Abstract
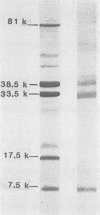
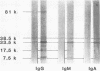
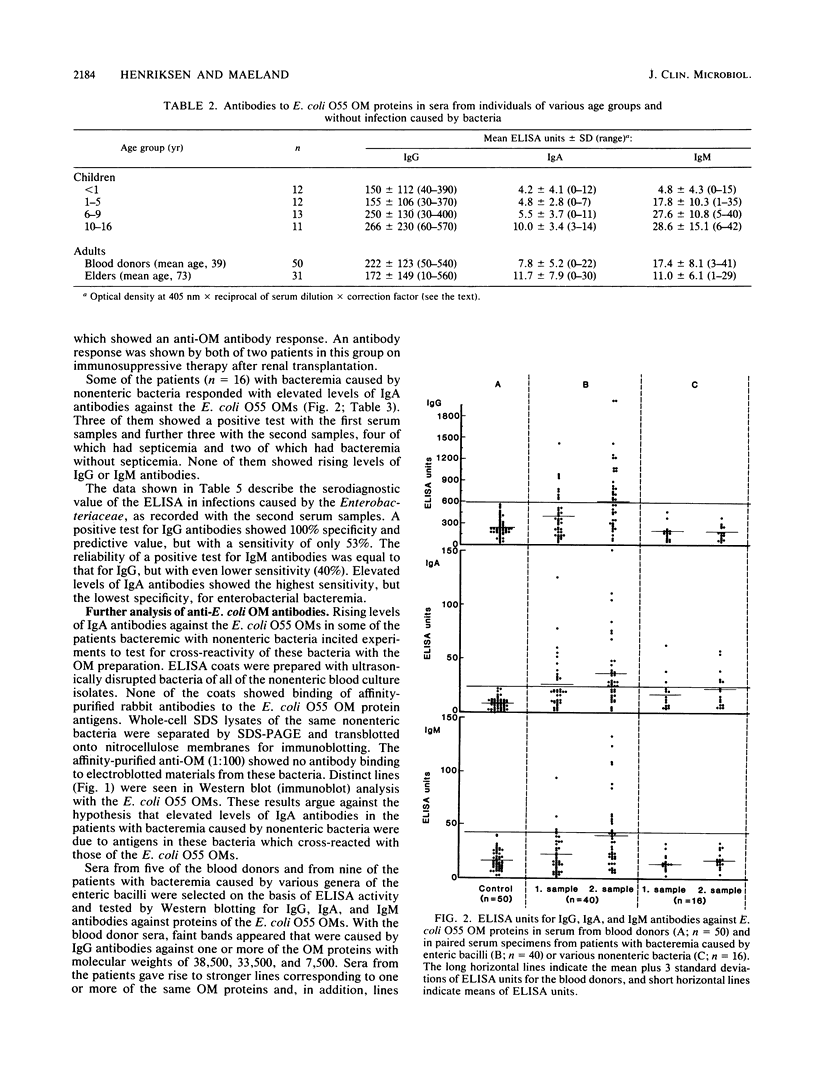
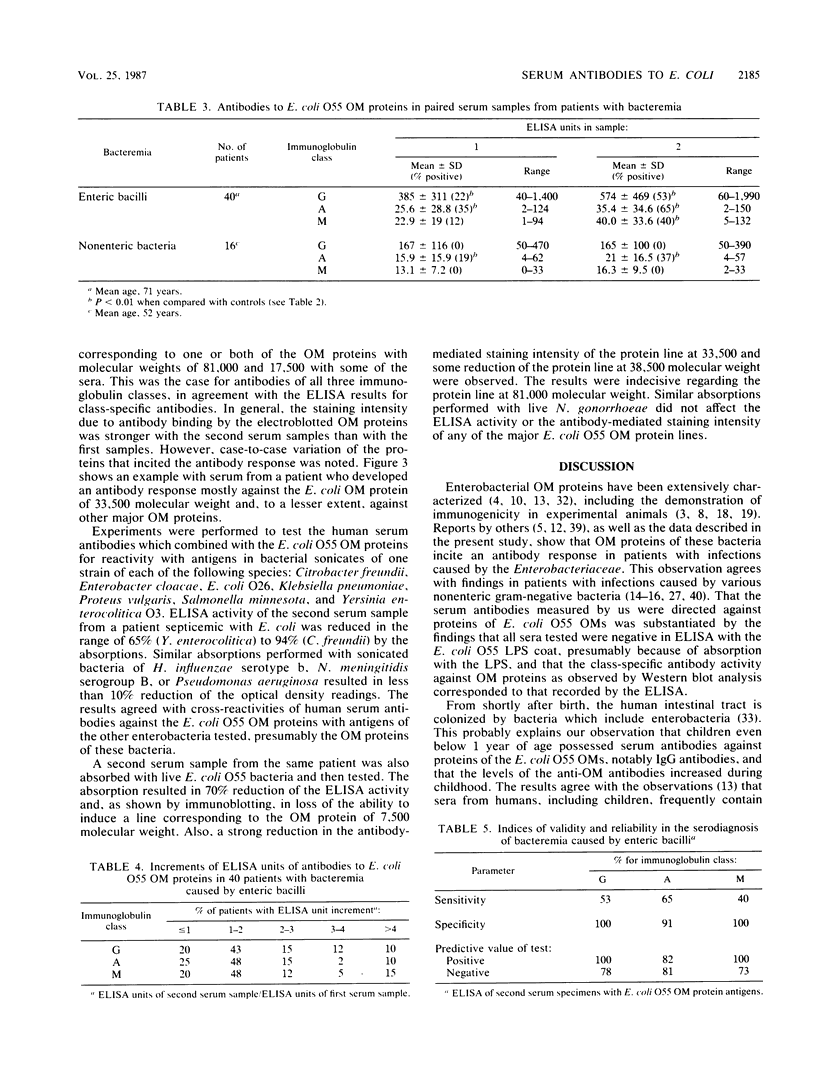
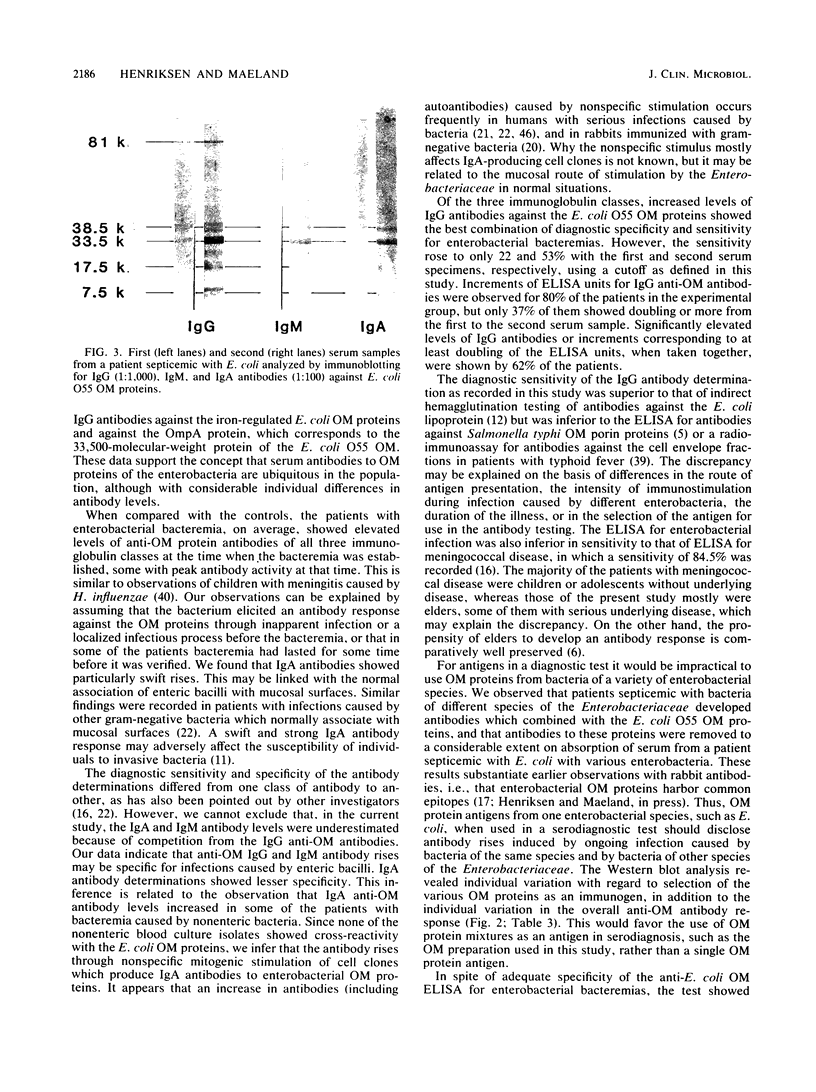
Antibodies to Escherichia coli outer membrane proteins in sera from healthy persons and from patients bacteremic with various enteric or nonenteric bacteria were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Outer membranes were prepared from E. coli O55. Serum was absorbed with E. coli O55 lipopolysaccharide and diluted 1:100 for immunoglobulin A (IgA) or IgM and 1:1,000 for IgG antibodies. Paired serum specimens were obtained from the 56 patients included in the study (the first specimen on the day of positive blood culture and the second specimen 8 to 12 days later) and compared with sera from blood donors (n = 50) as controls. On an average, the patients bacteremic with enterobacteria (n = 40) showed increased levels of antibodies of all three immunoglobulin classes in the first serum specimens and significantly higher levels in the second specimens compared with the controls, although with considerable case-to-case variation. Increased levels of IgG antibodies showed the best combination of diagnostic specificity (100%) and sensitivity (53%) for bacteremia caused by enteric bacilli. Mostly, the antibody response was directed against the major E. coli O55 outer membrane proteins at 81,000, 38,500, 33,500, and 7,500 molecular weights as shown by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis. Some of the patients bacteremic with nonenteric bacteria showed increased levels of IgA antibodies, but not of IgG or IgM antibodies. Cross-reactivity of the nonenteric blood culture isolates with the E. coli outer membrane preparation was not demonstrated. The cross-reactivity of the E. coli O55 outer membrane proteins with those of enteric bacilli of other genera was examined by absorption experiments. Western blots with serum absorbed with live E. coli O55 provided evidence that the epitopes of the outer membrane protein at 7,500 molecular weight were available for antibody binding at the bacterial surface, and that at least some of the epitopes of the 38,500- and 33,500-molecular -weight proteins were accessible to antibodies. The results suggest that an ELISA for the measurement of antibodies against cross-reactive outer membrane proteins from enteric bacilli may be useful in the diagnosis of serious infections caused by members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, and that antibodies to the major outer membrane proteins may have an immunobiological function.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley W. J., Joseph S. W., Weiss E. Improved serodiagnosis of Salmonella enteric fevers by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):106–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.106-114.