Abstract
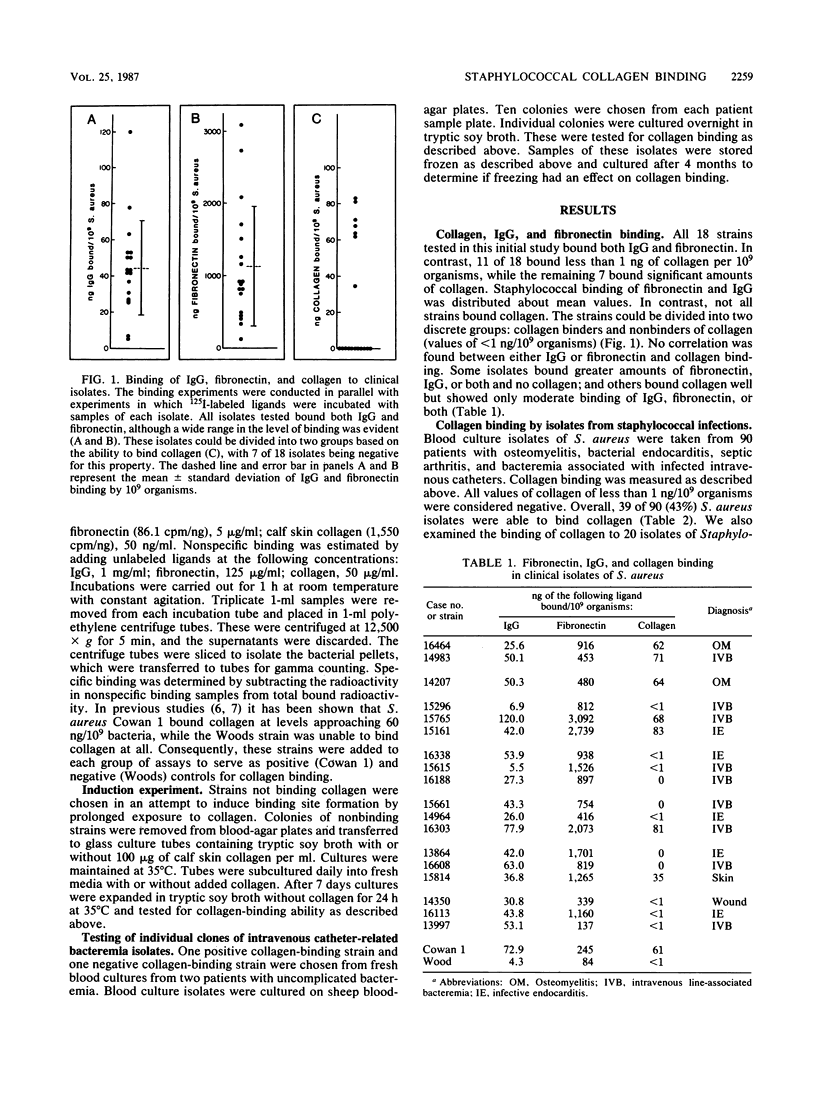
Collagen binding was examined in 90 strains of Staphylococcus aureus derived from patient samples. Slightly under one-half (39 of 90) of the S. aureus strains bound collagen. Collagen binding in S. aureus did not correlate with either immunoglobulin G or fibronectin binding by these organisms. Chi-square analysis of isolates obtained from patients with complicated bacteremia (bacteremia associated with deep tissue infection) compared with isolates from patients with uncomplicated bacteremia (bacteremia without other infection) showed that the former strains were significantly more likely to have collagen-binding ability. Subcloning of primary isolates from patients with bacteremia showed that all clones from individual patients were either all positive for collagen binding or all negative, suggesting a common clonal origin for this characteristic. The ability to bind collagen could not be induced in strains lacking collagen affinity by repeated subculture in media supplemented with collagen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carret G., Emonard H., Fardel G., Druguet M., Herbage D., Flandrois J. P. Gelatin and collagen binding to Staphylococcus aureus strains. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Mar-Apr;136A(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. Evidence for two forms of staphylococcal coagulase. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):427–436. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkle L. M., Blair L. L., Fortune K. P. Transformation of a plasmid encoding an adhesin of Staphylococcus aureus into a nonadherent staphylococcal strain. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):670–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Clumping of Staphylococcus aureus by human fibronectin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Oct;89(5):317–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00195_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Hall G. S., Ehrhart L. A. Collagen binding to Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.359-364.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Spech R. A., Ehrhart L. A. Specific binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jun;5(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Quantitation of staphylococcal protein A: Determination of equilibrium constant and number of protein A residues on bacteria. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miekka S. I., Ingham K. C., Menache D. Rapid methods for isolation of human plasma fibronectin. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 1;27(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Christman G., Mosher D. F. Fibronectin-induced agglutination of Staphylococcus aureus correlates with invasiveness. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Oct;104(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Mosher D. F., Olbrantz P. J. Fibronectin binding to Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14788–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Prendergast E., Mosher D. F. Fibronectin mediates attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to human neutrophils. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):681–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J. M., Pearlstein E. C1q, a subunit of the first component of complement, enhances binding of plasma fibronectin to bacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):664–669. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.664-669.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Raucci G., Visai L., Switalski L. M., Timpl R., Hök M. Binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.77-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Rydén C., Rubin K., Ljungh A., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to Staphylococcus strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):628–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.628-633.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water L., Destree A. T., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to some bacteria but does not promote their uptake by phagocytic cells. Science. 1983 Apr 8;220(4593):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.6338594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Phagocytosis and killing of staphylococci by human polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leucocytes. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):539–545. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Smith D. E., Nguyen B. Y., Hoidal J. R., Wilkinson B. J., Verhoef J., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin binding to staphylococcal surface protein and its relative inefficiency in promoting phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.811-819.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., McCarthy J. B., Lindholm P., Peterson P. K., Jacob H. S., Furcht L. T. Extracellular matrix proteins (fibronectin, laminin, and type IV collagen) bind and aggregate bacteria. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):13–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


