Abstract
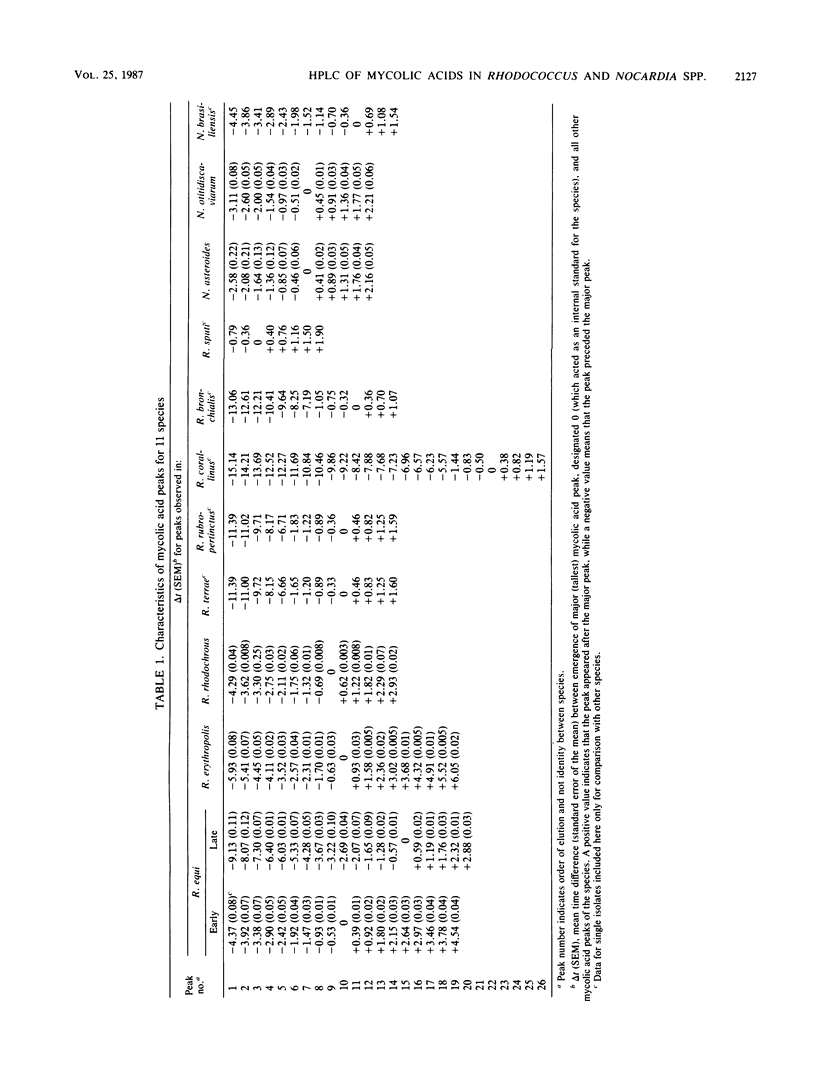
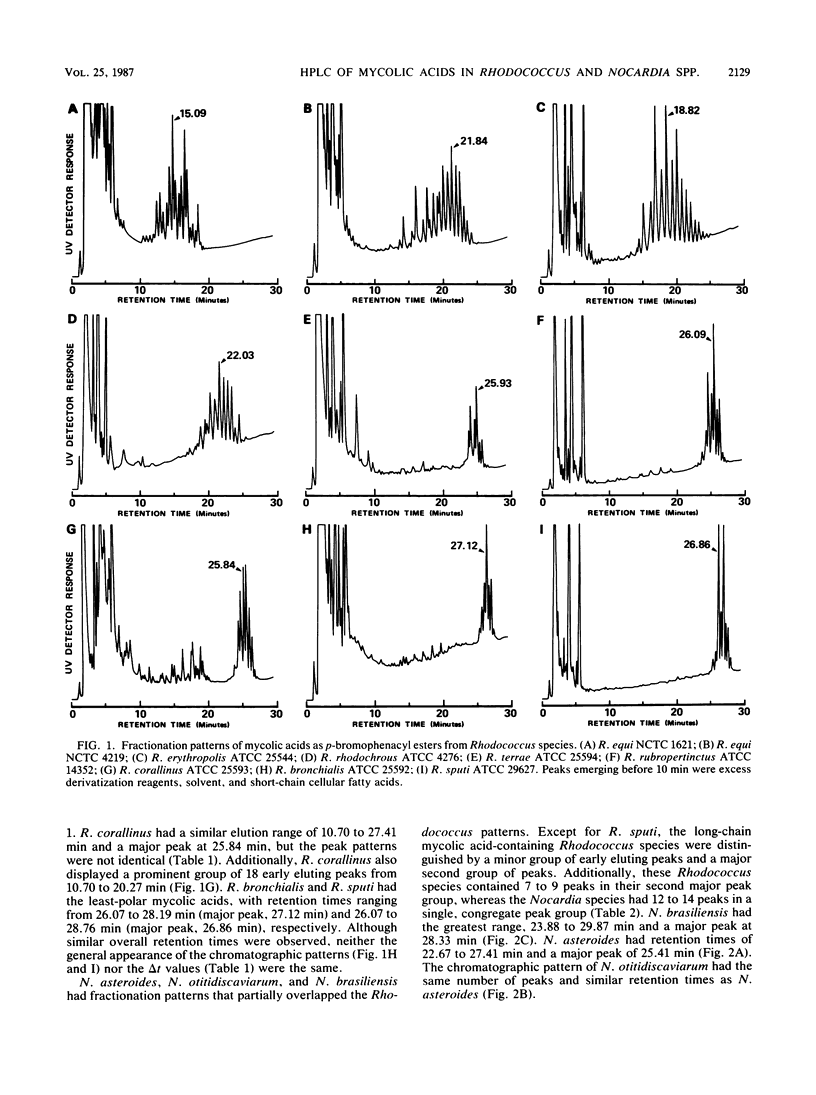
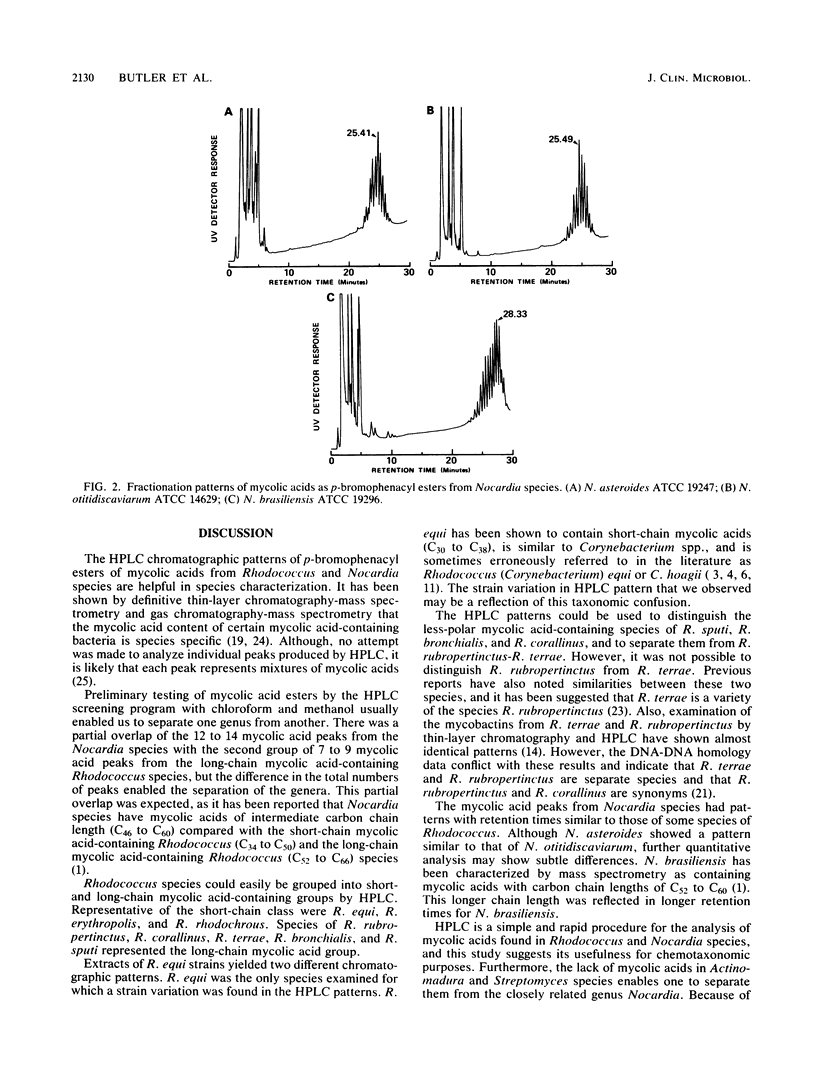
High-performance liquid chromatography analysis of the p-bromophenacyl esters of mycolic acids from whole organisms gave chromatographic patterns that were useful in differentiation of Rhodococcus and Nocardia species. Rhodococcus equi, R. erythropolis, and R. rhodochrous contained more-polar mycolic acids and were easily separated from the less-polar mycolic acid-containing species of R. sputi, R. bronchialis, R. corallinus, R. rubropertinctus, and R. terrae. The less-polar mycolic acid-containing Rhodococcus species showed chromatographic patterns that partially overlapped (in elution times) the patterns of Nocardia asteroides, N. otitidiscaviarum, and N. brasiliensis, but the larger number of peaks in the last species made separation between the genera possible. Distinct chromatographic patterns were found for most species, except for R. equi strains that showed two different patterns. Strains of R. rubropertinctus and R. terrae appeared identical. N. asteroides and N. otitidiscaviarum showed similar mycolic acid patterns.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alashamaony L., Goodfellow M., Minnikin D. E. Free mycolic acids as criteria in the classification of Nocardia and the 'rhodochrous' complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jan;92(1):188–199. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alshamaony L., Goodfellow M., Minnikin D. E., Mordarska H. Free mycolic acids as criteria in the classification of Gordona and the 'rhodochrous' complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jan;92(1):183–187. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-1-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Ahearn D. G., Kilburn J. O. High-performance liquid chromatography of mycolic acids as a tool in the identification of Corynebacterium, Nocardia, Rhodococcus, and Mycobacterium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):182–185. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.182-185.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durst H. D., Milano M., Kikta E. J., Jr, Connelly S. A., Grushka E. Phenacyl esters of fatty acids via crown ether catalysts for enhanced ultraviolet detection in liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1975 Sep;47(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1021/ac60361a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Alderson G. The actinomycete-genus Rhodococcus: a home for the "rhodochrous" complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 May;100(1):99–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-100-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Minnikin D. E. Nocardioform bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:159–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Orchard V. A. Antibiotic sensitivity of some nocardioform bacteria and its value as a criterion for taxonomy. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):375–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Weaver C. R., Minnikin D. E. Numerical classification of some Rhodococci, Corynebacteria and related organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Apr;128(4):731–745. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-4-731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. E. Some strains in search of a genus--Corynebacterium, Mycobacterium, Nocardia or what? J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):329–343. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haburchak D. R., Jeffery B., Higbee J. W., Everett E. D. Infections caused by Rhodochrous. Am J Med. 1978 Aug;65(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90823-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. M., Ratledge C. Distribution and application of mycobactins for the characterization of species within the genus Rhodococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Mar;132(3):853–856. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-3-853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn J. O., Takayama K. Effects of ethambutol on accumulation and secretion of trehalose mycolates and free mycolic acid in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):401–404. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier M. P., Horan A. C., Lechevalier H. Lipid composition in the classification of nocardiae and mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.313-318.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May D. C., Raff M. J., Collins J. C., Melo J. C. Acute synovitis caused by an organism of the Rhodochrous taxon. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Dec;18(3):433–436. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-3-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Alshamaony L., Goodfellow M. Differentiation of Mycobacterium, Nocardia, and related taxa by thin-layer chromatographic analysis of whole-organism methanolysates. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):200–204. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordarska H., Mordarski M., Goodfellow M. Chemotaxonomic characters and classification of some nocardioform bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):77–86. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano I., Kageyama K., Ohno Y., Masui M., Kusunose E., Kusunose M., Akimori N. Separation and analysis of molecular species of mycolic acids in Nocardia and related taxa by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1978 Jan;5(1):14–24. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200050104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano I., Saito K., Furukawa Y., Kusunose M. Structural analysis of molecular species of nocardomycolic acids from Nocardia erythropolis by the combined system of gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. FEBS Lett. 1972 Mar 15;21(2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