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beher M. G., Schnaitman C. A., Pugsley A. P. Major heat-modifiable outer membrane protein in gram-negative bacteria: comparison with the ompA protein of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):906–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.906-913.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Bosch V., Klumpp E. R., Neff I., Mayer H., Schlecht S. Antigenic determinants of murein lipoprotein and its exposure at the surface of Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):555–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):426–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón I., Lobos S. R., Rojas H. A., Palomino C., Rodríguez L. H., Mora G. C. Antibodies to porin antigens of Salmonella typhi induced during typhoid infection in humans. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):209–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.209-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg-Lagergård T. Target antigens for bactericidal and opsonizing antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1982 Aug;90(4):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb01440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J., Hofstra H. Antibodies against outer membrane proteins in rabbit antisera prepared against Escherichia coli O26 K60. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):311–320. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Hindennach I., Henning U. The major proteins of the Escherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane. Characterization of proteins II* and III, comparison of all proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Bertram M. A. Immunoepidemiology of meningococcal disease in military recruits. II. Blocking of serum bactericidal activity by circulating IgA early in the course of invasive disease. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):733–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E. K., Yoonessi S., Neter E. Antibody response to enterobacterial lipoprotein of patients with varied infections due to Enterobacteriaceae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Feb;154(2):246–249. doi: 10.3181/00379727-154-39647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Thorpe R., Chart H. Naturally occurring antibodies in human sera that react with the iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):808–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.808-813.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadfield S. G., Glynn A. A. Analysis of antibodies in local and disseminated Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections by means of gel electrophoresis-derived ELISA. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):283–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mouat E. C., Speert D. P. Quantitation and identification of antibodies to outer-membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in sera of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):220–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harthug S., Rosenqvist E., Høiby E. A., Gedde-Dahl T. W., Frøholm L. O. Antibody response in group B meningococcal disease determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with serotype 15 outer membrane antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):947–953. