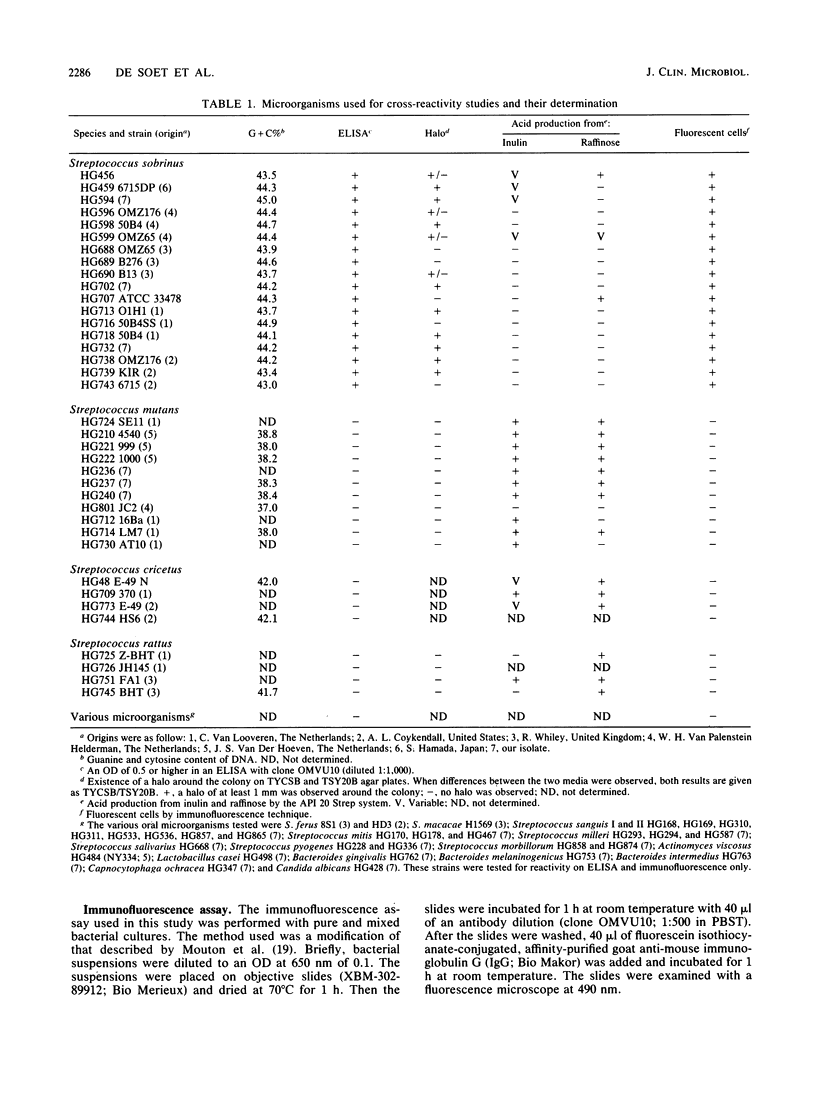
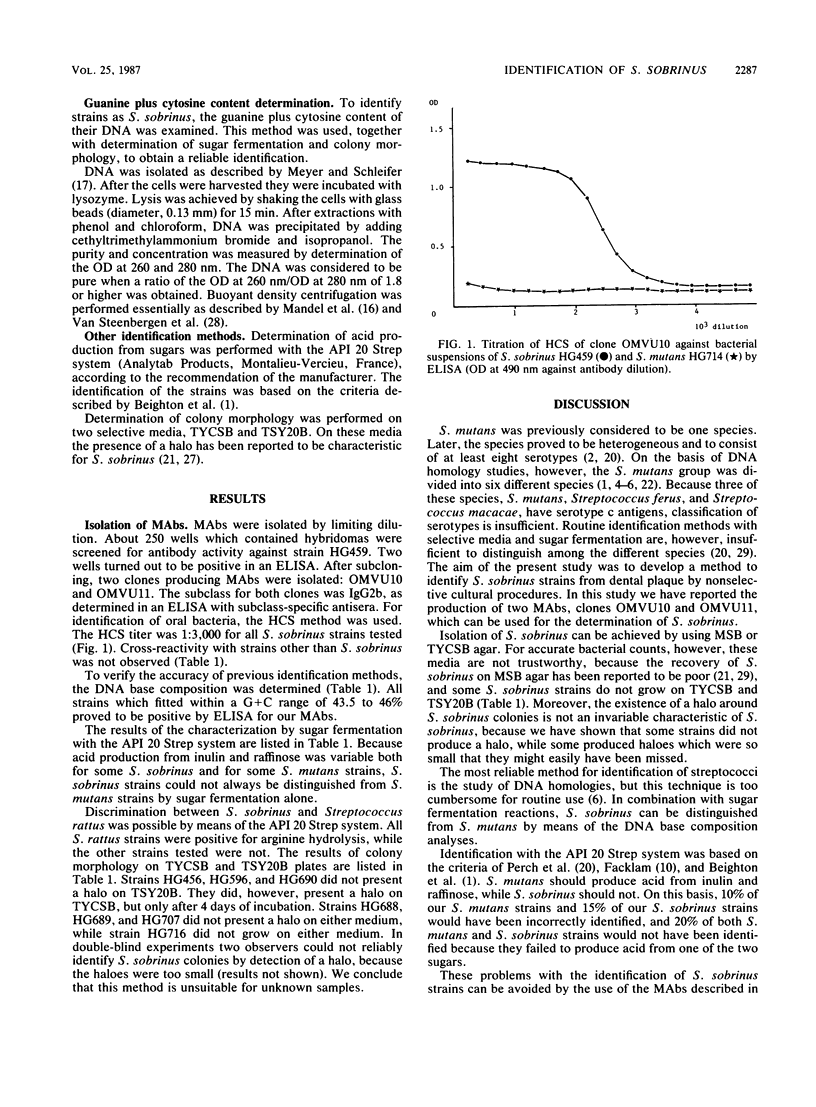
Abstract
Identification of Streptococcus sobrinus is often difficult to perform because of the great resemblance of the organism to other oral streptococcal species. Therefore, monoclonal antibodies were prepared which were shown to be highly specific for S. sobrinus. Cross-reactivity with other oral microorganisms has not been observed in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and an immunofluorescence assay. These monoclonal antibodies belonged to the subclass immunoglobulin G2b. To be certain that the strains used in cross-reactivity tests were S. sobrinus, their DNA base composition was measured as a golden standard. Additional tests like colony morphology and sugar fermentation with the API 20 Strep system (Analytab Products, Montalieu-Vercieu, France) were performed. These additional tests turned out to be necessary because 100% correct identification could not be obtained by separate tests. Immunological characterization with the clones OMVU10 and OMVU11 proved to be discriminative between S. sobrinus and other streptococcal species.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D., Köhler B. Streptococcus mutans serotypes: some aspects of their identification, distribution, antigenic shifts, and relationship to caries. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C15–C21. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500308011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Bochacki V., Reynolds H. S., Beanan J., Tatakis D. N., Zambon J. J., Genco R. J. The use of monoclonal antibodies to detect Bacteroides gingivalis in biological samples. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):798–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.798-803.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L. Four types of Streptococcus mutans based on their genetic, antigenic and biochemical characteristics. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):327–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emilson C. G., Bratthall D. Growth of Streptococcus mutans on various selective media. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):95–98. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.95-98.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emilson C. G., Kohler B., Bratthall D. Immunofluorescent determination of the relative proportions of Streptococcus mutans in human dental plaque: a comparison with cultural techniques. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Jan;20(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook W. P., Beighton D. Streptococcus mutans levels in saliva and distribution of serotypes among 9-year-old Icelandic children. Scand J Dent Res. 1987 Feb;95(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1987.tb01390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover C. I., Newbrun E., Mettraux G., Graf H. Microflora and chemical composition of dental plaque from subjects with hereditary fructose intolerance. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):853–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.853-859.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hus in 't Veld J., Bannet D., Van Palenstein Helderman W., Camargo P. S., Backer-Dirks O. Antibodies against Streptococcus mutans and glucosyltransferases in caries-free and caries-active military recruits. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:369–381. