Abstract
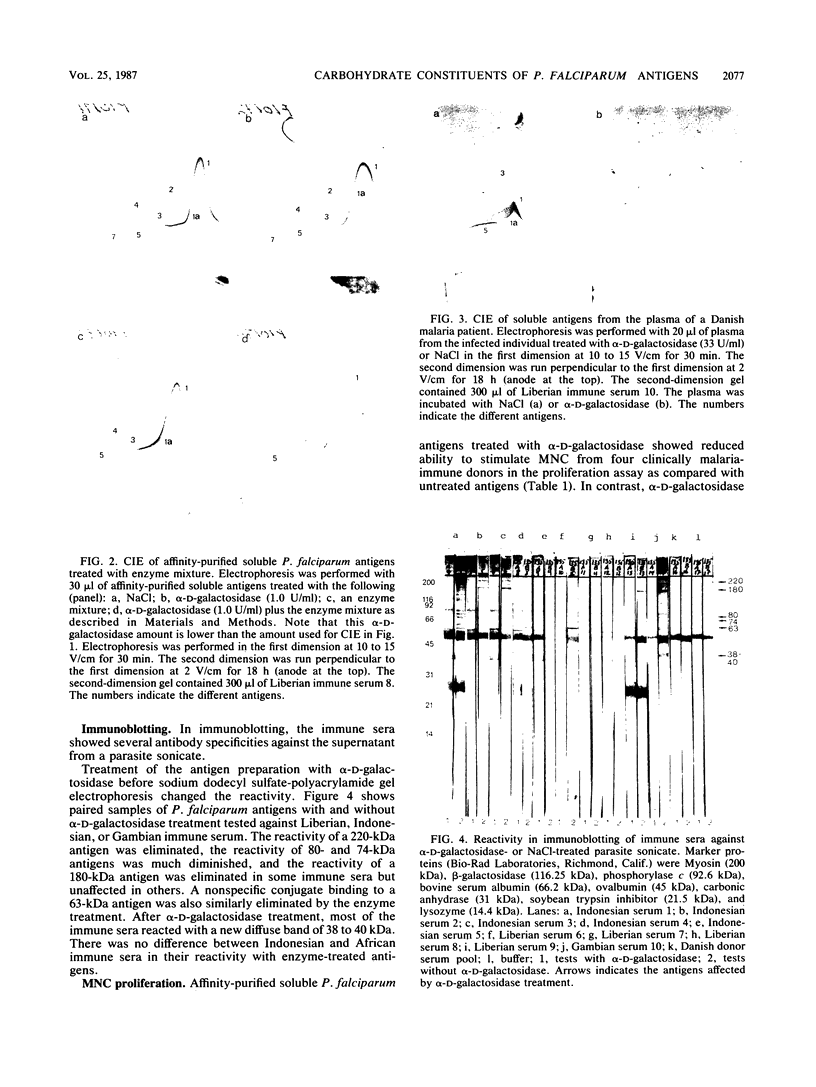
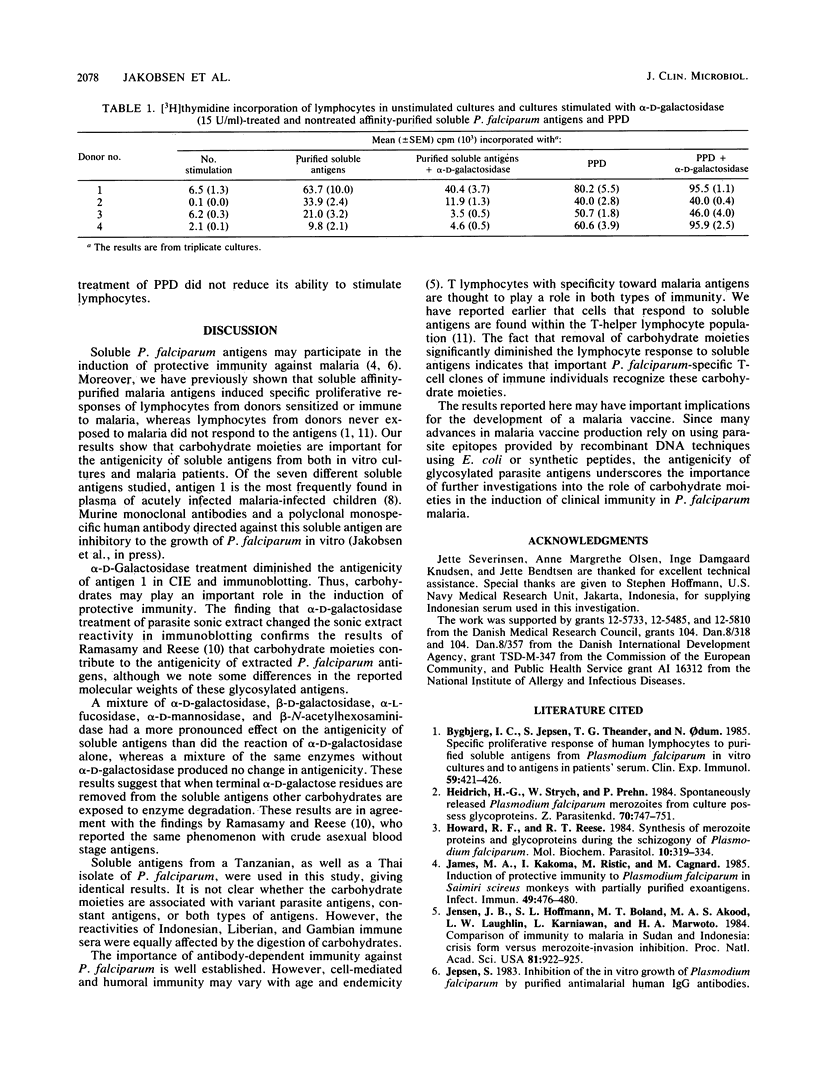
The importance of carbohydrate moieties for the antigenicity of purified soluble Plasmodium falciparum antigens from the asexual blood stage was tested. Digestion of the soluble antigens with alpha-D-galactosidase clearly affected the ability of the antigen to react with malaria-immune sera from different geographical origins in crossed immunoelectrophoresis and immunoblotting. Antigens of 220, 180, 80, and 74 kilodaltons were affected by the enzyme treatment. Furthermore, the enzyme digestion reduced the ability of the purified soluble antigen to stimulate lymphocytes from malaria-immune donors. The results might have important implications for the strategy of developing a malaria vaccine.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bygbjerg I. C., Jepsen S., Theander T. G., Odum N. Specific proliferative response of human lymphocytes to purified soluble antigens from Plasmodium falciparum in vitro cultures and to antigens from malaria patients' sera. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):421–426. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidrich H. G., Strych W., Prehm P. Spontaneously released Plasmodium falciparum merozoites from culture possess glycoproteins. Z Parasitenkd. 1984;70(6):747–751. doi: 10.1007/BF00927127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. F., Reese R. T. Synthesis of merozoite proteins and glycoproteins during the schizogony of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Mar;10(3):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. A., Kakoma I., Ristic M., Cagnard M. Induction of protective immunity to Plasmodium falciparum in Saimiri sciureus monkeys with partially purified exoantigens. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):476–480. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.476-480.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Hoffman S. L., Boland M. T., Akood M. A., Laughlin L. W., Kurniawan L., Marwoto H. A. Comparison of immunity to malaria in Sudan and Indonesia: crisis-form versus merozoite-invasion inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):922–925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen S., Andersen B. J. Immunoadsorbent isolation of antigens from the culture medium of in vitro cultivated Plasmodium falciparum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Apr;89(2):99–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen S., Axelsen N. H. Antigens and antibodies in Plasmodium falciparum malaria studied by immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Oct;88(5):263–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy R., Reese R. T. A role for carbohydrate moieties in the immune response to malaria. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1952–1955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy R., Reese R. T. Terminal galactose residues and the antigenicity of Plasmodium falciparum glycoproteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 May;19(2):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theander T. G., Bygbjerg I. C., Jepsen S., Svenson M., Kharazmi A., Larsen P. B., Bendtzen K. Proliferation induced by Plasmodium falciparum antigen and interleukin-2 production by lymphocytes isolated from malaria-immune individuals. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):221–225. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.221-225.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]