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.947-953.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen A. Z., Maeland J. A. Immunoadsorbent-purified antibodies in the study of antigenic relatedness of outer membrane proteins of enteric bacilli. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1986 Aug;94(4):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb03050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Dankert J. Preparation and quantitative determination of antibodies against major outer mambranes proteins of Escherichia coli O26 K60. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Apr;117(2):437–447. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-2-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Van Tol J. D., Dankert J. Cross-reactivity of major outer membrane proteins of Enterobacteriaceae, studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):328–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.328-337.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Bruins S. C., McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. II. Serological response to lipid A and the lipopolysaccharide of Re mutants. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.9-15.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H., Jousimies-Somer H., Peltola H., Mäketä P. H. Antibody response to capsular polysaccharides of groups A and C neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae type b during bacteremic disease. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):32–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H. The unspecific antibody response to N. meningitidis group A capsular polysaccharide often seen in bacteraemic diseases. Parasite Immunol. 1982 May;4(3):157–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. J., Marks M. I. Age-related prevalence of human serum IgG and IgM antibody to the core glycolipid of Escherichia coli strain J5, as measured by ELISA. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):988–994. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Human antibody response to individual outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1032-1036.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkamäki M. Antibodies to the enterobacterial common antigen: standardization of the passive hemagglutination test and levels in normal human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1074–1079. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1074-1079.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Bruins S. C., Craven D. E., Johns M. Cross-reactive antigens: their potential for immunization-induced immunity to Gram-negative bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S161–S166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kreger B. E., Johns M. Type-specific and cross-reactive antibodies in gram-negative bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 10;287(6):261–267. