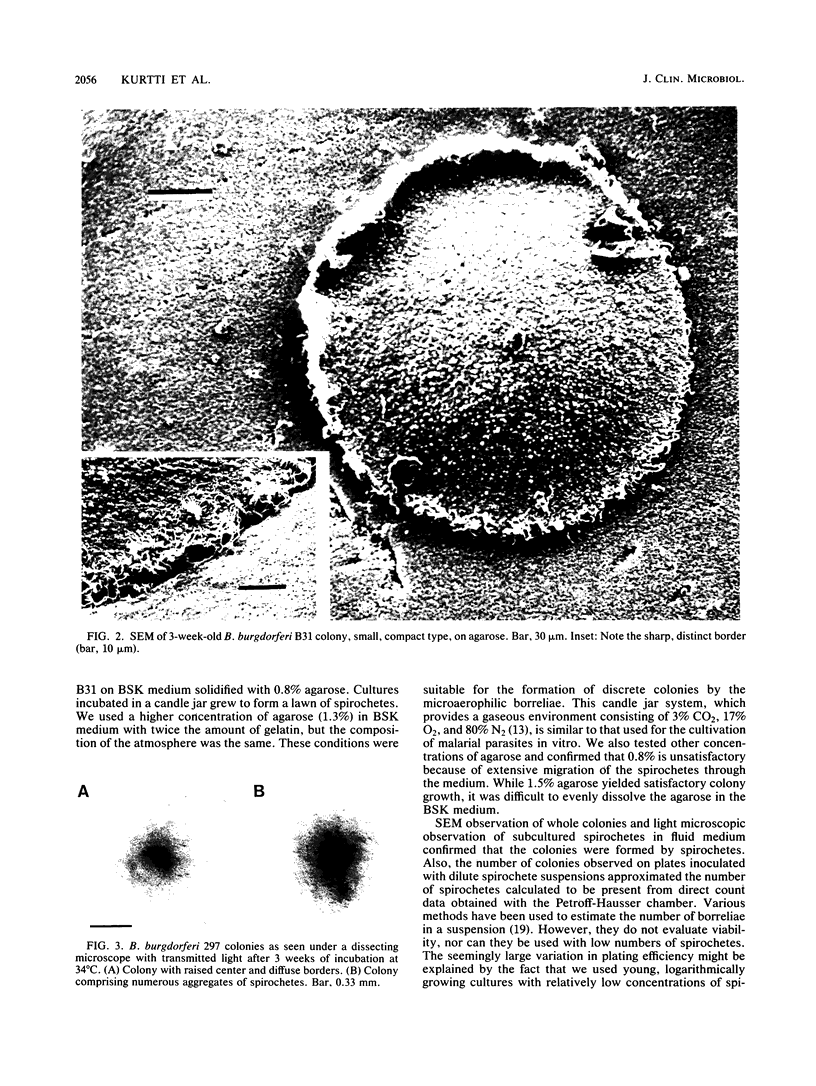
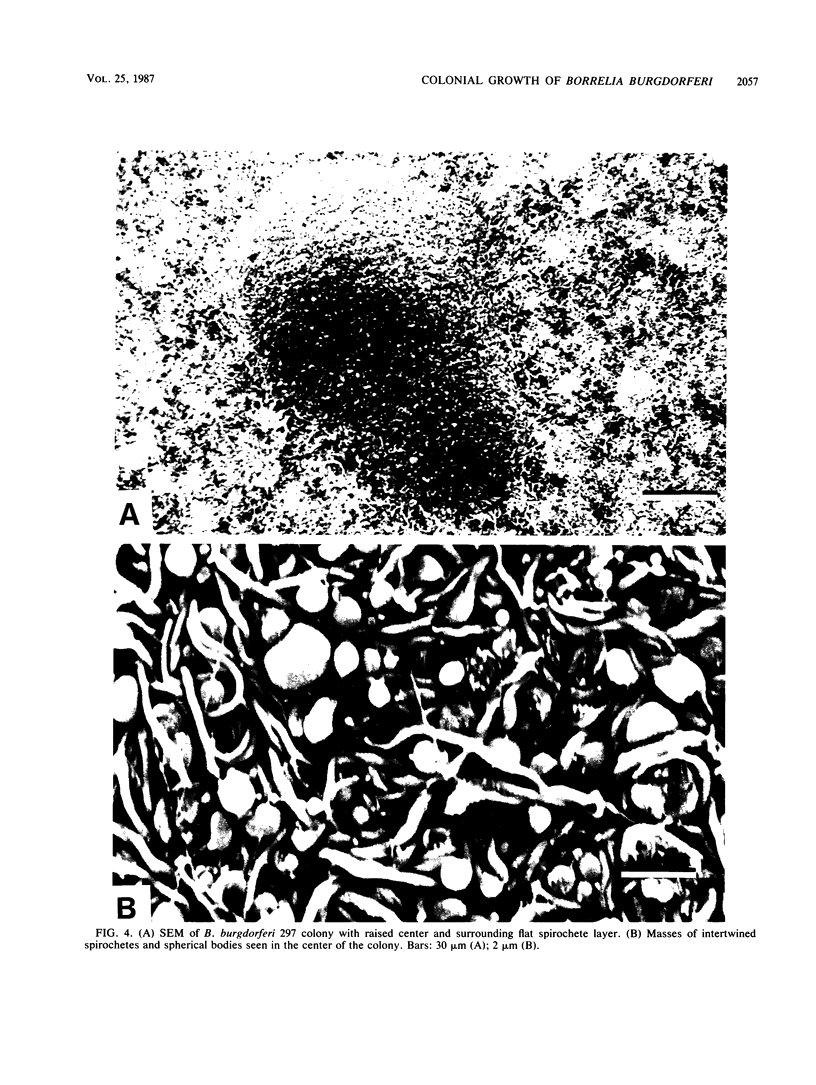
Two strains of Borrelia burgdorferi, B31 and 297, formed colonies when plated onto Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium solidified with agarose (1.3%) and incubated in a candle jar at 34 degrees C. Colonies differing in morphology were observed in both strains after 2 to 3 weeks of incubation. Strain B31 colonies were either compact, round (mean diameter, 0.43 mm), and restricted to the surface of the agarose medium or diffuse (mean diameter, 1.80 mm) and penetrating into the solid medium. Strain 297 colonies (mean diameter, 1.43 mm) either showed a raised center surrounded by a diffuse ring of spirochetes or consisted of numerous small spirochetal aggregates. Both colony types expanded into the agarose medium. Scanning electron and light microscopy confirmed that the colonies were formed by spirochetes. Twisted tangles of intertwined spirochetes were visible on the surface, with numerous spherical bodies among them, especially in the central regions. At the periphery, the borreliae were more loosely packed, and individual coils were discernible.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W. Involvement of birds in the epidemiology of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):394–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.394-396.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A. Avian and mammalian hosts for spirochete-infected ticks and insects in a Lyme disease focus in Connecticut. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):627–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F. Biology of Borrelia species. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):381–400. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.381-400.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. Discovery of the Lyme disease spirochete and its relation to tick vectors. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):515–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Gage K. L. Susceptibility of the black-legged tick, Ixodes scapularis, to the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):15–20. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Lane R. S., Barbour A. G., Gresbrink R. A., Anderson J. R. The western black-legged tick, Ixodes pacificus: a vector of Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Sep;34(5):925–930. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAINE S., VANDERHOEDEN J. VIRULENCE-LINKED COLONIAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL VARIATION IN LEPTOSPIRA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1493–1496. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1493-1496.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikura T. Studies on two colonial types of Leptospira icterohaemorrhagia with special reference to the bottle culture method. Jpn J Microbiol. 1966 Jul;10(2):79–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1966.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum in culture: use of outdated erthrocytes and description of the candle jar method. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):883–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. E., Klein G. C., Schmid G. P., Bowen G. S., Feeley J. C., Schulze T. Lyme disease: a selective medium for isolation of the suspected etiological agent, a spirochete. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):81–82. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.81-82.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. O., Dekker R. A., Bluemink J. G. Ligand-mediated osmium binding: its application in coating biological specimens for scanning electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Nov;45(3):254–258. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. T., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Antigenic variation is associated with DNA rearrangements in a relapsing fever Borrelia. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G. Biology of Borrelia hermsii in Kelly medium. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):540–543. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.540-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]