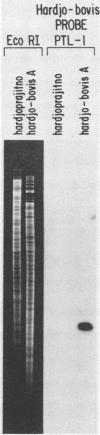
Abstract
A DNA probe is described for the diagnostic and taxonomic identification of the North American cattle pathogen Leptospira interrogans genotype hardjo-bovis. The probe is specific for this genotype and does not hybridize to genomic DNA of any other leptospire pathogen commonly found in North America.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahaman A. R., Marshall R. B., Moriarty K. M. Experimental trials on the use of radioimmunoassay for the detection of leptospiral antigens in urine. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jul;12(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Jr, Sulzer C. R., Pursell A. R. Improved microtechnique for the leptospiral microscopic agglutination test. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):976–980. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.976-980.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLINGHAUSEN H. C., Jr, MCCULLOUGH W. G. NUTRITION OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA AND GROWTH OF 13 OTHER SEROTYPES: A SERUM-FREE MEDIUM EMPLOYING OLEIC ALBUMIN COMPLEX. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., Songer J. G., Montgomery J., Cassells J. A. Prevalence of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo in the genital and urinary tracts of non-pregnant cattle. Vet Rec. 1986 Jan 4;118(1):11–13. doi: 10.1136/vr.118.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmety E. Main antigens as criterion for differentiating leptospiral serotypes. Ann Soc Belges Med Trop Parasitol Mycol. 1966;46(1):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Febvre R. B., Thiermann A. B. DNA homology studies of leptospires of serogroups Sejroe and Pomona from cattle and swine. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Apr;47(4):959–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Wilton B. E., Robinson A. J. Identification of Leptospira serovars by restriction-endonuclease analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):163–166. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Winter P. J., Thiermann A. B., Ellis W. A. Genotypes of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo in cattle in the UK. Vet Rec. 1985 Dec 21;117(25-26):669–670. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.25-26.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer C. R., Jones W. L. Evaluation of a hemagglutination test for human leptospirosis. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):655–657. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.655-657.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra W. J., Korver H., van Leeuwen J., Klatser P. R., Kolk A. H. The classification of Sejroe group serovars of Leptospira interrogans with monoclonal antibodies. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Jul;259(4):498–506. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra W. J., Schoone G. J., ter Schegget J. Detection of leptospiral DNA by nucleic acid hybridisation with 32P- and biotin-labelled probes. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Aug;22(1):23–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B. Bovine leptospirosis: bacteriologic versus serologic diagnosis of cows at slaughter. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Dec;44(12):2244–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Foley J. W., White F. H., Kingscote B. F. Reclassification of North American leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroups Mini and Sejroe by restriction endonuclease analysis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Moseley S. L., Kingscote B. New method for classification of leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroup pomona by restriction endonuclease analysis: serovar kennewicki. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.585-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitkins S. A., Hookey J. V. The detection of leptospires by a chemiluminescent immunoassay. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Jun;21(4):353–356. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-4-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]