Abstract
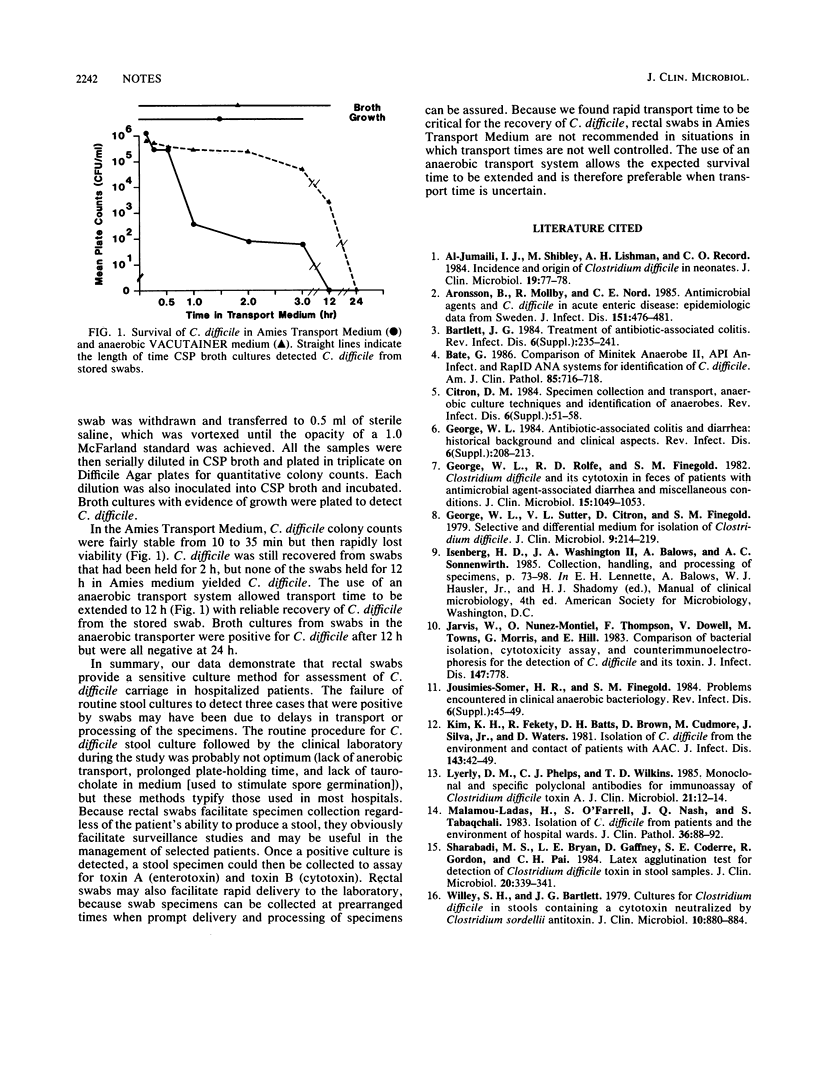
We compared the recovery of Clostridium difficile from hospitalized patients by two collection methods: rectal swabs and stool cultures. Rectal swab cultures were as sensitive as stool cultures and were more easily obtained. Transport of swabs in an anaerobic VACUTAINER system resulted in longer survival times compared with transport in Amies medium.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Jumaili I. J., Shibley M., Lishman A. H., Record C. O. Incidence and origin of Clostridium difficile in neonates. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):77–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.77-78.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronsson B., Möllby R., Nord C. E. Antimicrobial agents and Clostridium difficile in acute enteric disease: epidemiological data from Sweden, 1980-1982. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):476–481. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate G. Comparison of Minitek Anaerobe II, API An-Ident, and RapID ANA systems for identification of Clostridium difficile. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;85(6):716–718. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/85.6.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Rolfe R. D., Finegold S. M. Clostridium difficile and its cytotoxin in feces of patients with antimicrobial agent-associated diarrhea and miscellaneous conditions. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1049-1053.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis W., Nunez-Montiel O., Thompson F., Dowell V., Towns M., Morris G., Hill E. Comparison of bacterial isolation, cytotoxicity assay, and counterimmunoelectrophoresis for the detection of Clostridium difficile and its toxin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):778–778. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Fekety R., Batts D. H., Brown D., Cudmore M., Silva J., Jr, Waters D. Isolation of Clostridium difficile from the environment and contacts of patients with antibiotic-associated colitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):42–50. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Phelps C. J., Wilkins T. D. Monoclonal and specific polyclonal antibodies for immunoassay of Clostridium difficile toxin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):12–14. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.12-14.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamou-Ladas H., O'Farrell S., Nash J. Q., Tabaqchali S. Isolation of Clostridium difficile from patients and the environment of hospital wards. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jan;36(1):88–92. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahrabadi M. S., Bryan L. E., Gaffney D., Coderre S. E., Gordon R., Pai C. H. Latex agglutination test for detection of Clostridium difficile toxin in stool samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):339–341. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.339-341.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey S. H., Bartlett J. G. Cultures for Clostridium difficile in stools containing a cytotoxin neutralized by Clostridium sordellii antitoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):880–884. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.880-884.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