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208102870601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotimi V. O., Duerden B. I. The development of the bacterial flora in normal neonates. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):51–62. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rødahl E., Maeland J. A. Affinity chromatography for purification of antibodies to Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis lipopolysaccharides. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Oct;92(5):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Examination of the protein composition of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.882-889.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Mamay H. K., Weiss E., Joseph S. W., Beasley W. J. Outer membrane protein antigens in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Salmonella enteric fever and meningococcal meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):372–378. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.372-378.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll C., Schedel I., Peest D. Serum antibodies against common antigens of bacterial lipopolysaccharides in healthy adults and in patients with multiple myeloma. Infection. 1985 May-Jun;13(3):115–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01642869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen O. F., Hjort T. Antibodies against E. coli O-antigens and common enterobacterial antigen in kidney-transplant recipients. Comparison of antibody findings with evidence of urinary tract infection. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Dec;85B(6):455–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb02002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang R. S., Chau P. Y., Lam S. K., La Brooy J. T., Rowley D. Antibody response to the lipopolysaccharide and protein antigens of Salmonella typhi during typhoid infection. I. Measurement of serum antibodies by radioimmunoassay. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):508–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio T. J. Predictive value of a single diagnostic test in unselected populations. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 26;274(21):1171–1173. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605262742104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHANG H. Y., NETER E. STUDY OF HETEROGENETIC (KUNIN) ANTIBODIES IN SERUM OF HEALTHY SUBJECTS AND CHILDREN WITH ENTERIC AND URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS. J Pediatr. 1963 Sep;63:412–419. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., McCutchan J. A., Fierer J., Glauser M. P., Sadoff J. C., Douglas H., Braude A. I. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and shock with human antiserum to a mutant Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]