Abstract
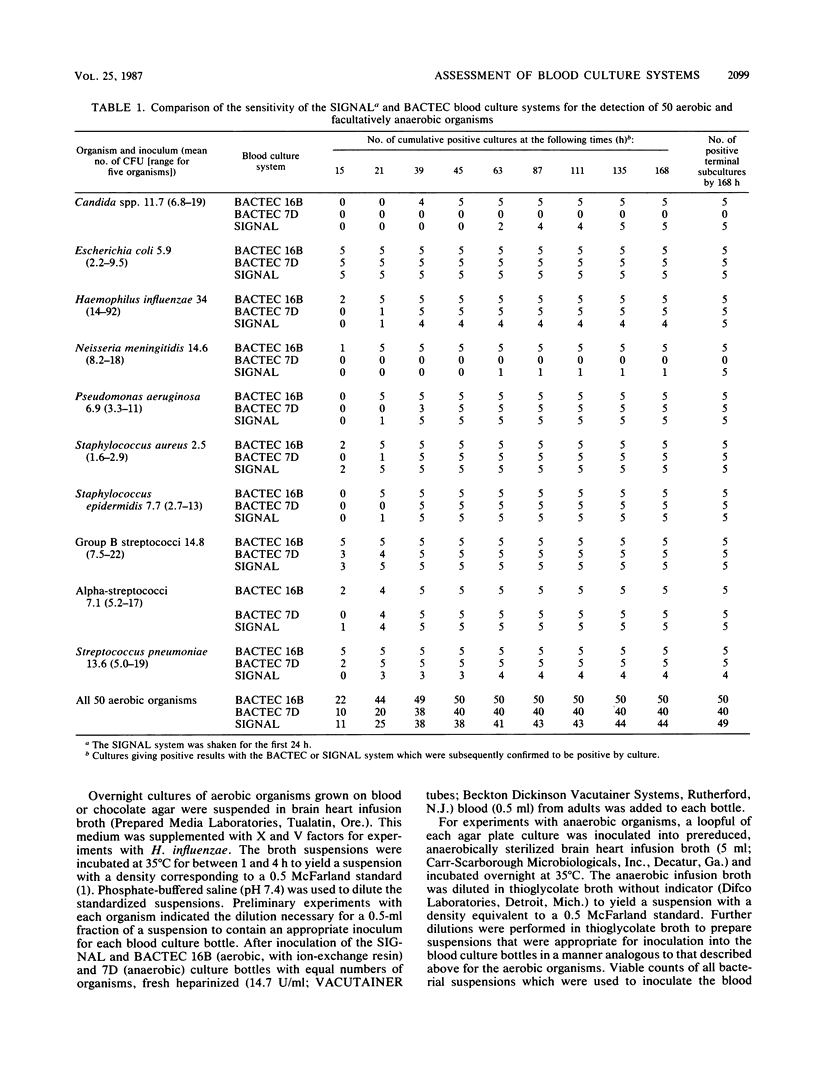
In the SIGNAL (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, United Kingdom) blood culture system, gas produced by bacterial metabolism displaces medium from the culture bottle into an upper reservoir via a hollow needle. Displacement of media may provide a visual indication of the presence of both aerobic and anaerobic organisms in a single medium. The single-bottle SIGNAL system was compared with paired BACTEC 16B and 7D (Johnston Laboratories, Inc., Towson, Md.) radiometric system bottles by using bacterial inocula and conditions which simulated those found in neonatal and pediatric populations. The single SIGNAL bottle was a good as the combined BACTEC media for Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, but was slower for Candida spp., Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, group B streptococci, alpha-streptococci, and pneumococci. The SIGNAL system failed to detect four of five isolates of Neisseria meningitidis and four of eight anaerobic organisms. The SIGNAL system is not suitable for neonatal blood cultures at its present state of development.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell L. M., Alpert G., Campos J. M., Plotkin S. A. Routine quantitative blood cultures in children with Haemophilus influenzae or Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia. Pediatrics. 1985 Dec;76(6):901–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette V. S., Zipursky A. Assessment of anemia in newborn infants. Clin Perinatol. 1984 Jun;11(2):489–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B. Clinical comparison of the Isolator 1.5 microbial tube and the BACTEC radiometric system for detection of bacteremia in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):634–638. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.634-638.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzman D. E., Fischer G. W., Schoenknecht F. D. Neonatal Escherichia coli septicemia--bacterial counts in blood. J Pediatr. 1974 Jul;85(1):128–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Bone G., Phillips I. Comparison of radiometric and gas capture system for blood cultures. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;39(6):661–665. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.6.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal P. R., Kleiman M. B., Reynolds J. K., Allen S. D., Lemons J. A., Yu P. L. Volume of blood submitted for culture from neonates. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):353–356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.353-356.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley A. H., Wald E. R. Incubation period necessary to detect bacteremia in neonates. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;5(5):590–591. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198609000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney D., Hinder S., Swaine D., Bridson E. Y. Novel method for detecting micro-organisms in blood cultures. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;39(11):1259–1263. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.11.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan T. D., LaScolea L. J., Jr, Neter E. Relationship between the magnitude of bacteremia in children and the clinical disease. Pediatrics. 1982 Jun;69(6):699–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