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V. Cultural methods for the identification and quantitation of Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli in oral samples. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1986 Nov;1(1):23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1986.tb00312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little W. A., Korts D. C., Thomson L. A., Bowen W. H. Comparative recovery of Streptococcus mutans on ten isolation media. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):578–583. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.578-583.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Navia J. M. Virulence of Streptococcus mutans: a sensitive method for evaluating cariogenicity in young gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):69–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.69-75.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P. G., Slots J., Reed M. J., Genco R. J. Identification of Bacteroides gingivalis by fluorescent antibody staining. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Jul-Aug;132B(1):69–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Kjems E., Ravn T. Biochemical and serological properties of Streptococcus mutans from various human and animal sources. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):357–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeken M. J., van der Hoeven J. S., Franken H. C. Comparative recovery of Streptococcus mutans on five isolation media, including a new simple selective medium. J Dent Res. 1986 Jun;65(6):906–908. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650060901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kilpper-Bälz R., Kraus J., Gehring F. Relatedness and classification of Streptococcus mutans and "mutans-like" streptococci. J Dent Res. 1984 Aug;63(8):1047–1050. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630080701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson L. G., Merrell B. R., Rouse R. F., Shklair I. L. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Bacteroides gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1986 Feb;65(2):95–97. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650021801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Börjesson A. C., Laskowski L., Kurasz A. B., Testa M. Glucose-sucrose-potassium tellurite-bacitracin agar, an alternative to mitis salivarius-bacitracin agar for enumeration of Streptococcus mutans. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):653–659. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.653-659.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Palenstein Helderman W. H., Ijsseldijk M., Huis in 't Veld J. H. A selective medium for the two major subgroups of the bacterium Streptococcus mutans isolated from human dental plaque and saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1983;28(7):599–603. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(83)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade W. G., Aldred M. J., Walker D. M. An improved medium for isolation of Streptococcus mutans. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Dec;22(4):319–323. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-4-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haan P., de Jonge A. J., Verbrugge T., Boorsma D. M. Three epitope-specific monoclonal antibodies against the hapten penicillin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76(1):42–46. doi: 10.1159/000233659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



